Abstract
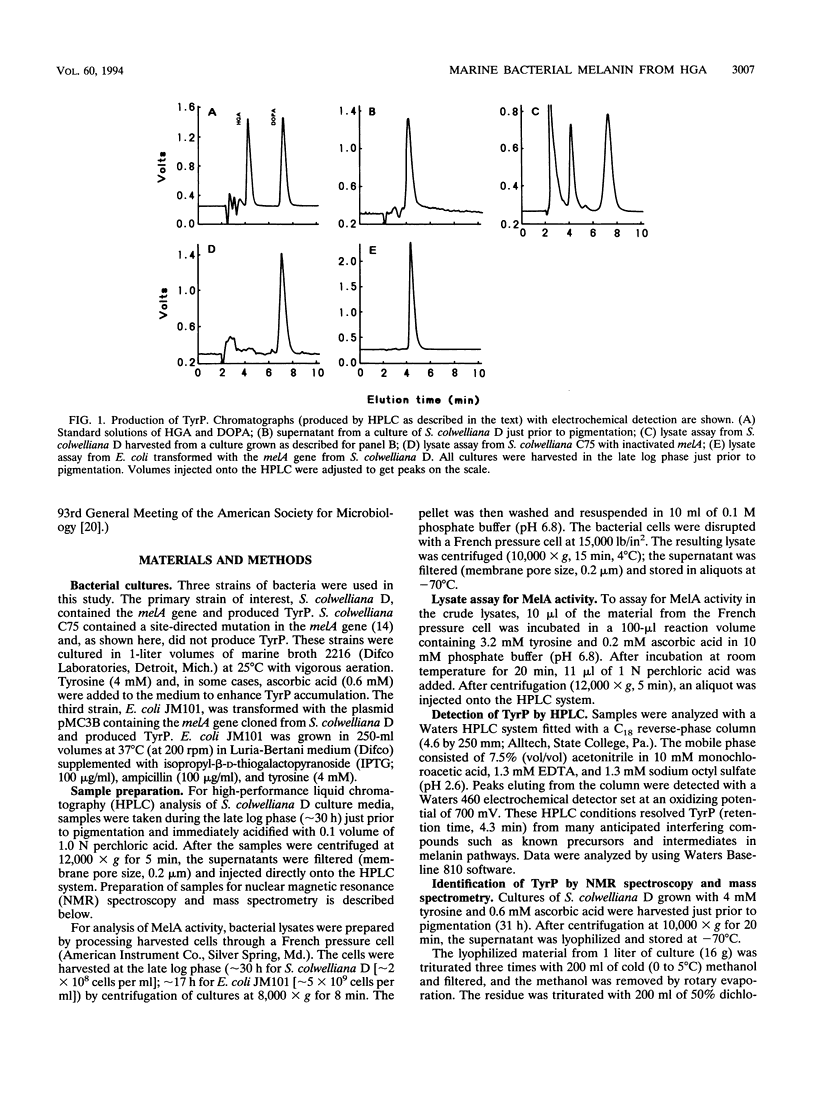
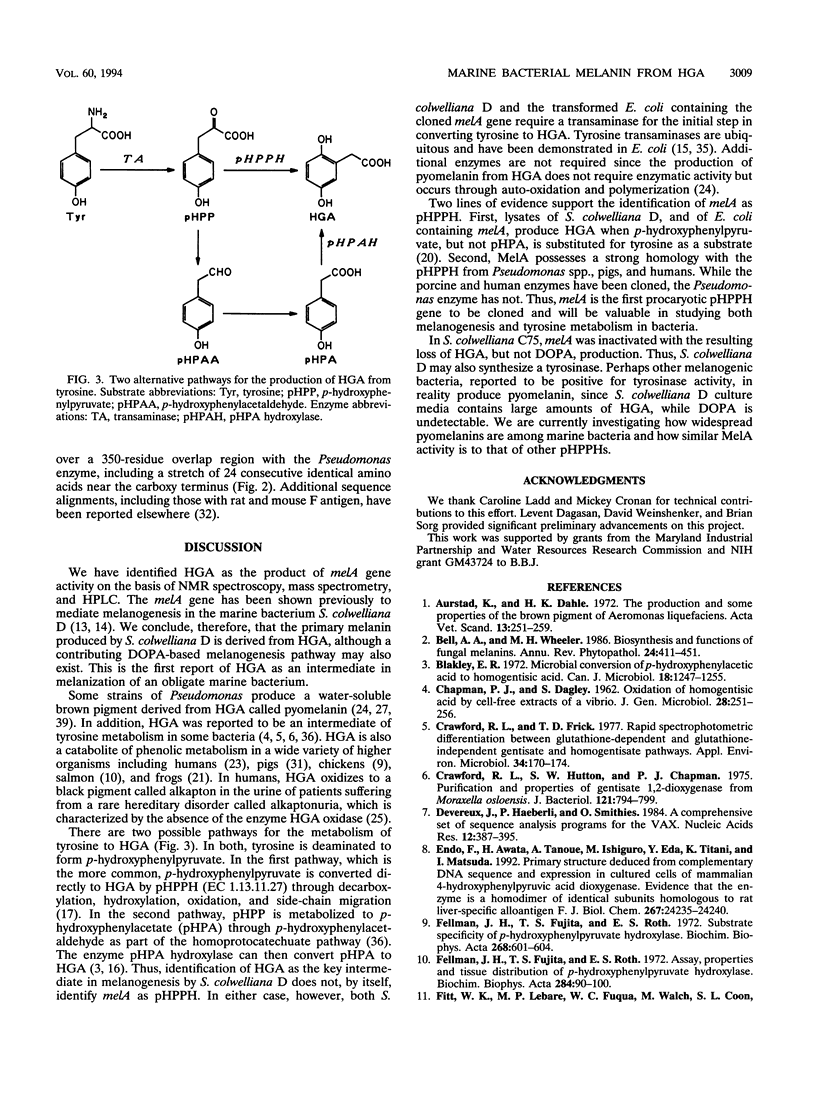
Shewanella colwelliana D is a marine procaryote which produces a diffusible brown pigment that correlates with melA gene expression. Previously, melA had been cloned, sequenced, and expressed in Escherichia coli; however, the reaction product of MelA had not been identified. This report identifies that product as homogentisic acid, provides evidence that the pigment is homogentisic acid-melanin (pyomelanin), and suggests that MelA is p-hydroxyphenylpyruvate hydroxylase. This is the first report of pyomelanin in an obligate marine bacterium.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aurstad K., Dahle H. K. The production and some properties of the brown pigment of Aeromonas liquefaciens. Acta Vet Scand. 1972;13(2):251–259. doi: 10.1186/BF03548579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blakley E. R. Microbial conversion of p-hydroxyphenylacetic acid to homogentisic acid. Can J Microbiol. 1972 Aug;18(8):1247–1255. doi: 10.1139/m72-193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHAPMAN P. J., DAGLEY S. Oxidation of homogentistic acid by cell-free extracts of a vibrio. J Gen Microbiol. 1962 Jun;28:251–256. doi: 10.1099/00221287-28-2-251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colwell C. S., Page T. L. The electroretinogram of the cockroach Leucophaea maderae. Comp Biochem Physiol A Comp Physiol. 1989;92(1):117–123. doi: 10.1016/0300-9629(89)90752-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawford R. L., Frick T. D. Rapid spectrophotometric differentiation between glutathione-dependent and glutathione-independent gentisate and homogentisate pathways. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Aug;34(2):170–174. doi: 10.1128/aem.34.2.170-174.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawford R. L., Hutton S. W., Chapman P. J. Purification and properties of gentisate 1,2-dioxygenase from Moraxella osloensis. J Bacteriol. 1975 Mar;121(3):794–799. doi: 10.1128/jb.121.3.794-799.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endo F., Awata H., Tanoue A., Ishiguro M., Eda Y., Titani K., Matsuda I. Primary structure deduced from complementary DNA sequence and expression in cultured cells of mammalian 4-hydroxyphenylpyruvic acid dioxygenase. Evidence that the enzyme is a homodimer of identical subunits homologous to rat liver-specific alloantigen F. J Biol Chem. 1992 Dec 5;267(34):24235–24240. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fellman J. H., Fujita T. S., Roth E. S. Assay, properties and tissue distribution of p-hydroxyphenylpyruvate hydroxylase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Sep 19;284(1):90–100. