Abstract
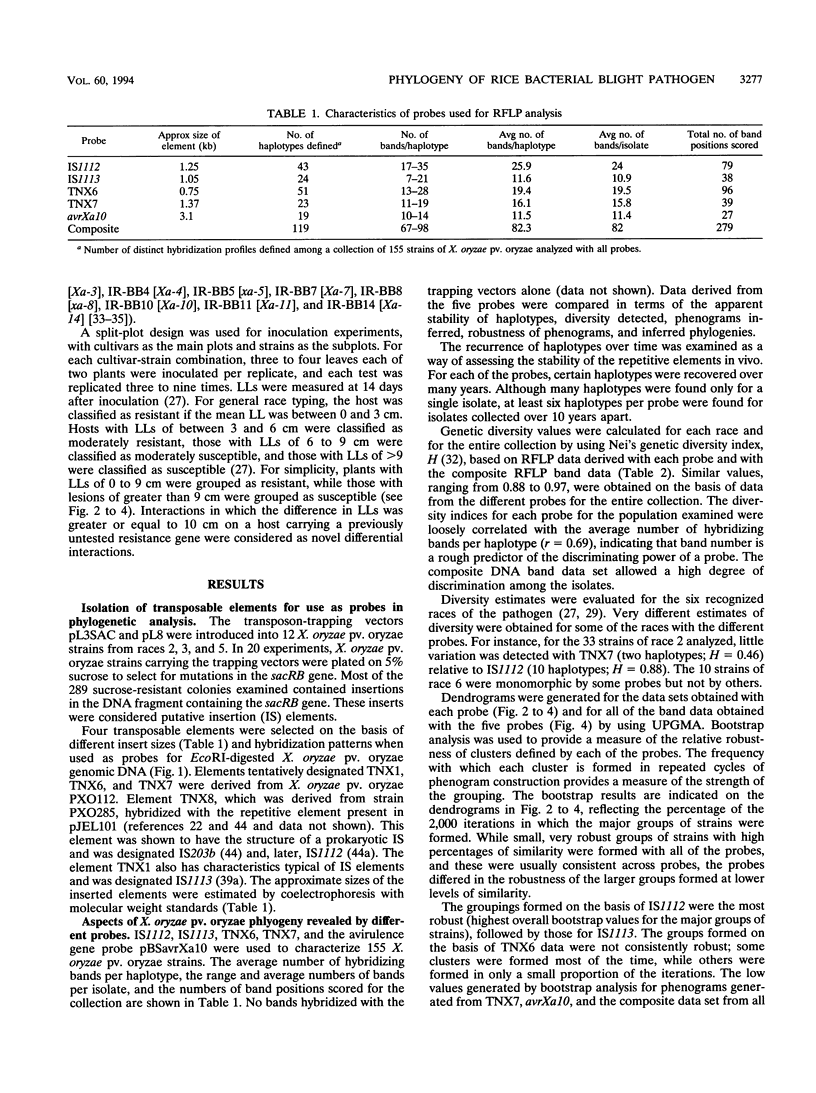
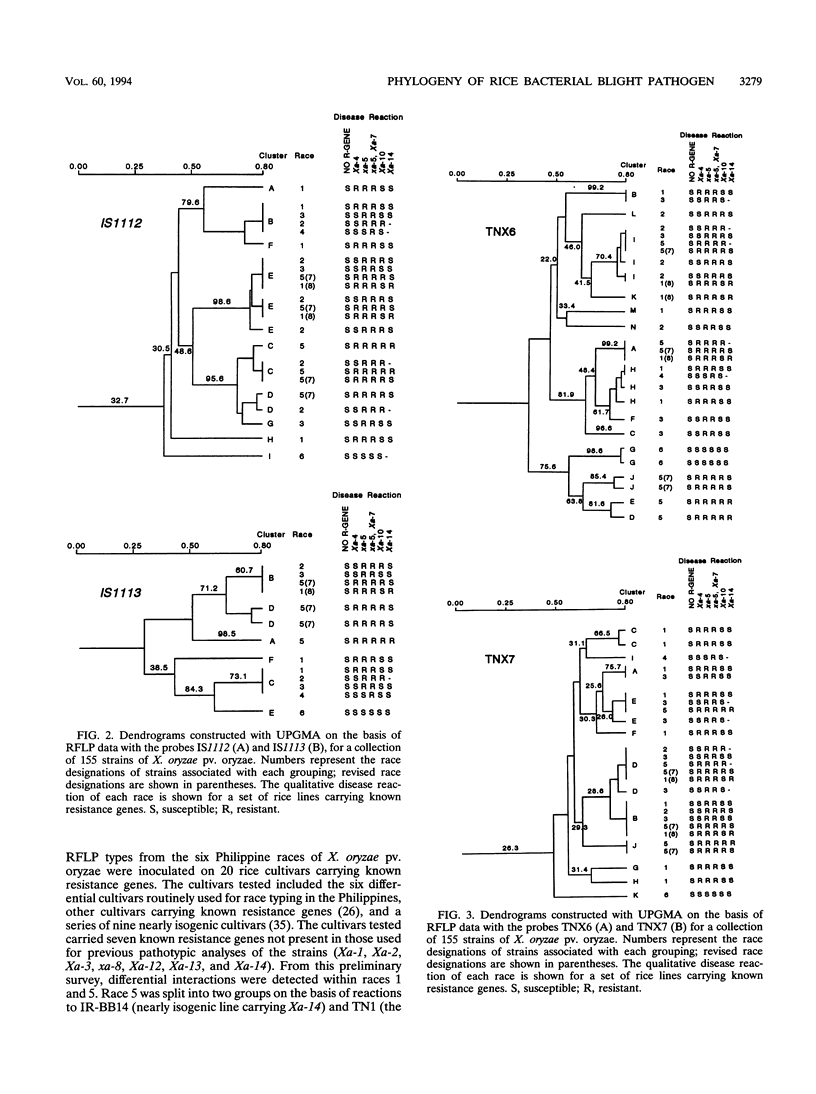
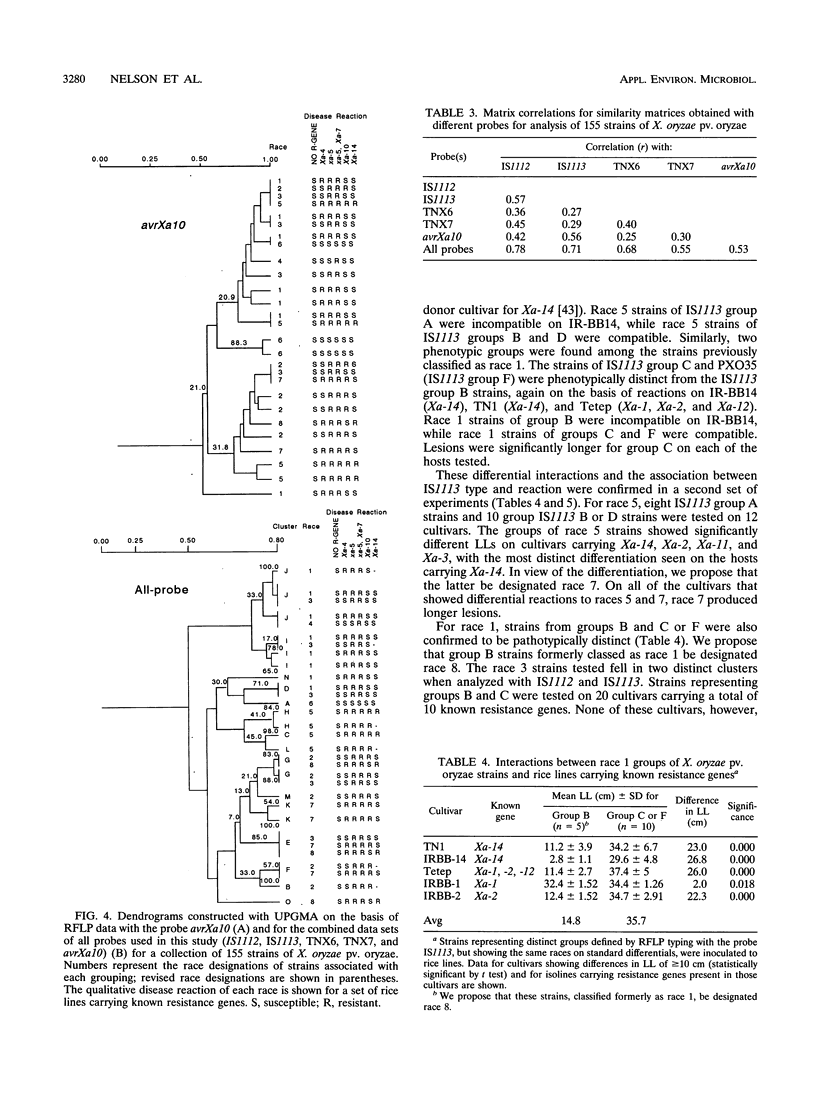
Several transposable elements were isolated from the genome of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae. These elements and an avirulence gene isolated from X. oryzae pv. oryzae were used as hybridization probes for a collection of X. oryzae pv. oryzae strains from the Philippines. Each of the sequences was present in multiple copies in all strains examined and showed distinct patterns of hybridizing bands. Phenograms were derived from the restriction fragment length polymorphism data obtained for each of the individual probes and for pooled data from multiple probes. The phenograms derived from the different probes differed in topology and, on the basis of bootstrap analysis, were not equally robust. For all of the probes, including the avirulence gene, some groups (even some haplotypes) consisted of multiple races. The strains were grouped into four major clusters on the basis of the two probes giving the highest bootstrap values. These groups were inferred to represent phylogenetic lineages. Three of the six races of X. oryzae pv. oryzae appeared in more than one of the lineages, and another was present in two sublineages. For three of the races, strains representing different phenetic groups were inoculated on rice cultivars carrying 10 resistance genes. Two new races were differentiated, corresponding to pathogen lineages identified by DNA typing. On the basis of DNA and pathotypic analyses, together with information on the spatial and temporal distribution of the pathogen types from this and other studies, a general picture of X. oryzae pv. oryzae evolution in the Philippines is presented.