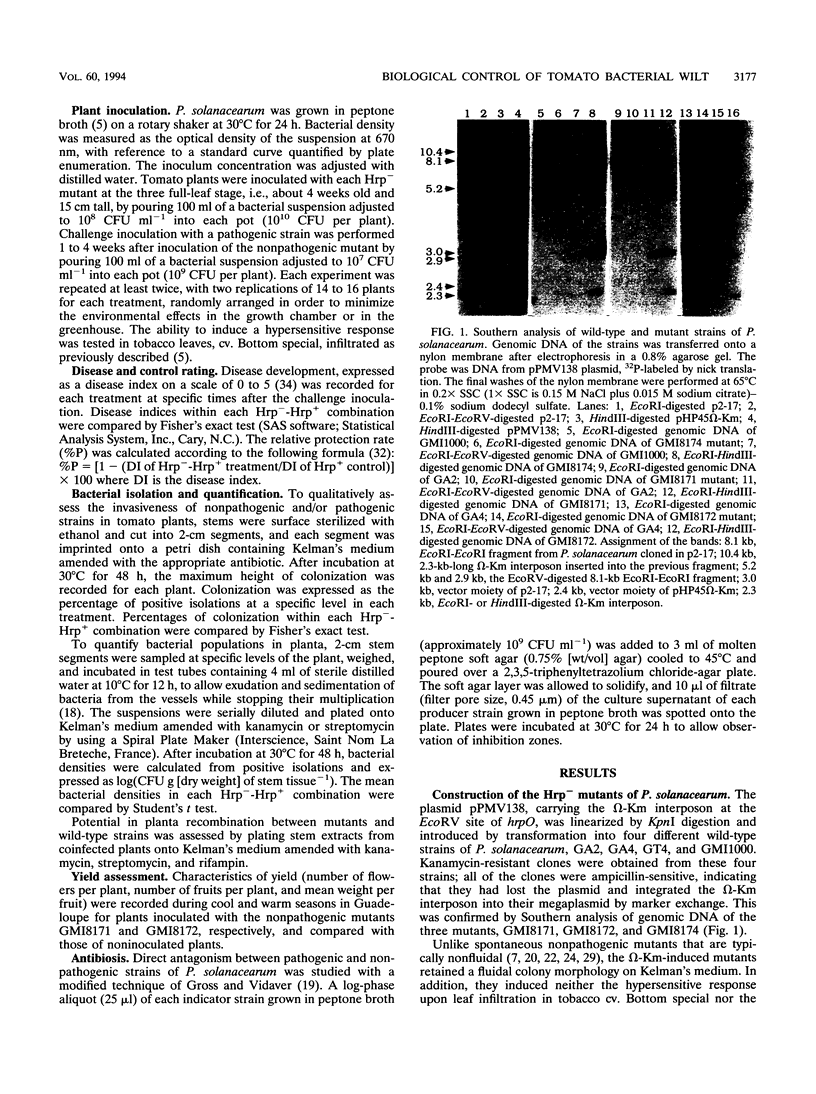
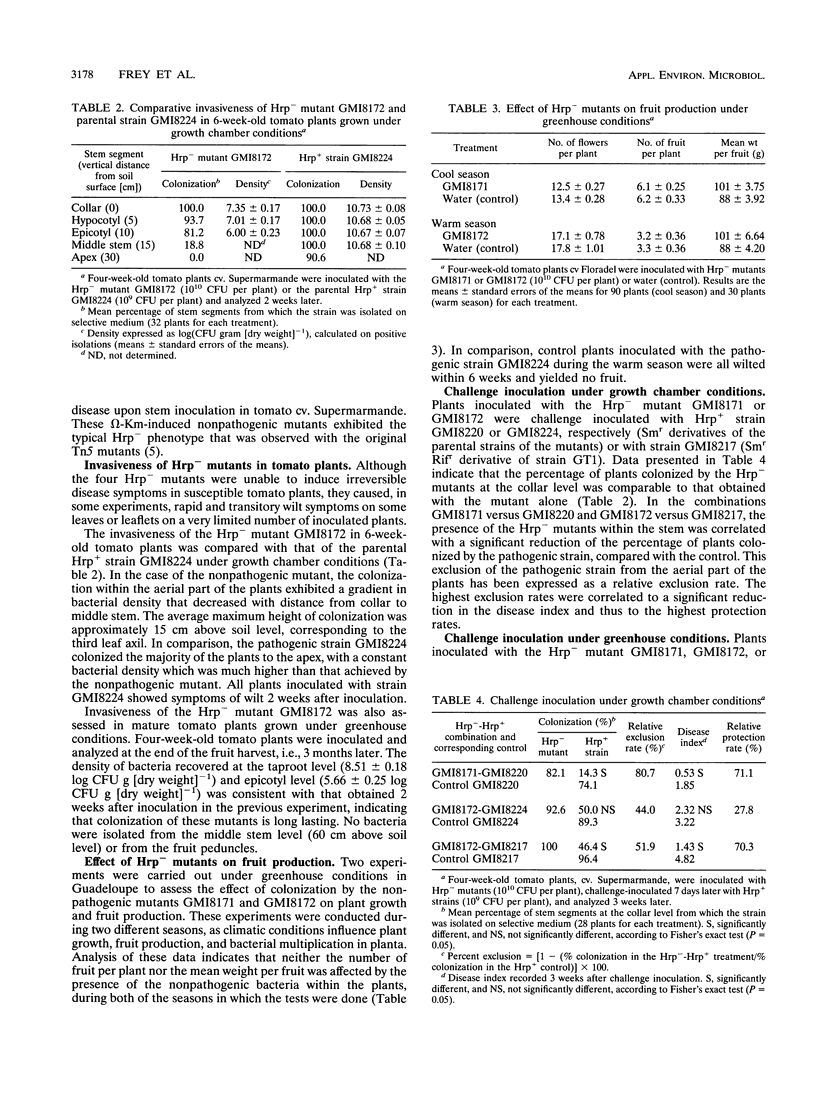
Abstract
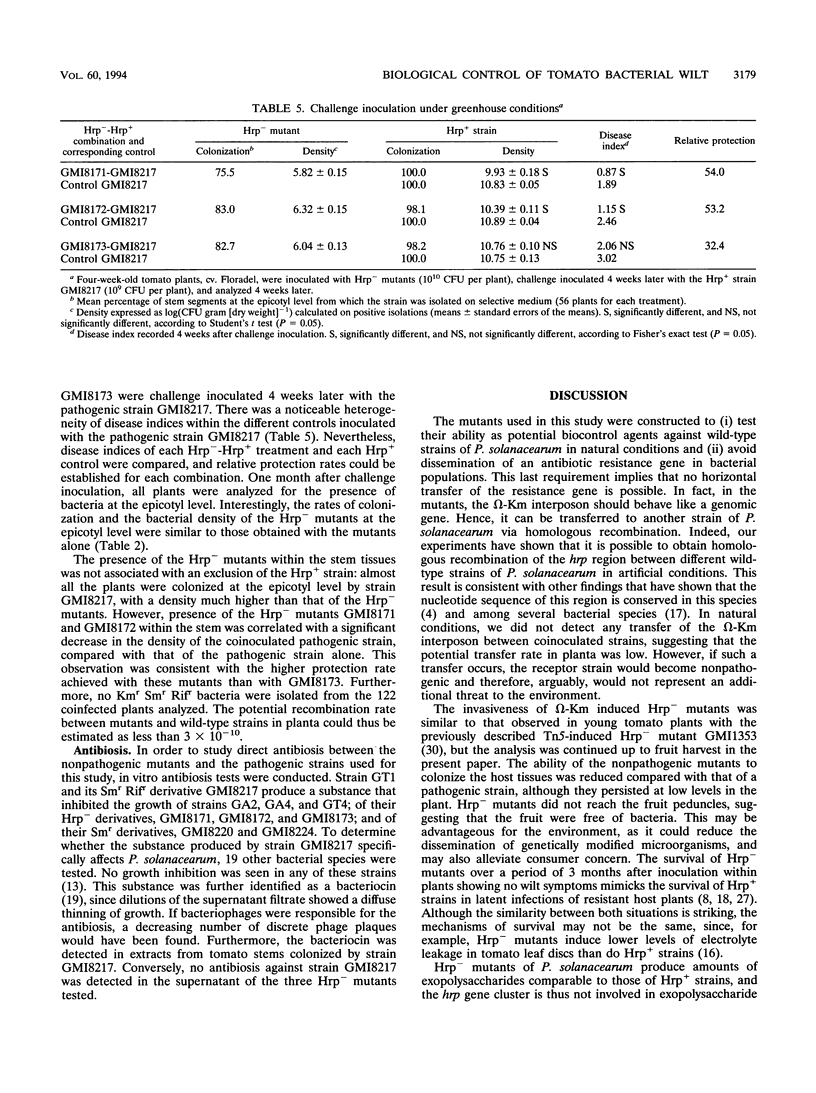
There have been many attempts to control bacterial wilt with antagonistic bacteria or spontaneous nonpathogenic mutants of Pseudomonas solanacearum that lack the ability to colonize the host, but they have met with limited success. Since a large gene cluster (hrp) is involved in the pathogenicity of P. solanacearum, we developed a biological control strategy using genetically engineered Hrp- mutants of P. solanacearum. Three pathogenic strains collected in Guadeloupe (French West Indies) were rendered nonpathogenic by insertion of an ω-Km interposon within the hrp gene cluster of each strain. The resulting Hrp- mutants were tested for their ability to control bacterial wilt in challenge inoculation experiments conducted either under growth chamber conditions or under greenhouse conditions in Guadeloupe. Compared with the colonization by a pathogenic strain which spread throughout the tomato plant, colonization by the mutants was restricted to the roots and the lower part of the stems. The mutants did not reach the fruit. Moreover, the presence of the mutants did not affect fruit production. When the plants were challenge inoculated with a pathogenic strain, the presence of Hrp- mutants within the plants was correlated with a reduction