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(72)90048-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fellman J. H., Fujita T. S., Roth E. S. Substrate specificity of p-hydroxyphenylpyruvate hydroxylase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 May 12;268(2):601–604. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(72)90358-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuqua W. C., Coyne V. E., Stein D. C., Lin C. M., Weiner R. M. Characterization of melA: a gene encoding melanin biosynthesis from the marine bacterium Shewanella colwelliana. Gene. 1991 Dec 20;109(1):131–136. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(91)90598-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuqua W. C., Weiner R. M. The melA gene is essential for melanin biosynthesis in the marine bacterium Shewanella colwelliana. J Gen Microbiol. 1993 May;139(5):1105–1114. doi: 10.1099/00221287-139-5-1105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hareland W. A., Crawford R. L., Chapman P. J., Dagley S. Metabolic function and properties of 4-hydroxyphenylacetic acid 1-hydroxylase from Pseudomonas acidovorans. J Bacteriol. 1975 Jan;121(1):272–285. doi: 10.1128/jb.121.1.272-285.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ivins B. E., Holmes R. K. Factors affecting phaeomelanin production by a melanin-producing (mel) mutant of Vibrio cholerae. Infect Immun. 1981 Dec;34(3):895–899. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.3.895-899.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz E., Thompson C. J., Hopwood D. A. Cloning and expression of the tyrosinase gene from Streptomyces antibioticus in Streptomyces lividans. J Gen Microbiol. 1983 Sep;129(9):2703–2714. doi: 10.1099/00221287-129-9-2703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskowska-Klita T. Purification of p-hydroxyphenylpyruvate hydroxylase and its natural inhibitor from liver of the frog, Rana esculenta. Acta Biochim Pol. 1969;16(1):35–44. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerch K., Ettinger L. Purification and characterization of a tyrosinase from Streptomyces glaucescens. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Dec 18;31(3):427–437. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb02549.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindblad B., Lindstedt S., Olander B., Omfeldt M. Purification of p-hydroxyphenylpyruvate hydroxylase from human liver. Acta Chem Scand. 1970;25(1):329–330. doi: 10.3891/acta.chem.scand.25-0329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann S. Uber melaninbildende Stämme von Psuedomonas aeruginosa. Arch Mikrobiol. 