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams J., Oeller P. W. Structure of evolving populations of Saccharomyces cerevisiae: adaptive changes are frequently associated with sequence alterations involving mobile elements belonging to the Ty family. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(18):7124–7127. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.18.7124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Comai L., Kosuge T. Transposable element that causes mutations in a plant pathogenic Pseudomonas sp. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jun;154(3):1162–1167. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.3.1162-1167.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felsenstein J. Phylogenies from molecular sequences: inference and reliability. Annu Rev Genet. 1988;22:521–565. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.22.120188.002513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gay P., Le Coq D., Steinmetz M., Berkelman T., Kado C. I. Positive selection procedure for entrapment of insertion sequence elements in gram-negative bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1985 Nov;164(2):918–921. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.2.918-921.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamer J. E., Farrall L., Orbach M. J., Valent B., Chumley F. G. Host species-specific conservation of a family of repeated DNA sequences in the genome of a fungal plant pathogen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(24):9981–9985. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.24.9981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopkins C. M., White F. F., Choi S. H., Guo A., Leach J. E. Identification of a family of avirulence genes from Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 1992 Nov-Dec;5(6):451–459. doi: 10.1094/mpmi-5-451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kearney B., Staskawicz B. J. Characterization of IS476 and its role in bacterial spot disease of tomato and pepper. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jan;172(1):143–148. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.1.143-148.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leach J. E., Rhoads M. L., Vera Cruz C. M., White F. F., Mew T. W., Leung H. Assessment of genetic diversity and population structure of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae with a repetitive DNA element. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992 Jul;58(7):2188–2195. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.7.2188-2195.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy M., Romao J., Marchetti M. A., Hamer J. E. DNA Fingerprinting with a Dispersed Repeated Sequence Resolves Pathotype Diversity in the Rice Blast Fungus. Plant Cell. 1991 Jan;3(1):95–102. doi: 10.1105/tpc.3.1.95. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray M. G., Thompson W. F. Rapid isolation of high molecular weight plant DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Oct 10;8(19):4321–4325. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.19.4321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saitou N., Nei M. The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol. 1987 Jul;4(4):406–425. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]