Abstract
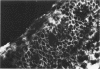
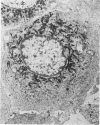
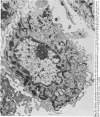
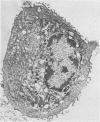
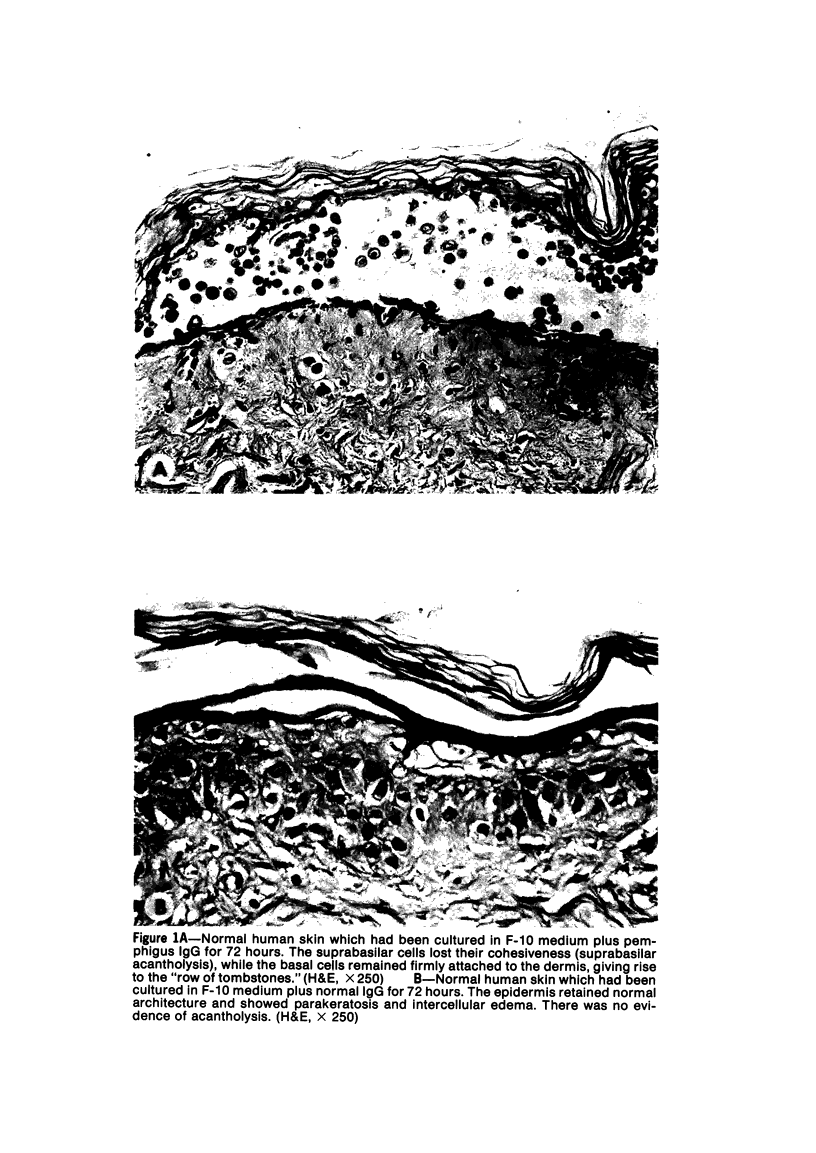
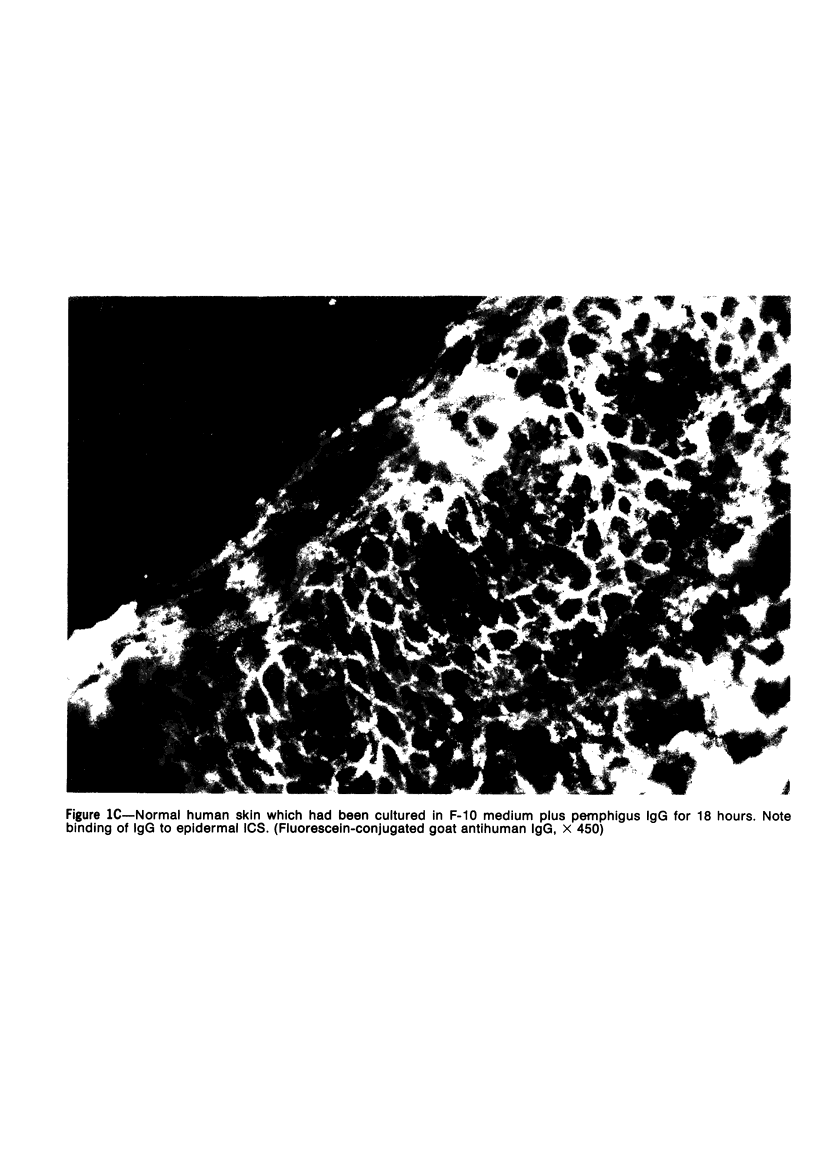
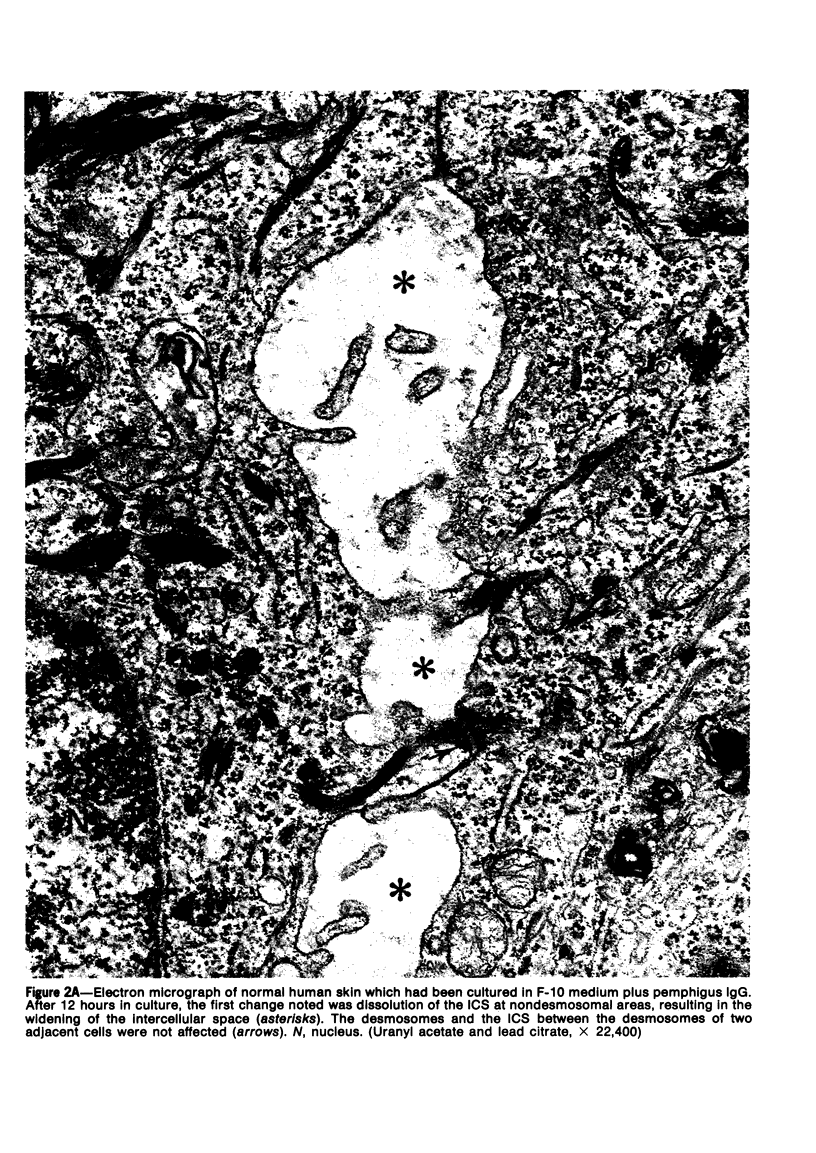
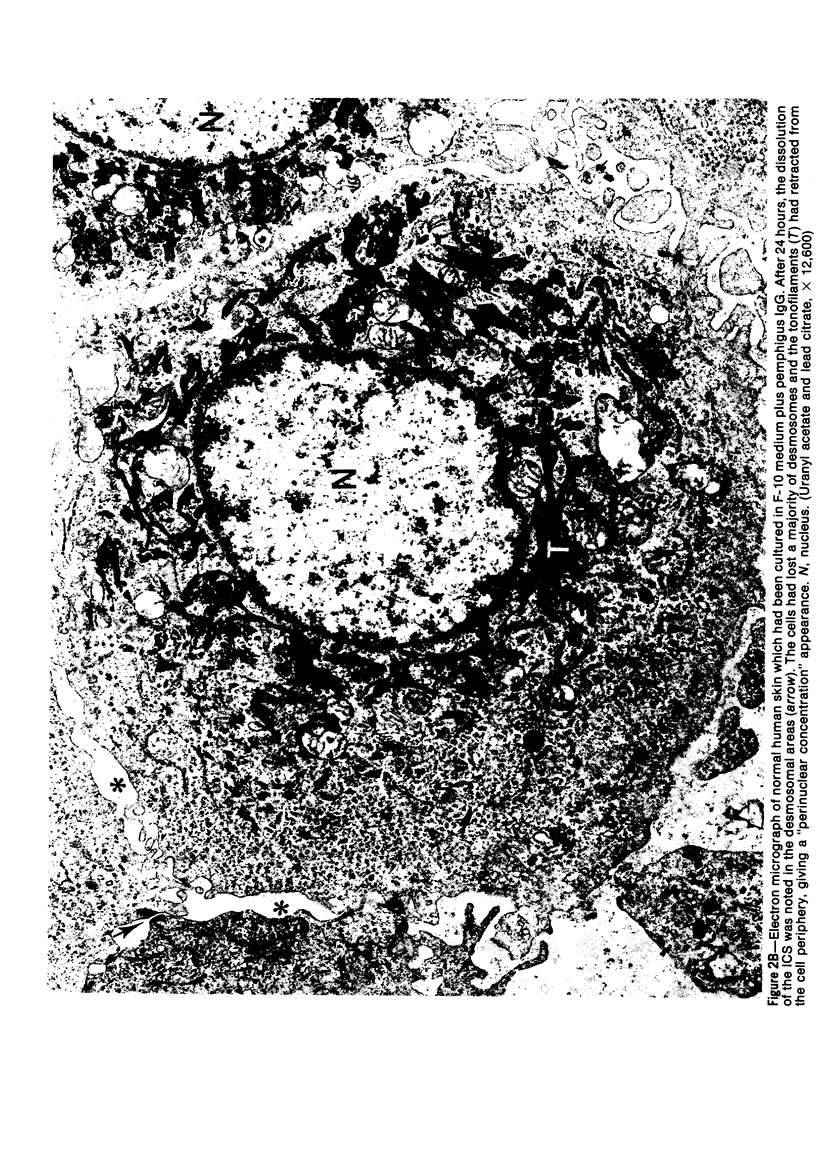
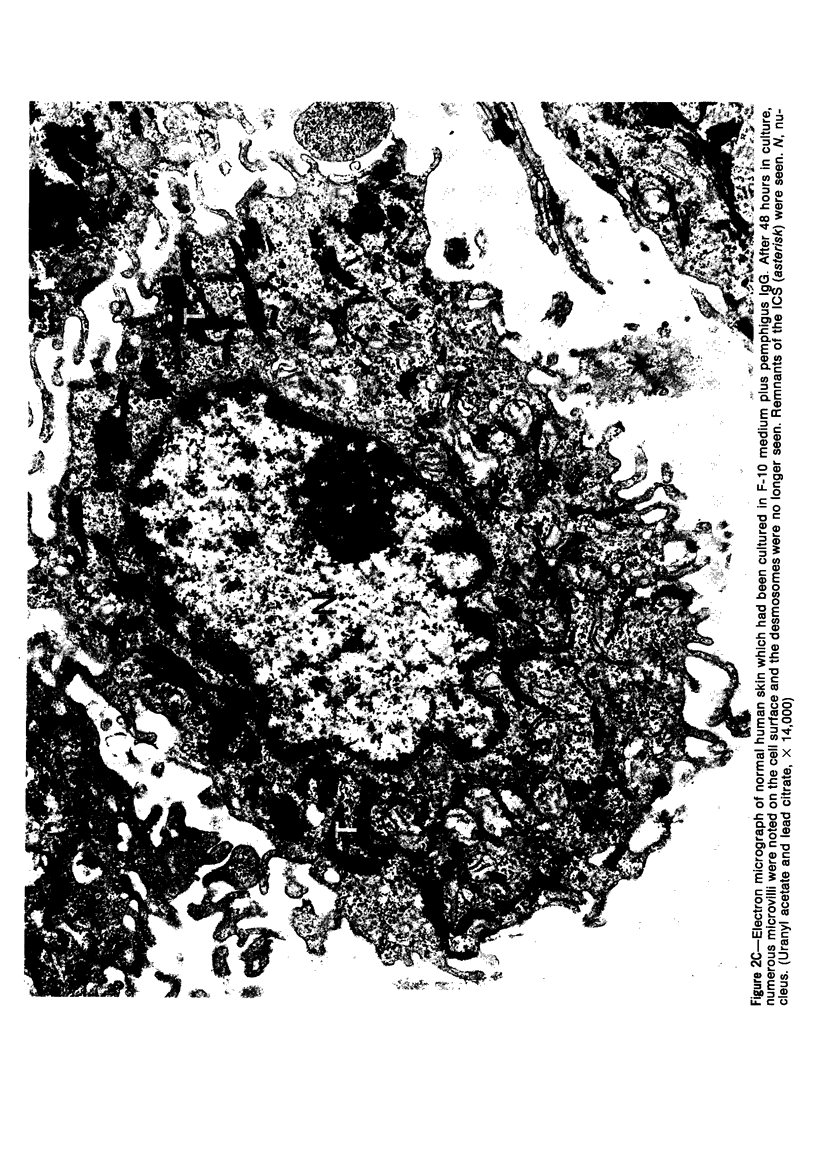
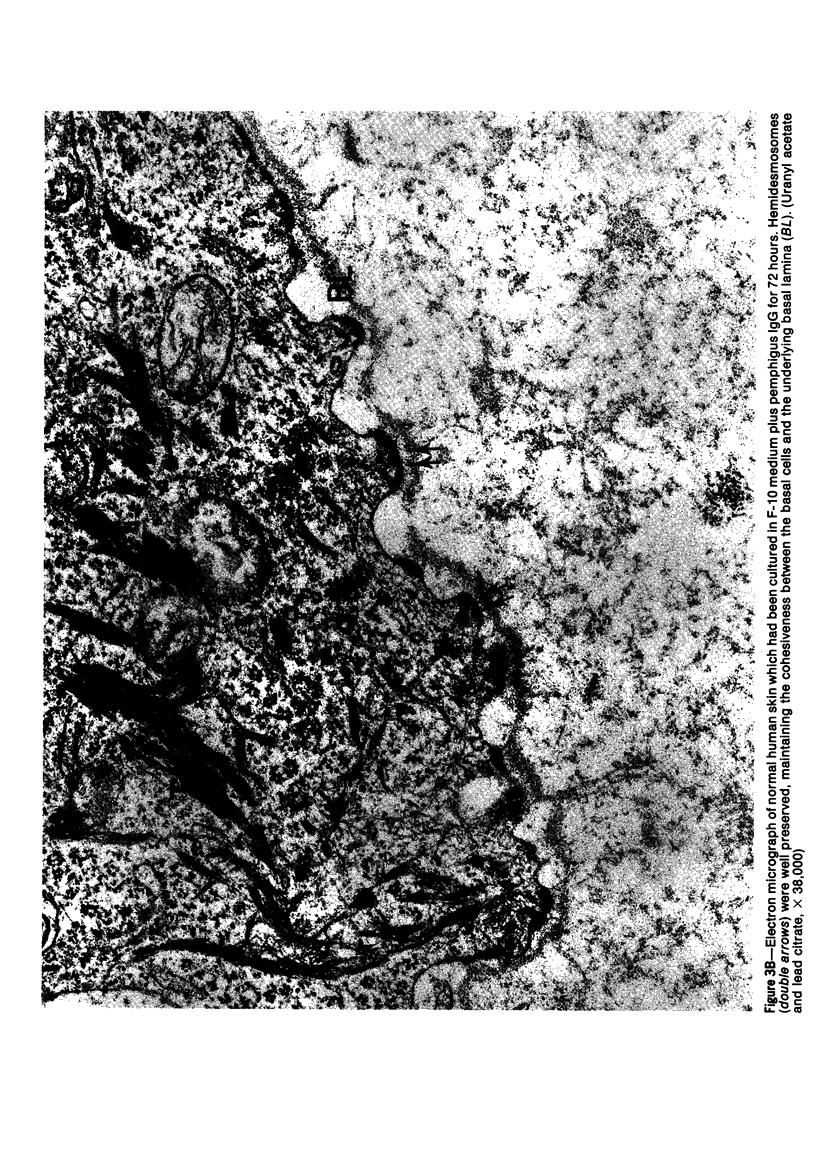
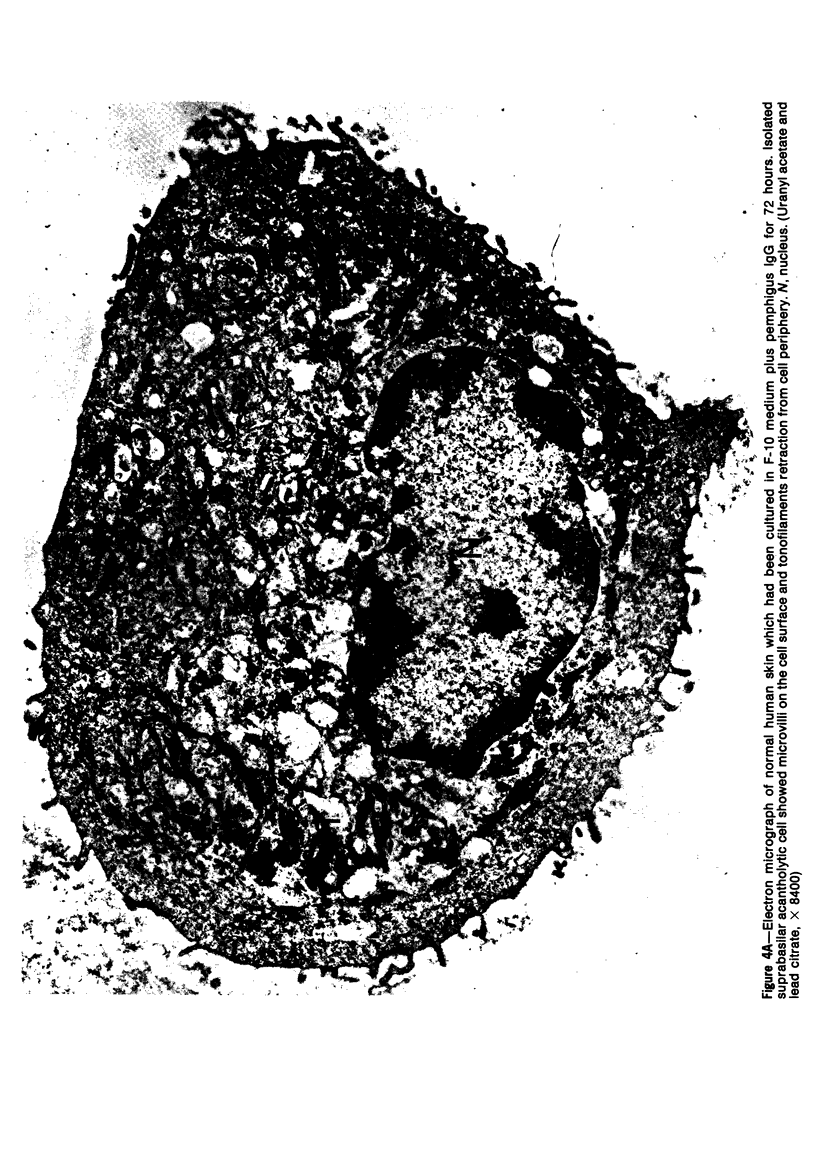
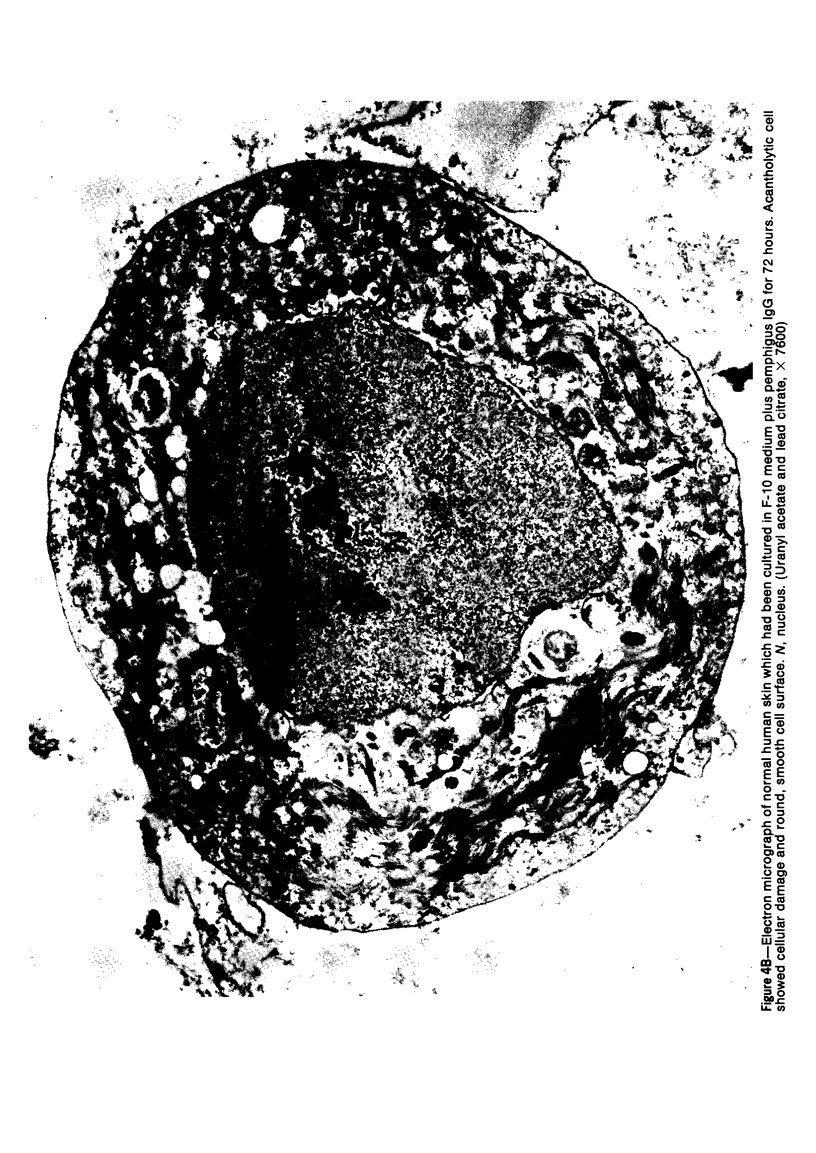
Suprabasilar acantholysis can be produced in organ culture of normal human skin in the presence of pemphigus IgG autoantibody. We have examined this in vitro system by electron microscopy. The earliest ultrastructural changes at 12 hours included widening of the intercellular spaces and disruption of the intercellular cement substance in the nondesmosomal areas. After 24 to 48 