1969;65(4):359–379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menon I. A., Persad S. D., Haberman H. F., Basu P. K., Norfray J. F., Felix C. C., Kalyanaraman B. Characterization of the pigment from homogentisic acid and urine and tissue from an alkaptonuria patient. Biochem Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;69(4):269–273. doi: 10.1139/o91-041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogunnariwo J., Hamilton-Miller J. M. Brown- and red-pigmented Pseudomonas aeruginosa: differentiation between melanin and pyorubrin. J Med Microbiol. 1975 Feb;8(1):199–203. doi: 10.1099/00222615-8-1-199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pomerantz S. H., Murthy V. V. Purification and properties of tyrosinases from Vibrio tyrosinaticus. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1974 Jan;160(1):73–82. doi: 10.1016/s0003-9861(74)80010-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prota G. Progress in the chemistry of melanins and related metabolites. Med Res Rev. 1988 Oct-Dec;8(4):525–556. doi: 10.1002/med.2610080405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roche P. A., Moorehead T. J., Hamilton G. A. Purification and properties of hog liver 4-hydroxyphenylpyruvate dioxygenase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1982 Jun;216(1):62–73. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(82)90188-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rüetschi U., Dellsén A., Sahlin P., Stenman G., Rymo L., Lindstedt S. Human 4-hydroxyphenylpyruvate dioxygenase. Primary structure and chromosomal localization of the gene. Eur J Biochem. 1993 May 1;213(3):1081–1089. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1993.tb17857.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rüetschi U., Odelhög B., Lindstedt S., Barros-Söderling J., Persson B., Jörnvall H. Characterization of 4-hydroxyphenylpyruvate dioxygenase. Primary structure of the Pseudomonas enzyme. Eur J Biochem. 1992 Apr 15;205(2):459–466. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb16800.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shivprasad S., Page W. J. Catechol Formation and Melanization by Na -Dependent Azotobacter chroococcum: a Protective Mechanism for Aeroadaptation? Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Jul;55(7):1811–1817. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.7.1811-1817.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sparnins V. L., Chapman P. J. Catabolism of L-tyrosine by the homoprotocatechuate pathway in gram-positive bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1976 Jul;127(1):362–366. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.1.362-366.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner R. M., Segall A. M., Colwell R. R. Characterization of a Marine Bacterium Associated with Crassostrea virginica (the Eastern Oyster). Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Jan;49(1):83–90. doi: 10.1128/aem.49.1.83-90.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



