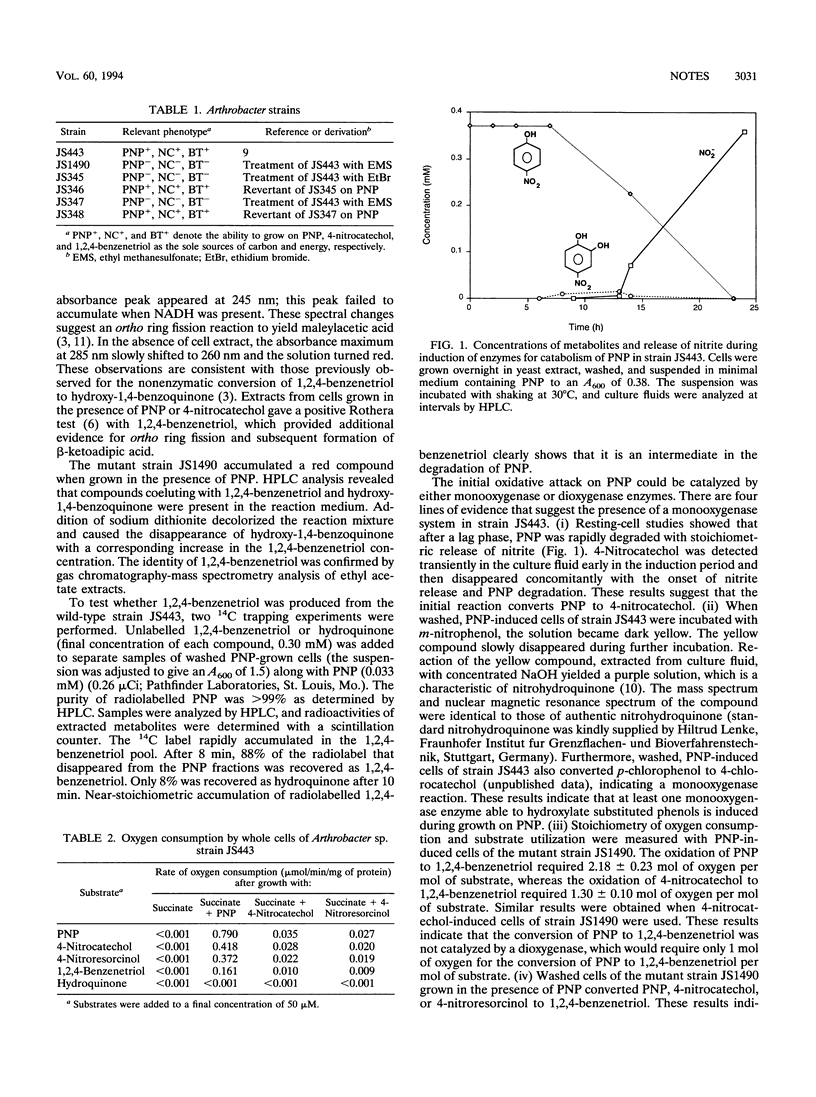
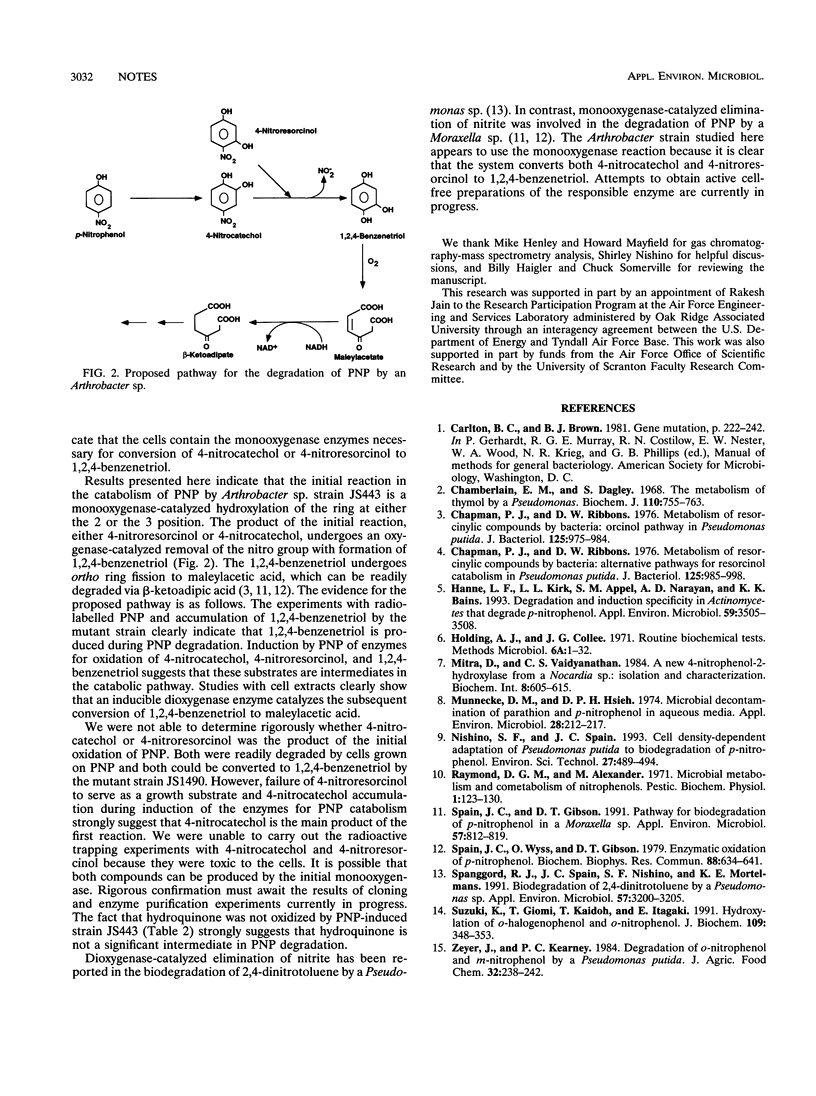
Abstract
The degradation of p-nitrophenol (PNP) by Moraxella and Pseudomonas spp. involves an initial monooxygenase-catalyzed removal of the nitro group. The resultant hydroquinone is subject to ring fission catalyzed by a dioxygenase enzyme. We have isolated a strain of an Arthrobacter sp., JS443, capable of degrading PNP with stoichiometric release of nitrite. During induction of the enzymes required for growth on PNP, 1,2,4-benzenetriol was identified as an intermediate by gas chromatography-mass spectroscopy (GC-MS) and radiotracer studies. 1,2,4-Benzenetriol was converted to maleylacetic acid, which was further degraded by the beta-ketoadipate pathway. Conversion of PNP to 1,2,4-benzenetriol is catalyzed by a monooxygenase system in strain JS443 through the formation of 4-nitrocatechol, 4-nitroresorcinol, or both. Our results clearly indicate the existence of an alternative pathway for the biodegradation of PNP.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chamberlain E. M., Dagley S. The metabolism of thymol by a Pseudomonas. Biochem J. 1968 Dec;110(4):755–763. doi: 10.1042/bj1100755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman P. J., Ribbons D. W. Metabolism of resorcinylic compounds by bacteria: alternative pathways for resorcinol catabolism in Pseudomonas putida. J Bacteriol. 1976 Mar;125(3):985–998. doi: 10.1128/jb.125.3.985-998.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman P. J., Ribbons D. W. Metabolism of resorcinylic compounds by bacteria: orcinol pathway in Pseudomonas putida. J Bacteriol. 1976 Mar;125(3):975–984. doi: 10.1128/jb.125.3.975-984.