hours in culture, the tonofilaments retracted from the cell periphery, desmosomes were lost, and extensive cell surface digitation occurred. By 72 hours, isolated cells without noticeable desmosomes were seen in the suprabasilar areas, whereas basal cells, with intact hemidesmosomes, remained attached to the basal lamina. Control cultures which were grown in the presence of normal IgG or F-10 medium alone did not manifest these changes. The ultrastructural features support the conclusion that the acantholysis produced in this system is similar and probably identical to that of naturally occurring pemphigus.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BELLONE A. G., LEONE V. Ricerche sull'influenza esercitata da sieri di soggetti sani o affetti da pemfigo su pelle umana normale e pemfigosa coltivata in vitro. Soc Ital Dermatol Sifilogr Sezioni Interprov Soc Ital Dermatol Sifilogr. 1956 Mar-Apr;97(2):97–109. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BEUTNER E. H., JORDON R. E. DEMONSTRATION OF SKIN ANTIBODIES IN SERA OF PEMPHIGUS VULGARIS PATIENTS BY INDIRECT IMMUNOFLUORESCENT STAINING. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1964 Nov;117:505–510. doi: 10.3181/00379727-117-29622. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BEUTNER E. H., LEVER W. F., WITEBSKY E., JORDON R., CHERTOCK B. AUTOANTIBODIES IN PEMPHIGUS VULGARIS: RESPONSE TO AN INTERCELLULAR SUBSTANCE OF EPIDERMIS. JAMA. 1965 May 24;192:682–688. doi: 10.1001/jama.1965.03080210026006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnett M. L., Beutner E. H., Chorzelski T. P. Organ culture studies of pemphigus antibodies. II. Ultrastructural comparison between acantholytic changes in vitro and human pemphigus lesions. J Invest Dermatol. 