in disease severity, although pathogenic bacteria colonized the stem tissue at a higher density than the nonpathogenic bacteria. Challenge inoculation experiments conducted under growth chamber conditions led, in some cases, to exclusion of the pathogenic strain from the aerial part of the plant, resulting in high protection rates. Furthermore, there was evidence that one of the pathogenic strains used for the challenge inoculations produced a bacteriocin that inhibited the in vitro growth of the nonpathogenic mutants.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boucher C. A., Van Gijsegem F., Barberis P. A., Arlat M., Zischek C. Pseudomonas solanacearum genes controlling both pathogenicity on tomato and hypersensitivity on tobacco are clustered. J Bacteriol. 1987 Dec;169(12):5626–5632. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.12.5626-5632.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duvick J. P., Sequeira L. Interaction of Pseudomonas solanacearum Lipopolysaccharide and Extracellular Polysaccharide with Agglutinin from Potato Tubers. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Jul;48(1):192–198. doi: 10.1128/aem.48.1.192-198.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fellay R., Frey J., Krisch H. Interposon mutagenesis of soil and water bacteria: a family of DNA fragments designed for in vitro insertional mutagenesis of gram-negative bacteria. Gene. 1987;52(2-3):147–154. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90041-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frey J., Krisch H. M. Omega mutagenesis in gram-negative bacteria: a selectable interposon which is strongly polar in a wide range of bacterial species. Gene. 1985;36(1-2):143–150. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90078-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gough C. L., Genin S., Lopes V., Boucher C. A. Homology between the HrpO protein of Pseudomonas solanacearum and bacterial proteins implicated in a signal peptide-independent secretion mechanism. Mol Gen Genet. 1993 Jun;239(3):378–392. doi: 10.1007/BF00276936. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gough C. L., Genin S., Zischek C., Boucher C. A. hrp genes of Pseudomonas solanacearum are homologous to pathogenicity determinants of animal pathogenic bacteria and are conserved among plant pathogenic bacteria. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 1992 Sep-Oct;5(5):384–389. doi: 10.1094/mpmi-5-384. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prentki P., Krisch H. M. In vitro insertional mutagenesis with a selectable DNA fragment. Gene. 1984 Sep;29(3):303–313. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90059-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




