Abstract
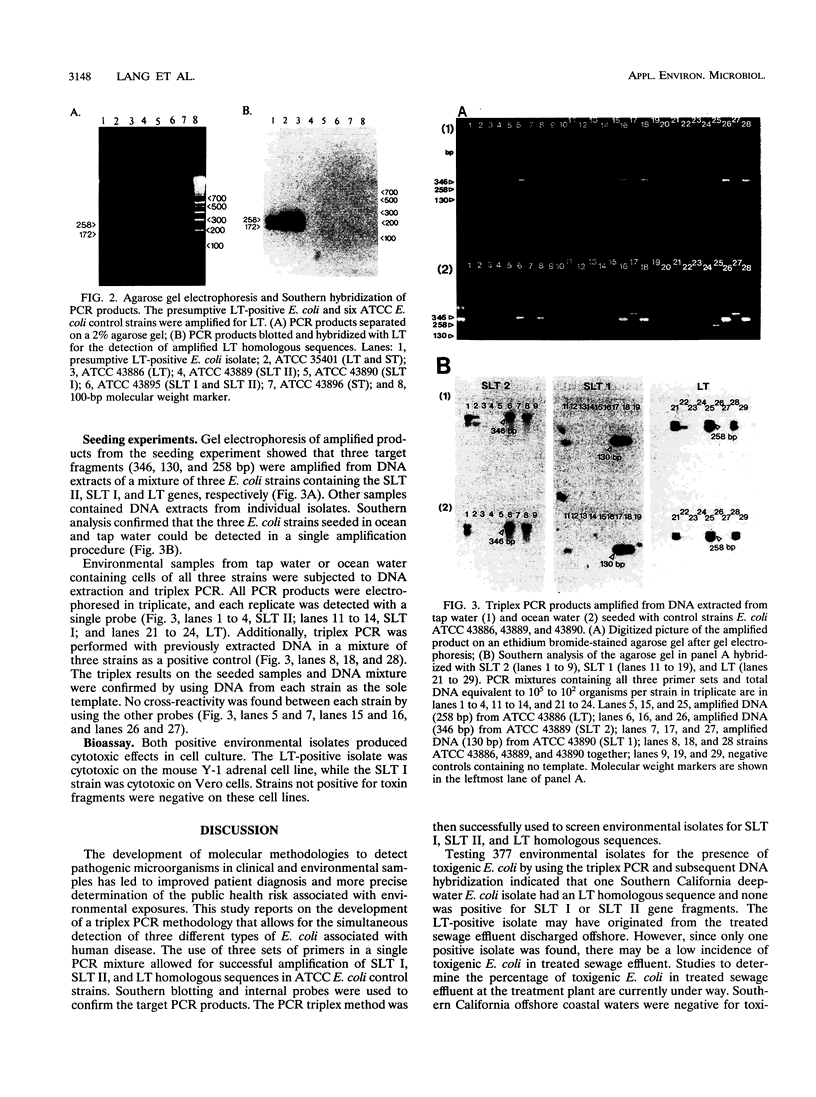
A triplex PCR method was developed to simultaneously amplify a heat-labile toxin sequence (LT) of 258 bp, a shiga-like toxin I sequence (SLT I) of 130 bp, and a shiga-like toxin II sequence (SLT II) of 346 bp from toxigenic strains of Escherichia coli. This method was used to screen 377 environmental E. coli isolates from marine waters or estuaries located in Southern California and North Carolina for enterotoxigenic or enterohemorrhagic E. coli strains. Of the 377 E. coli screened, one isolate was found to belong to the enterotoxigenic group, since it contained a LT homologous sequence, and one isolate was found to belong to the enterohemorrhagic group, since it contained a SLT I homologous sequence. None was found to contain SLT II homologous sequences. The pathogenicity of the positive environmental E. coli isolates was confirmed by standard bioassays with Y-1 adrenal cells and Vero cells to confirm toxin production. Our results suggest that toxigenic E. coli occurs infrequently in environmental waters and that there is a low public health risk from toxigenic E. coli in coastal waters.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bej A. K., McCarty S. C., Atlas R. M. Detection of coliform bacteria and Escherichia coli by multiplex polymerase chain reaction: comparison with defined substrate and plating methods for water quality monitoring. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Aug;57(8):2429–2432. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.8.2429-2432.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bej A. K., Steffan R. J., DiCesare J., Haff L., Atlas R. M. Detection of coliform bacteria in water by polymerase chain reaction and gene probes. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Feb;56(2):307–314. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.2.307-314.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edberg S. C., Patterson J. E., Smith D. B. Differentiation of distribution systems, source water, and clinical coliforms by DNA analysis. J Clin Microbiol. 1994 Jan;32(1):139–142. doi: 10.1128/jcm.32.1.139-142.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gannon V. P., King R. K., Kim J. Y., Thomas E. J. Rapid and sensitive method for detection of Shiga-like toxin-producing Escherichia coli in ground beef using the polymerase chain reaction. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992 Dec;58(12):3809–3815. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.12.3809-3815.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh A. R., Nair G. B., Naik T. N., Sarkar S. K., Mazumdar R., Pal S. C., Sen D. Serovars of multi-antibiotic resistant Escherichia coli from the freshwater environs of Calcutta, India. Microbiol Immunol. 1991;35(4):273–287. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1991.tb01557.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M. M. Escherichia coli that cause diarrhea: enterotoxigenic, enteropathogenic, enteroinvasive, enterohemorrhagic, and enteroadherent. J Infect Dis. 1987 Mar;155(3):377–389. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.3.377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moseley S. L., Echeverria P., Seriwatana J., Tirapat C., Chaicumpa W., Sakuldaipeara T., Falkow S. Identification of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli by colony hybridization using three enterotoxin gene probes. J Infect Dis. 1982 Jun;145(6):863–869. doi: 10.1093/infdis/145.6.863. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien A. D., Holmes R. K. Shiga and Shiga-like toxins. Microbiol Rev. 1987 Jun;51(2):206–220. doi: 10.1128/mr.51.2.206-220.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer C. J., Tsai Y. L., Lang A. L., Sangermano L. R. Evaluation of colilert-marine water for detection of total coliforms and Escherichia coli in the marine environment. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1993 Mar;59(3):786–790. doi: 10.1128/aem.59.3.786-790.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollard D. R., Johnson W. M., Lior H., Tyler S. D., Rozee K. R. Rapid and specific detection of verotoxin genes in Escherichia coli by the polymerase chain reaction. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Mar;28(3):540–545. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.3.540-545.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riley L. W., Remis R. S., Helgerson S. D., McGee H. B., Wells J. G., Davis B. R., Hebert R. J., Olcott E. S., Johnson L. M., Hargrett N. T. Hemorrhagic colitis associated with a rare Escherichia coli serotype. N Engl J Med. 1983 Mar 24;308(12):681–685. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198303243081203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saliba L. J., Helmer R. Health risks associated with pollution of coastal bathing waters. World Health Stat Q. 1990;43(3):177–187. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swerdlow D. L., Woodruff B. A., Brady R. C., Griffin P. M., Tippen S., Donnell H. D., Jr, Geldreich E., Payne B. J., Meyer A., Jr, Wells J. G. A waterborne outbreak in Missouri of Escherichia coli O157:H7 associated with bloody diarrhea and death. Ann Intern Med. 1992 Nov 15;117(10):812–819. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-117-10-812. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai Y. L., Palmer C. J., Sangermano L. R. Detection of Escherichia coli in sewage and sludge by polymerase chain reaction. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1993 Feb;59(2):353–357. doi: 10.1128/aem.59.2.353-357.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valentini S. R., Gomes T. A., Falcão D. P. Lack of virulence factors in Escherichia coli strains of enteropathogenic serogroups isolated from water. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992 Jan;58(1):412–414. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.1.412-414.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woo T. H., Cheng A. F., Ling J. M. An application of a simple method for the preparation of bacterial DNA. Biotechniques. 1992 Nov;13(5):696–698. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]