Abstract
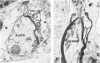
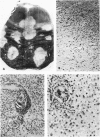
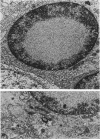
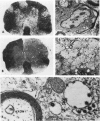
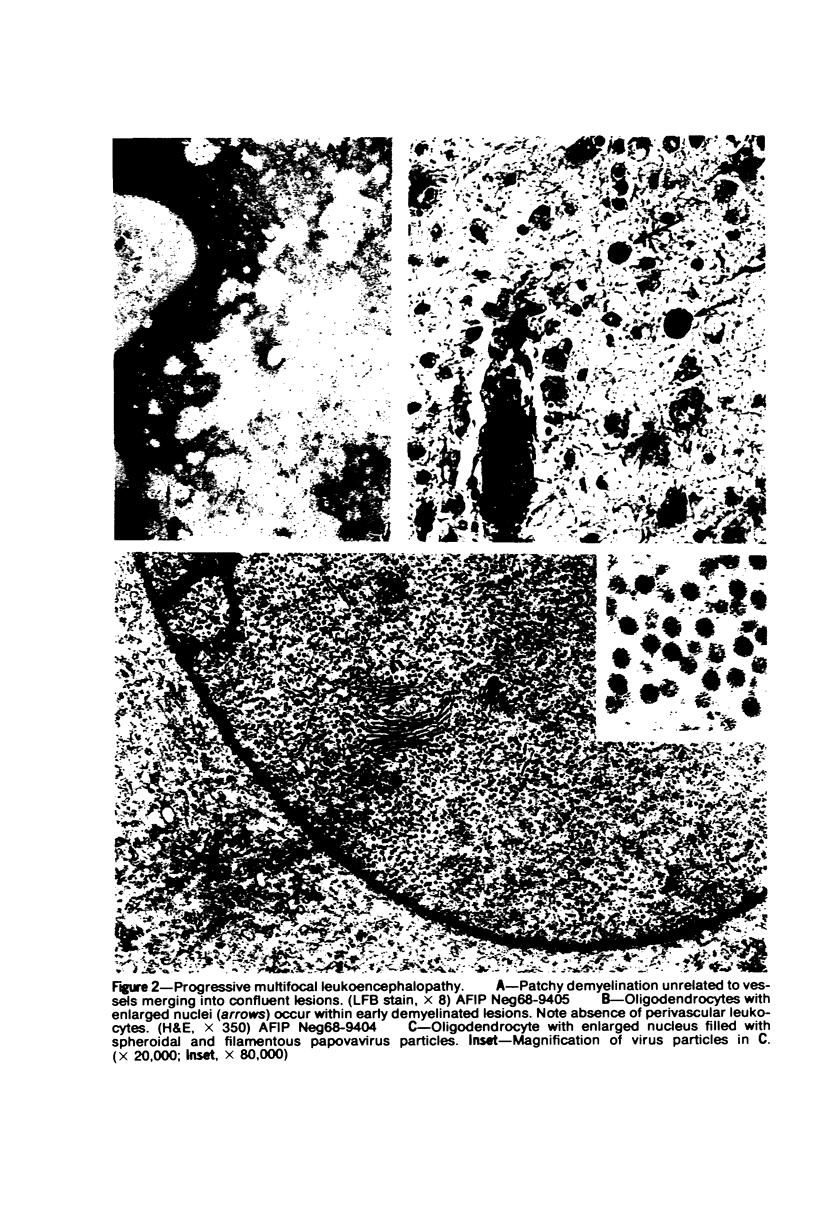
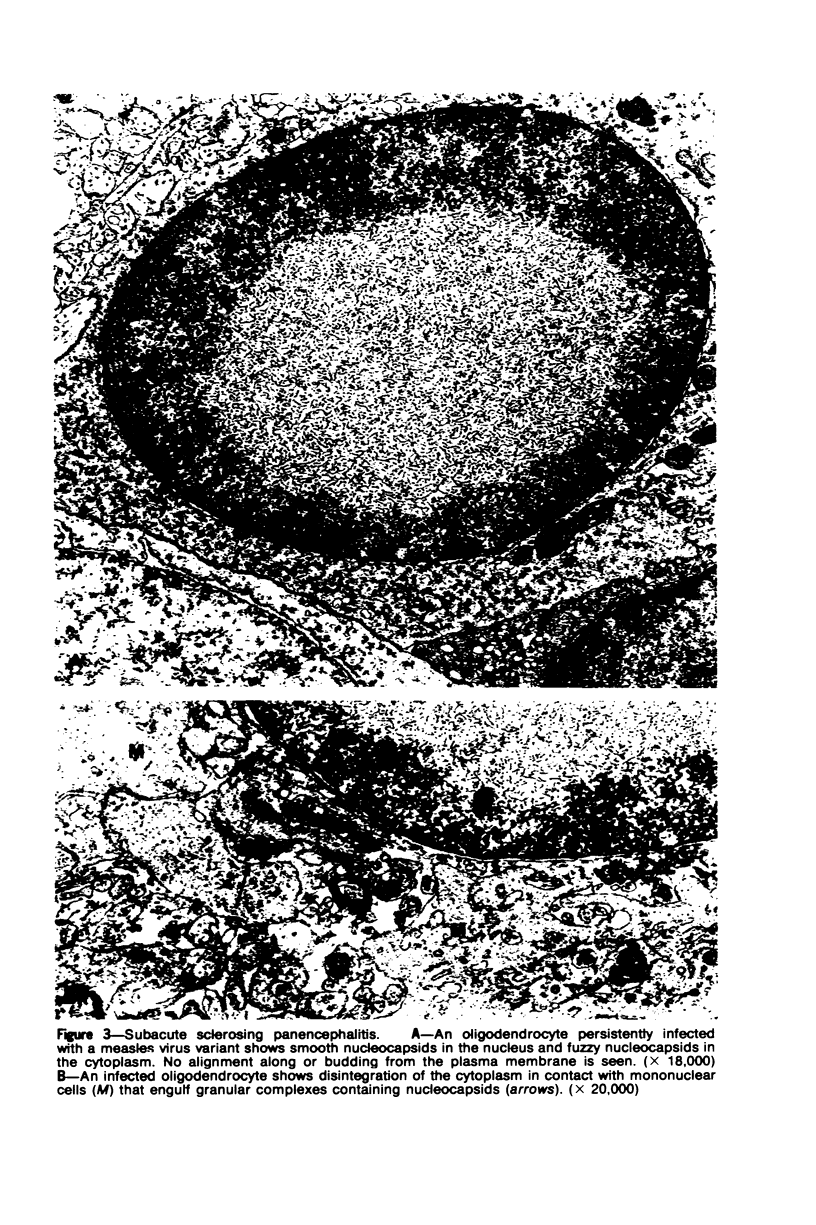
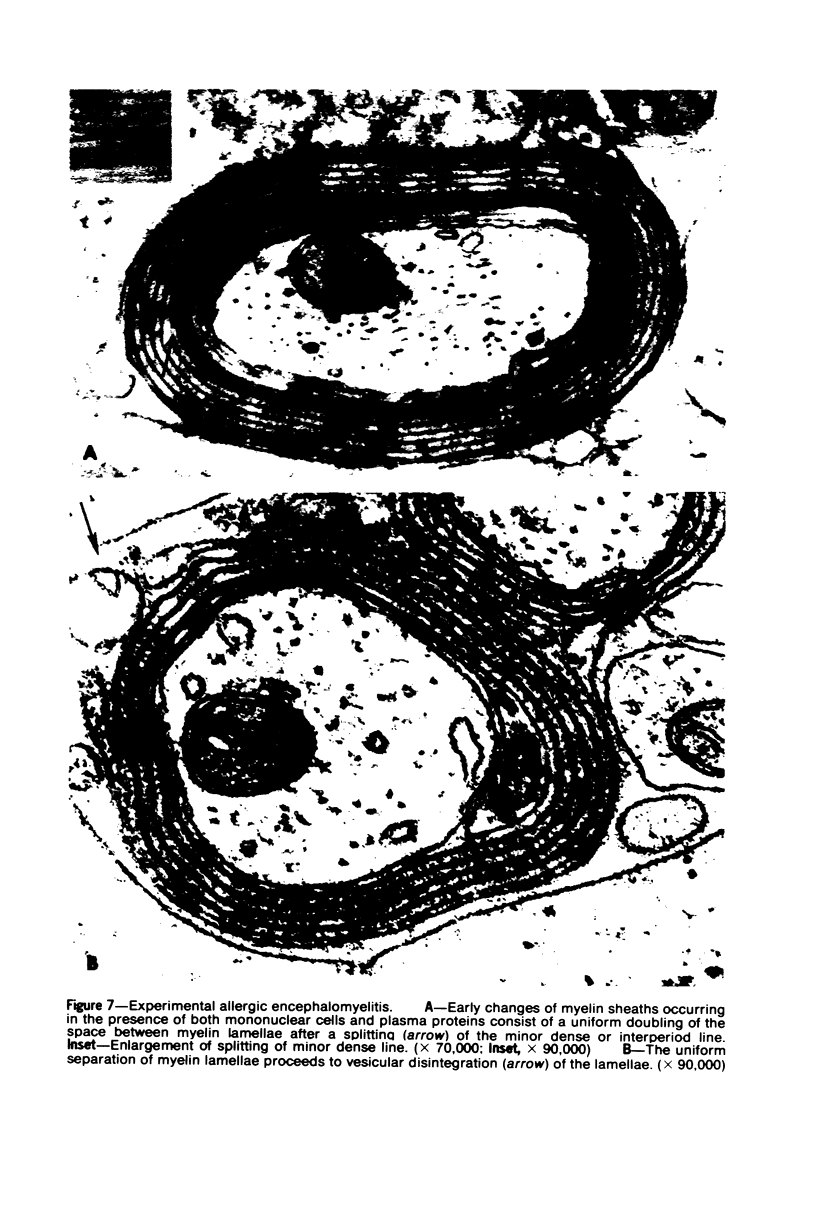
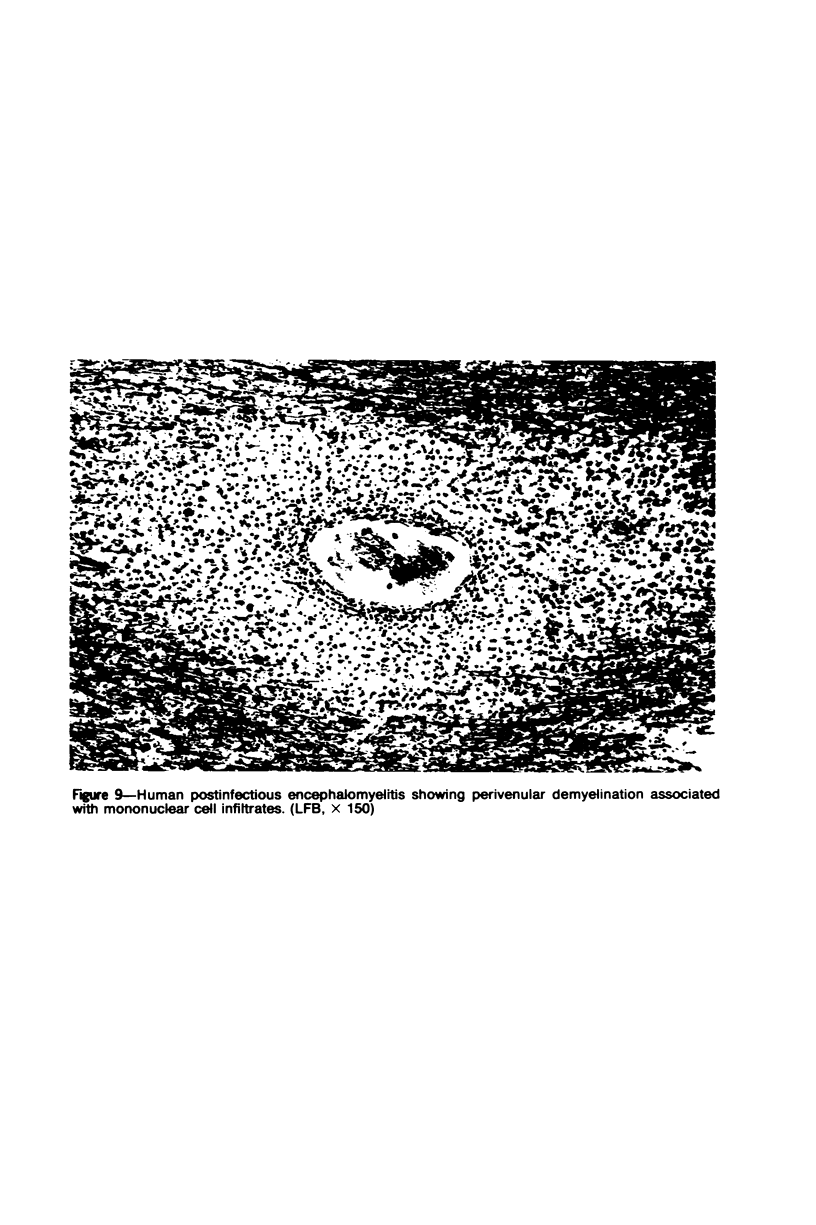
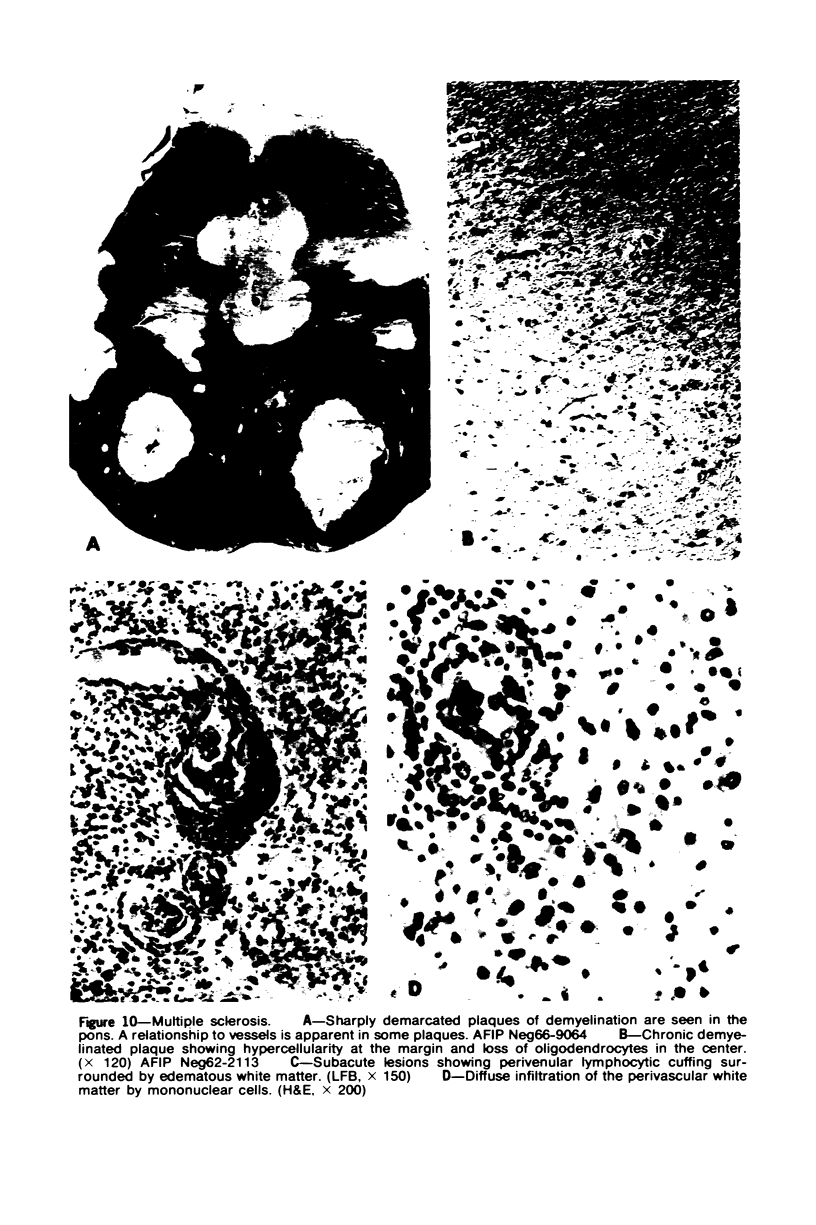
Patterns of demyelination are described in several autoimmune and virus-induced demyelinating diseases of the peripheral and central nervous system. Myelin can be destroyed by injuries that affect either the myelin-supporting cells and/or the myelin lamellae. After destruction of the supporting cells, the related disintegrating sheaths are stripped off axons by invading phagocytes. Virus-induced cytolysis can occur with or without participation of immune responses, as demonstrated in subacute sclerosing panencephalitis and progressive mutlifocal leukoencephalopathy, respectively. Autoimmune demyelination is characterized by disintegration of myelin sheaths in periventular, mononuclear cell infiltrates. Myelin lamellae rather than the myelin-supporting cells are the target of the allergic reaction. The lamellae are lysed in focal areas when in contact with presumably sensitized mononuclear cells. The damaged sheaths are then removed in a nonspecific manner by invading macrophages that strip the myelin remnant off the axons. This sequence of changes is best revealed in experimental and human autoimmune demyelination of peripheral nerves, ie, allergic neuritis and idiopathic polyneutris (the Guillain-Barré syndrome). Autoimmune demyelination triggered by virus infection is described in Marek's disease and postinfectious Theiler's virus myelitis. Changes in canine distemper are discussed with reference to both autoimmune and virus-induced demyelination. The observations are compared with lesions in multiple sclerosis, the most common human demyelinating disease of unknown etiology.
