Abstract
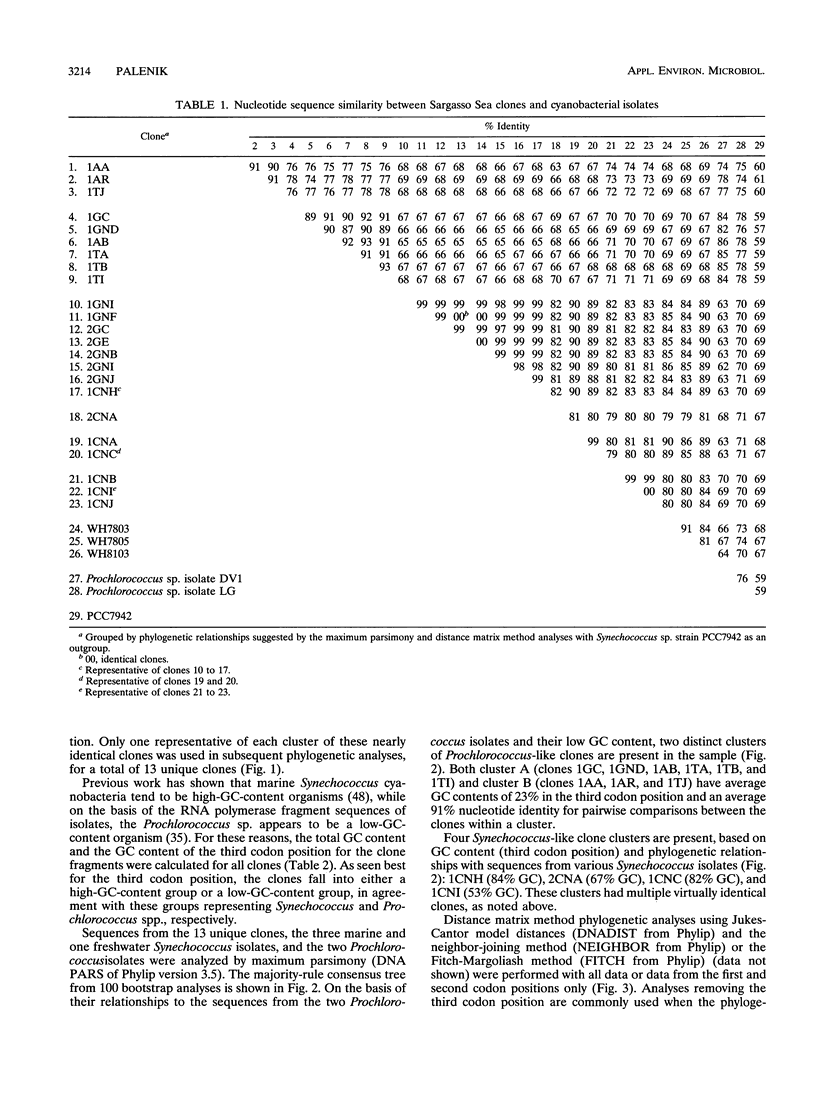
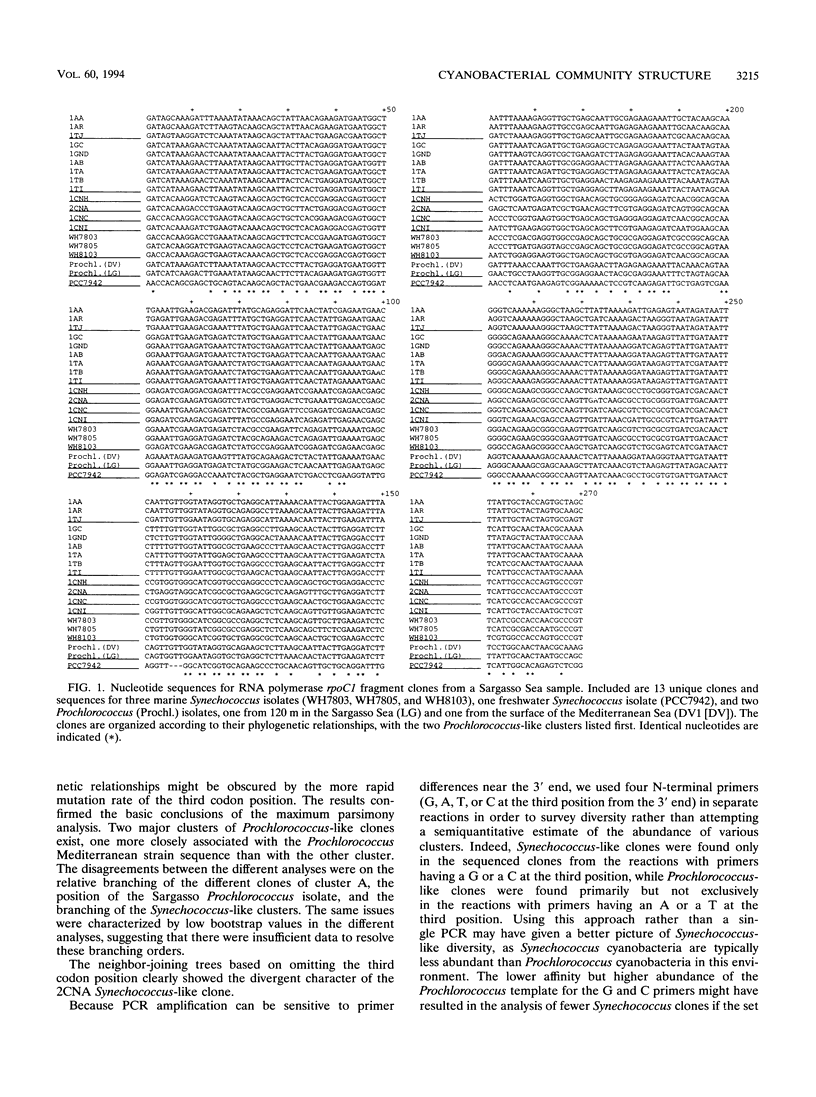
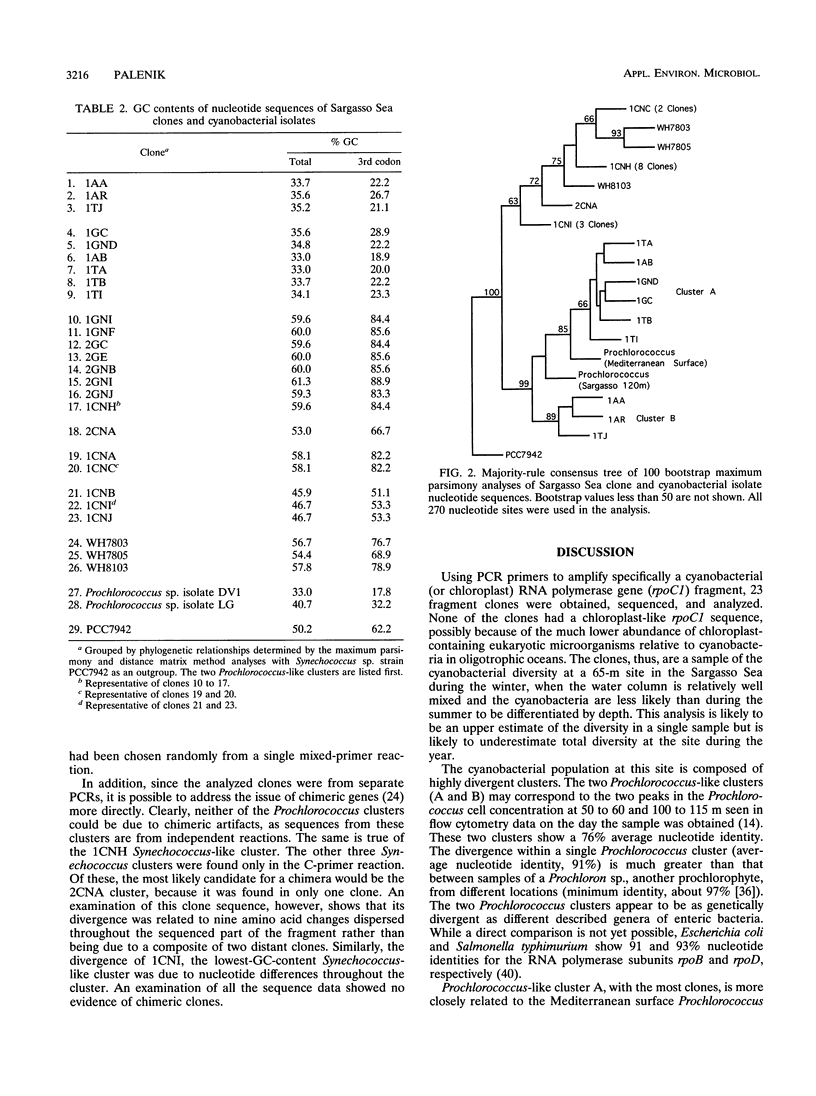
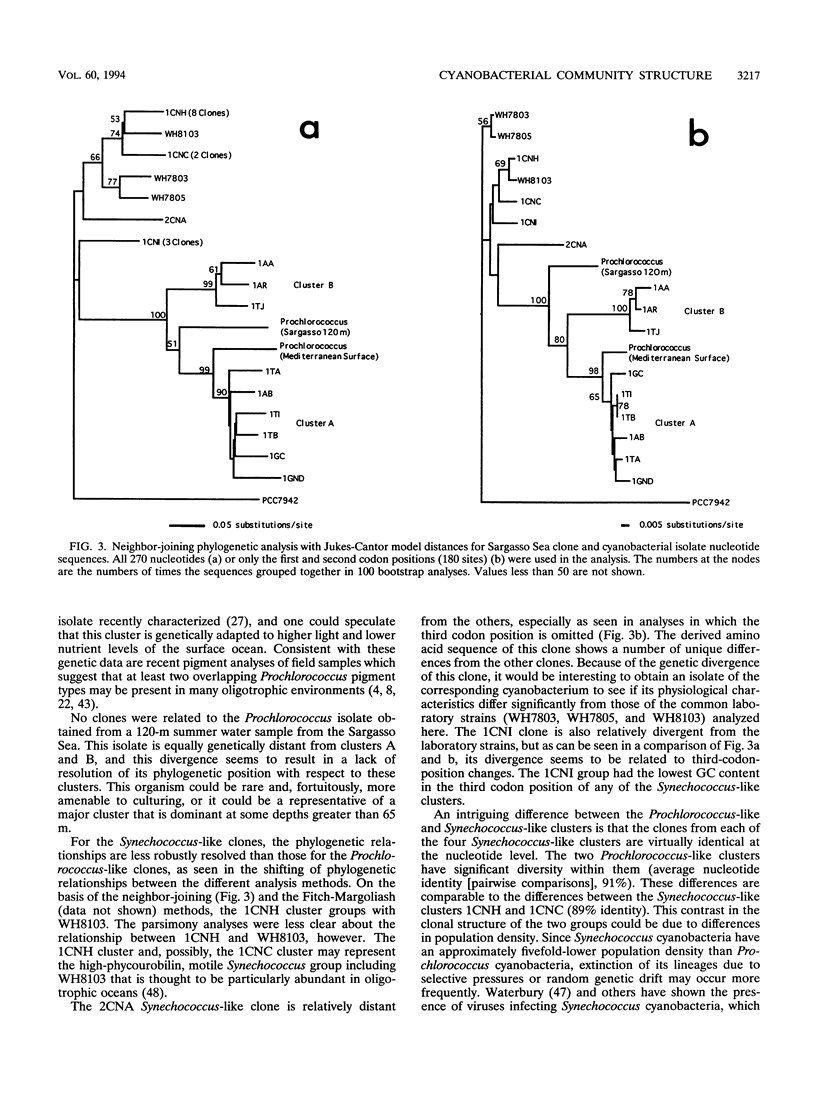
PCR was used to amplify DNA-dependent RNA polymerase gene sequences specifically from the cyanobacterial population in a seawater sample from the Sargasso Sea. Sequencing and analysis of the cloned fragments suggest that the population in the sample consisted of two distinct clusters of Prochlorococcus-like cyanobacteria and four clusters of Synechococcus-like cyanobacteria. The diversity within these clusters was significantly different, however. Clones within each Synechococcus-like cluster were 99 to 100% identical, while each Prochlorococcus-like cluster was only 91% identical at the nucleotide level. One Prochlorococcus-like cluster was significantly more closely related to a Mediterranean Sea (surface) Prochlorococcus isolate than to the other cluster, showing the highly divergent nature of this group even in one sample. The approach described here can be used as a general method for examining cyanobacterial diversity, while an oligotrophic ocean ecosystem such as the Sargasso Sea may be an ideal model for examining diversity in relation to environmental parameters.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bergsland K. J., Haselkorn R. Evolutionary relationships among eubacteria, cyanobacteria, and chloroplasts: evidence from the rpoC1 gene of Anabaena sp. strain PCC 7120. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jun;173(11):3446–3455. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.11.3446-3455.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Britschgi T. B., Giovannoni S. J. Phylogenetic analysis of a natural marine bacterioplankton population by rRNA gene cloning and sequencing. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Jun;57(6):1707–1713. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.6.1707-1713.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell L., Carpenter E. J., Iacono V. J. Identification and enumeration of marine chroococcoid cyanobacteria by immunofluorescence. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Sep;46(3):553–559. doi: 10.1128/aem.46.3.553-559.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLong E. F. Archaea in coastal marine environments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jun 15;89(12):5685–5689. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.12.5685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas S. E., Carr N. Examination of Genetic Relatedness of Marine Synechococcus spp. by Using Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphisms. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Dec;54(12):3071–3078. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.12.3071-3078.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuhrman J. A., McCallum K., Davis A. A. Novel major archaebacterial group from marine plankton. Nature. 1992 Mar 12;356(6365):148–149. doi: 10.1038/356148a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuhrman J. A., McCallum K., Davis A. A. Phylogenetic diversity of subsurface marine microbial communities from the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1993 May;59(5):1294–1302. doi: 10.1128/aem.59.5.1294-1302.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giovannoni S. J., Britschgi T. B., Moyer C. L., Field K. G. Genetic diversity in Sargasso Sea bacterioplankton. Nature. 1990 May 3;345(6270):60–63. doi: 10.1038/345060a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins D. G., Bleasby A. J., Fuchs R. CLUSTAL V: improved software for multiple sequence alignment. Comput Appl Biosci. 1992 Apr;8(2):189–191. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/8.2.189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kopczynski E. D., Bateson M. M., Ward D. M. Recognition of chimeric small-subunit ribosomal DNAs composed of genes from uncultivated microorganisms. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1994 Feb;60(2):746–748. doi: 10.1128/aem.60.2.746-748.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson K., Selander R. K. Evolutionary genetics of the proline permease gene (putP) and the control region of the proline utilization operon in populations of Salmonella and Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1992 Nov;174(21):6886–6895. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.21.6886-6895.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson K., Whittam T. S., Selander R. K. Nucleotide polymorphism and evolution in the glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase gene (gapA) in natural populations of Salmonella and Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 1;88(15):6667–6671. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.15.6667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palenik B., Haselkorn R. Multiple evolutionary origins of prochlorophytes, the chlorophyll b-containing prokaryotes. Nature. 1992 Jan 16;355(6357):265–267. doi: 10.1038/355265a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palenik B. Polymerase evolution and organism evolution. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1992 Dec;2(6):931–936. doi: 10.1016/s0959-437x(05)80118-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruff-Roberts A. L., Kuenen J. G., Ward D. M. Distribution of cultivated and uncultivated cyanobacteria and Chloroflexus-like bacteria in hot spring microbial mats. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1994 Feb;60(2):697–704. doi: 10.1128/aem.60.2.697-704.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt T. M., DeLong E. F., Pace N. R. Analysis of a marine picoplankton community by 16S rRNA gene cloning and sequencing. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jul;173(14):4371–4378. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.14.4371-4378.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selander R. K., Levin B. R. Genetic diversity and structure in Escherichia coli populations. Science. 1980 Oct 31;210(4469):545–547. doi: 10.1126/science.6999623. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp P. M. Determinants of DNA sequence divergence between Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium: codon usage, map position, and concerted evolution. J Mol Evol. 1991 Jul;33(1):23–33. doi: 10.1007/BF02100192. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urbach E., Robertson D. L., Chisholm S. W. Multiple evolutionary origins of prochlorophytes within the cyanobacterial radiation. Nature. 1992 Jan 16;355(6357):267–270. doi: 10.1038/355267a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waterbury J. B., Valois F. W. Resistance to co-occurring phages enables marine synechococcus communities to coexist with cyanophages abundant in seawater. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1993 Oct;59(10):3393–3399. doi: 10.1128/aem.59.10.3393-3399.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