1977 May;68(5):265–271. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12494207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun-Falco O., Vogell W. Elektronenmikroskopische Untersuchungen zur Dynamik der Acantholyse bei Pemphigus vulgaris. I. Die klinisch normal aussehende Haut in der Umgebung von Blasen mit positivem Nikolski-Phänomen. Arch Klin Exp Dermatol. 1965 Oct 21;223(4):328–346. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun-Falco O., Vogell W. Elektronenmikroskopische Untersuchungen zur Dynamik der Akantholyse bei Pemphigus vulgaris. II. Die akantholytische Blase. Arch Klin Exp Dermatol. 1965 Dec 16;223(6):533–550. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun-Falco O., Wolff H. H. Elektronenmikroskopie von Mundschleimhautläsionen des Pemphigus vulgaris. Hautarzt. 1975 Sep;26(9):483–488. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter C. B., d'Apice A. J., Abbas A. K. The role of antibodies in the rejection and enhancement of organ allografts.?7318. Adv Immunol. 1976;22:1–65. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60547-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DIRECTOR W. Pemphigus vlugaris; a clinicopathologic study. AMA Arch Derm Syphilol. 1952 Feb;65(2):155–169. doi: 10.1001/archderm.1952.01530210034005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoto K., Lever W. F. An electron microscopic study on pemphigus vulgaris of the mouth and the skin with special reference to the intercellular cement. J Invest Dermatol. 1967 Jun;48(6):540–552. doi: 10.1038/jid.1967.86. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoto K., Lever W. F. An ultrastructural study of cell junctions in pemphigus vulgaris. Arch Dermatol. 1970 Mar;101(3):287–298. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoto K., Lever W. F. The intercellular cement in pemphigus vulgaris, an electron microscopic study. Dermatologica. 1967;135(1):27–34. doi: 10.1159/000254157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordon R. E., Sams W. M., Jr, Diaz G., Beutner E. H. Negative complement immunofluorescence in pemphigus. J Invest Dermatol. 1971 Dec;57(6):407–410. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12293273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komura J., Ofuji S. Phosphotungstic acid stain and epidermal cell surface. An electron microscopic study. J Invest Dermatol. 1967 Oct;49(4):391–395. doi: 10.1038/jid.1967.154. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STOUGHTON R. B., BAGATELL F. The nature of cantharidin acantholysis. J Invest Dermatol. 1959 Nov;33:287–292. doi: 10.1038/jid.1959.152. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sams W. M., Jr, Schur P. H. Studies of the antibodies in pemphigoid and pemphigus. J Lab Clin Med. 1973 Aug;82(2):249–254. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiltz J. R., Michel B. Production of epidermal acantholysis in normal human skin in vitro by the IgG fraction from pemphigus serum. J Invest Dermatol. 1976 Aug;67(2):254–260. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12513454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILGRAM G. F., CAULFIELD J. B., LEVER W. F. An electron microscopic study of acantholysis in pemphigus vulgaris. J Invest Dermatol. 1961 May;36:373–382. doi: 10.1038/jid.1961.58. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WISLOCKI G. B., FAWCETT D. W., DEMPSEY E. W. Staining of stratified squamous epithelium of mucous membranes and skin of man and monkey by the periodic acid-Schiff method. Anat Rec. 1951 Jul;110(3):359–375. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091100307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolff K., Schreiner E. An electron microscopic study on the extraneous coat of keratinocytes and the intercellular space of the epidermis. J Invest Dermatol. 1968 Dec;51(6):418–430. doi: 10.1038/jid.1968.150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolff K., Schreiner E. Ultrastructural localization of pemphigus autoantibodies within e epidermis. Nature. 1971 Jan 1;229(5279):59–61. doi: 10.1038/229059a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolff K., Tappeiner J., Schreiner E. Akantholyse. I. Der Pathomechanismus der Cantharidin-"Akantholyse". Eine elektronenmikroskopische Studie. Arch Klin Exp Dermatol. 1968;232(3):325–344. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]