Full text
PDF




























Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANGULO J. J., DE CAMPOS E. P., DE GOMES L. F. POSTVACCINAL MENINGOENCEPHALITIS; ISOLATION OF THE VIRUS FROM THE BRAIN. JAMA. 1964 Jan 11;187:151–153. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- APPEL S. H., BORNSTEIN M. B. THE APPLICATION OF TISSUE CULTURE TO THE STUDY OF EXPERIMENTAL ALLERGIC ENCEPHALOMYELITIS. II. SERUM FACTORS RESPONSIBLE FOR DEMYELINATION. J Exp Med. 1964 Feb 1;119:303–312. doi: 10.1084/jem.119.2.303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ASTROM K. E., MANCALL E. L., RICHARDSON E. P., Jr Progressive multifocal leuko-encephalopathy; a hitherto unrecognized complication of chronic lymphatic leukaemia and Hodgkin's disease. Brain. 1958 Mar;81(1):93–111. doi: 10.1093/brain/81.1.93. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Addinger H. K., Calnek B. W. Pathogenesis of Marek's disease: early distribution of virus and viral antigens in infected chickens. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1973 May;50(5):1287–1298. doi: 10.1093/jnci/50.5.1287. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnason B. G., Chelmicka-Szorc E. Passive transfer of experimental allergic neuritis in Lewis rats by direct injection of sensitized lymphocytes into sciatic nerve. Acta Neuropathol. 1972;22(1):1–6. doi: 10.1007/BF00687545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnason B. G., Winkler G. F., Hadler N. M. Cell-mediated demyelination of peripheral nerve in tissue culture. Lab Invest. 1969 Jul;21(1):1–10. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asbury A. K., Arnason B. G., Adams R. D. The inflammatory lesion in idiopathic polyneuritis. Its role in pathogenesis. Medicine (Baltimore) 1969 May;48(3):173–215. doi: 10.1097/00005792-196905000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BORNSTEIN M. B., APPEL S. H. TISSUE CULTURE STUDIES OF DEMYELINATION. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1965 Mar 31;122:280–286. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1965.tb20212.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behan P. O., Geschwind N., Lamarche J. B., Lisak R. P., Kies M. W. Delayed hypersensitivity to encephalitogenic protein in disseminated encephalomyelitis. Lancet. 1968 Nov 9;2(7576):1009–1012. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(68)91299-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behan P. O., Lamarche J. B., Feldman R. G., Sheramata W. A. Lymphocyte transformation in the Guillain-Barré syndrome. Lancet. 1970 Feb 21;1(7643):421–421. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(70)91560-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bornstein M. B., Raines C. S. The initial structural lesion in serum-induced demyelination in vitro. Lab Invest. 1976 Oct;35(4):391–401. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bunge R. P. Glial cells and the central myelin sheath. Physiol Rev. 1968 Jan;48(1):197–251. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1968.48.1.197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burg R. W., Feldbush T., Morris C. A., Maag T. A. Depression of thymus-and bursa-dependent immune systems chicks with Marek's disease. Avian Dis. 1971 Oct-Dec;15(4):662–671. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byington D. P., Johnson K. P. Experimental subacute sclerosing panencephalitis in the hamster: correlation of age with chronic inclusion-cell encephalitis. J Infect Dis. 1972 Jul;126(1):18–26. doi: 10.1093/infdis/126.1.18. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CAVANAGH J. B., GREENBAUM D., MARSHALL A. H., RUBINSTEIN L. J. Cerebral demyelination associated with disorders of the reticuloendothelial system. Lancet. 1959 Oct 10;2(7102):524–529. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(59)91774-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carp R. I., Merz G. S., Licursi P. C. A small virus-like agent found in association with multiple sclerosis material. Neurology. 1976 Jun;26(6 Pt 2):70–71. doi: 10.1212/wnl.26.6_part_2.70. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DANIELS J. B., PAPPENHEIMER A. M., RICHARDSON S. Observations on encephalomyelitis of mice (DA strain). J Exp Med. 1952 Dec;96(6):517–530. doi: 10.1084/jem.96.6.517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dal Canto M. C., Lipton H. L. Primary demyelination in Theiler's virus infection. An ultrastructural study. Lab Invest. 1975 Dec;33(6):626–637. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eylar E. H., Salk J., Beveridge G. C., Brown L. V. Experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. An encephalitogenic basic protein from bovine myelin. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1969 Jun;132(1):34–48. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(69)90336-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonatas N. K., Gonatas J. O., Stieber A., Lisak R., Suzuki K., Martenson R. E. The significance of circulating and cell-bound antibodies in experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. Am J Pathol. 1974 Sep;76(3):529–548. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonatas N. K., Howard J. C. Inhibition of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis in rats severely depleted of T cells. Science. 1974 Nov 29;186(4166):839–841. doi: 10.1126/science.186.4166.839. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herndon R. M., Price D. L., Weiner L. P. Regeneration of oligodendroglia during recovery from demyelinating disease. Science. 