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanne L. F., Kirk L. L., Appel S. M., Narayan A. D., Bains K. K. Degradation and induction specificity in actinomycetes that degrade p-nitrophenol. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1993 Oct;59(10):3505–3508. doi: 10.1128/aem.59.10.3505-3508.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitra D., Vaidyanathan C. S. A new 4-nitrophenol 2-hydroxylase from a Nocardia sp. Biochem Int. 1984 May;8(5):609–615. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munnecke D. M., Hsieh D. P. Microbial decontamination of parathion and p-nitrophenol in aqueous media. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Aug;28(2):212–217. doi: 10.1128/am.28.2.212-217.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spain J. C., Gibson D. T. Pathway for Biodegradation of p-Nitrophenol in a Moraxella sp. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Mar;57(3):812–819. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.3.812-819.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spain J. C., Wyss O., Gibson D. T. Enzymatic oxidation of p-nitrophenol. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 May 28;88(2):634–641. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)92095-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spanggord R. J., Spain J. C., Nishino S. F., Mortelmans K. E. Biodegradation of 2,4-dinitrotoluene by a Pseudomonas sp. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Nov;57(11):3200–3205. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.11.3200-3205.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki K., Gomi T., Kaidoh T., Itagaki E. Hydroxylation of o-halogenophenol and o-nitrophenol by salicylate hydroxylase. J Biochem. 1991 Feb;109(2):348–353. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