1977 Feb 18;195(4279):693–694. doi: 10.1126/science.190678. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirano A., Dembitzer H. M. A structural analysis of the myelin sheath in the central nervous system. J Cell Biol. 1967 Aug;34(2):555–567. doi: 10.1083/jcb.34.2.555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirano A., Dembitzer H. M., Becker N. H., Levine S., Zimmerman H. M. Fine structural alterations of the blood-brain barrier in experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1970 Jul;29(3):432–440. doi: 10.1097/00005072-197007000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann-Fezer G., Schmahl W., Hoffmann R. Zur Pathogenese der Nervenläsionen bei Marekscher Krankheit des Huhnes. II. Ubertragbarkeit von Nervenveränderungen mit Milzzellen Marek-kranker Tiere. Z Immunitatsforsch Exp Klin Immunol. 1975 Oct;150(4):300–308. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horta-Barbosa L., Fuccillo D. A., London W. T., Jabbour J. T., Zeman W., Sever J. L. Isolation of measles virus from brain cell cultures of two patients with subacute sclerosing panencephalitis. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1969 Oct;132(1):272–277. doi: 10.3181/00379727-132-34196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwasaki Y., Koprowski H. Cell to cell transmission of virus in the central nervous system. I. Subacute sclerosing panencephalitis. Lab Invest. 1974 Aug;31(2):187–196. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson A. B., Wiśniewski H. M., Raine C. S., Eylar E. H., Terry R. D. Specific binding of peroxidase-labeled myelin basic protein in allergic encephalomyelitis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Nov;68(11):2694–2698. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.11.2694. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joseph B. S., Oldstone M. B. Immunologic injury in measles virus infection. II. Suppression of immune injury through antigenic modulation. J Exp Med. 1975 Oct 1;142(4):864–876. doi: 10.1084/jem.142.4.864. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kibler R. F., Shapira R. Isolation and properties of an encephalitogenic protein from bovine, rabbit, and human central nervous system tissue. J Biol Chem. 1968 Jan 25;243(2):281–286. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim S. U., Murray M. R., Tourtellotte W. W., Parker J. A. Demonstration in tissue culture of myelinotoxicity in cerebrospinal fluid and brain extracts from multiple sclerosis patients. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1970 Jul;29(3):420–431. doi: 10.1097/00005072-197007000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krakowka S., McCullough B., Koestner A., Olsen R. Myelin-specific autoantibodies associated with central nervous system demyelination in canine distemper virus infection. Infect Immun. 1973 Nov;8(5):819–827. doi: 10.1128/iai.8.5.819-827.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreth W. H., Käckell M. Y., ter Meulen V. Demonstration of in vitro lymphocyte-mediated cytotoxicity against measles virus in SSPE. J Immunol. 1975 Mar;114(3):1042–1046. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurtzke J. F., Kurland L. T., Goldberg I. D. Mortality and migration in multiple sclerosis. Neurology. 1971 Dec;21(12):1186–1197. doi: 10.1212/wnl.21.12.1186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAMPERT P., CARPENTER S. ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC STUDIES ON THE VASCULAR PERMEABILITY AND THE MECHANISM OF DEMYELINATION IN EXPERIMENTAL ALLERGIC ENCEPHALOMYELITIS. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1965 Jan;24:11–24. doi: 10.1097/00005072-196501000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVINE S., WENK E. J. A HYPERACUTE FORM OF ALLERGIC ENCEPHALOMYELITIS. Am J Pathol. 1965 Jul;47:61–88. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVINE S., WENK E. J. Effect of induced localization on incidence and distribution of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. Neurology. 1960 Dec;10:1090–1095. doi: 10.1212/wnl.10.12.1090. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lampert F., Lampert P. Editorial: Multiple scierosis. morphotogic evidence of intranuctearparamyxovirus of altered chromatin fibers? Arch Neurol. 1975 Jul;32(7):425–427. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1975.00490490029001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lampert P. W., Gajdusek D. C., Gibbs C. J., Jr Subacute spongiform virus encephalopathies. Scrapie, Kuru and Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease: a review. Am J Pathol. 1972 Sep;68(3):626–652. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lampert P. W. Mechanism of demyelination in experimental allergic neuritis. Electron microscopic studies. Lab Invest. 1969 Feb;20(2):127–138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lampert P. W., Sims J. K., Kniazeff A. J. Mechanism of demyelination in JHM virus encephalomyelitis. Electron microscopic studies. Acta Neuropathol. 1973 Mar 30;24(1):76–85. doi: 10.1007/BF00691421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lampert P. Electron microscopic studies on ordinary and hyperacute experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. Acta Neuropathol. 1967 Oct 20;9(2):99–126. doi: 10.1007/BF00691436. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lampert P., Garrett R., Powell H. Demyelination in allergic and Marek's disease virus induced neuritis. Comparative electron microscopic studies. Acta Neuropathol. 1977 Oct 10;40(2):103–110. doi: 10.1007/BF00688697. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrich J. R., Arnason B. G. Suppression of experimental allergic neuritis in rats by prior immunization with nerve in saline. Acta Neuropathol. 1971;18(2):144–149. doi: 10.1007/BF00687602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy N. L., Auerbach P. S., Hayes E. C. A blood test for multiple sclerosis based on the adherence of lymphocytes to measles-infected cells. N Engl J Med. 1976 Jun 24;294(26):1423–1427. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197606242942604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lincoln S. D., Gorham J. R., Ott R. L., Hegreberg G. A. Etiologic studies of old dog encephalitis. I. Demonstration of canine distemper viral antigen in the brain in two cases. Vet Pathol. 1971;8(1):1–8. doi: 10.1177/030098587100800101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipton H. L., Dal Canto M. C. Theiler's virus-induced demyelination: prevention by immunosuppression. Science. 1976 Apr 2;192(4234):62–64. doi: 10.1126/science.176726. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipton H. L. Theiler's virus infection in mice: an unusual biphasic disease process leading to demyelination. Infect Immun. 1975 May;11(5):1147–1155. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.5.1147-1155.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lisak R. P., Mitchell M., Zweiman B., Orrechio E., Asbury A. K. Guillain-Barré syndrome and Hodgkin's disease: three cases with immunological studies. Ann Neurol. 1977 Jan;1(1):72–78. doi: 10.1002/ana.410010107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oldstone M. B., Dixon F. J. Immunohistochemical study of allergic encephalomyelitis. Am J Pathol. 1968 Feb;52(2):251–263. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oldstone M. B., Dixon F. J., Mitchell G. F., McDevitt H. O. Histocompatibility-linked genetic control of disease susceptibility. Murine lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus infection. J Exp Med. 1973 May 1;137(5):1201–1212. doi: 10.1084/jem.137.5.1201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oldstone M. B., Holmstoen J., Welsh R. M., Jr Alterations of acetylcholine enzymes in neuroblastoma cells persistently infected with lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus. J Cell Physiol. 1977 Jun;91(3):459–472. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040910316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oldstone M. B. Virus neutralization and virus-induced immune complex disease. Virus-antibody union resulting in immunoprotection or immunologic injury--two sides of the same coin. Prog Med Virol. 1975;19:84–119. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ortiz-Ortiz L., Weigle W. O. Cellular events in the induction of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis in rats. J Exp Med. 1976 Sep 1;144(3):604–616. doi: 10.1084/jem.144.3.604. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padgett B. L., Walker D. L. Prevalence of antibodies in human sera against JC virus, an isolate from a case of progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. J Infect Dis. 1973 Apr;127(4):467–470. doi: 10.1093/infdis/127.4.467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne F. E., Baublis J. V., Itabashi H. H. Isolation of measles virus from cell cultures of brain from a patient with subacute sclerosing panencephalitis. N Engl J Med. 1969 Sep 11;281(11):585–589. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196909112811103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne L. N., Frazier J. A., Powell P. C. Pathogenesis of Marek's disease. Int Rev Exp Pathol. 1976;16:59–154. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell H. C., Lampert P. W. Oligodendrocytes and their myelin-plasma membrane connections in JHM mouse hepatitis virus encephalomyelitis. Lab Invest. 1975 Oct;33(4):440–445. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prineas J. W. Acute idiopathic polyneuritis. An electron microscope study. Lab Invest. 1972 Feb;26(2):133–147. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prineas J. W. Demyelination and remyelination in recurrent idiopathic polyneuropathy. An electron microscope study. Acta Neuropathol. 1971;18(1):34–57. doi: 10.1007/BF00684474. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prineas J. W., Wright R. G. The fine structure of peripheral nerve lesions in a virus-induced demyelinating disease in fowl (Marek's disease). Lab Invest. 1972 May;26(5):548–557. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prineas J. Pathology of the early lesion in multiple sclerosis. Hum Pathol. 1975 Sep;6(5):531–554. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(75)80040-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prineas J., Raine C. S., Wísniewski H. An ultrastructural study of experimental demyelination and remyelination. 3. Chronic experimental allergic encephalomyelitis in the central nervous system. Lab Invest. 1969 Dec;21(6):472–483. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Périer O., Grégoire A. Electron microscopic features of multiple sclerosis lesions. Brain. 1965 Dec;88(5):937–952. doi: 10.1093/brain/88.5.937. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raine C. S., Snyder D. H., Valsamis M. P., Stone S. H. Chronic experimental allergic encephalomyelitis in inbred guinea pigs. An ultrastructural study. Lab Invest. 1974 Oct;31(4):369–380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rocklin R. E., Sheremata W. A., Feldman R. G., Kies M. W., David J. R. The Guillain-Barré syndrome and multiple sclerosis. In vitro cellular responses to nervous-tissue antigens. N Engl J Med. 1971 Apr 15;284(15):803–808. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197104152841501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouse B. T., Wells R. J., Warner N. L. Proportion of T and B lymphocytes in lesions of Marek's disease: theoretical implications for pathogenesis. J Immunol. 1973 Feb;110(2):534–539. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STONE S. H., LERNER E. M., 2nd CHRONIC DISSEMINATED ALLERGIC ENCEPHALOMYELITIS IN GUINEA PIGS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1965 Mar 31;122:227–241. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1965.tb20206.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmahl W., Hoffmann-Fezer G., Hoffmann R. Zur Pathogenese der Nervenläsionen bei Marekscher Krankheit des Huhnes I. Allergische Hautreaktion gegen Myelin peripherer Nerven. Z Immunitatsforsch Exp Klin Immunol. 1975 Sep;150(2):175–183. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seil F. J., Falk G. A., Kies M. W., Alvord E. C., Jr The in vitro demyelinating activity of sera from guinea pigs sensitized with whole CNS and with purified encephalitogen. Exp Neurol. 1968 Dec;22(4):545–555. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(68)90148-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seil F. J. Tissue culture studies of demyelinating disease: a critical review. Ann Neurol. 1977 Oct;2(4):345–355. doi: 10.1002/ana.410020417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheremata W., Cosgrove J. B., Eylar E. H. Multiple sclerosis and cell-mediated hypersensitivity to myelin A1 protein. J Neurol Sci. 1976 Apr;27(4):413–425. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(76)90212-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder D. H., Valsamis M. P., Stone S. H., Raine C. S. Progressive demyelination and reparative phenomena in chronic experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1975 May;34(3):209–221. doi: 10.1097/00005072-197505000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki K., Andrews J. M., Waltz J. M., Terry R. D. Ultrastructural studies of multiple sclerosis. Lab Invest. 1969 May;20(5):444–454. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swierkosz J. E., Swanborg R. H. Suppressor cell control of unresponsiveness to experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. J Immunol. 1975 Sep;115(3):631–633. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka R., Iwasaki Y., Koprowski H. Intracisternal virus-like particles in brain of a multiple sclerosis patient. J Neurol Sci. 1976 May;28(1):121–126. doi: 10.1016/0022-510X(76)90053-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tellez-Negal I., Harter D. H. Subacute sclerosing leukoencephalitis: ultrastructure of intranuclear and intracytoplasmic inclusions. Science. 1966 Nov 18;154(3751):899–901. doi: 10.1126/science.154.3751.899. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tourtellotte W. W. Cerebrospinal fluid immunoglobulins and the central nervous system as an immunological organ particularly in multiple sclerosis and subacute sclerosing panencephalitis. Res Publ Assoc Res Nerv Ment Dis. 1971;49:112–155. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WAKSMAN B. H., ADAMS R. D. Allergic neuritis: an experimental disease of rabbits induced by the injection of peripheral nervous tissue and adjuvants. J Exp Med. 1955 Aug 1;102(2):213–236. doi: 10.1084/jem.102.2.213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner L. P. Pathogenesis of demyelination induced by a mouse hepatitis. Arch Neurol. 1973 May;28(5):298–303. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1973.00490230034003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westall F. C., Thompson M., Lennon V. A. Hyperacute autoimmune encephalomyelitis induced by a synthetic autoantigen. Nature. 1977 Sep 29;269(5627):425–427. doi: 10.1038/269425a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams R. M., Moore M. J. Linkage of susceptibility to experimental allergic encephalomyelitis to the major histocompatibility locus in the rat. J Exp Med. 1973 Oct 1;138(4):775–783. doi: 10.1084/jem.138.4.775. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiśniewski H., Prineas J., Raine C. S. An ultrastructural study of experimental demyelination and remyelination. I. Acute experimental allergic encephalomyelitis in the peripheral nervous system. Lab Invest. 1969 Aug;21(2):105–118. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiśniewski H., Raine C. S., Kay W. J. Observations on viral demyelinating encephalomyelitis. Canine distemper. Lab Invest. 1972 May;26(5):589–599. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiśniewski H., Terry R. D., Whitaker J. N., Cook S. D., Dowling P. C. Landry-Guillain-Barré syndrome. A primary demyelinating disease. Arch Neurol. 1969 Sep;21(3):269–276. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1969.00480150059008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zu Rhein G. M. Association of papova-virions with a human demyelinating disease (progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy). Prog Med Virol. 1969;11:185–247. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ter Meulen V., Katz M., Müller D. Subacute sclerosing panencephalitis: a review. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1972;57:1–38. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-65297-4_1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ter Meulen V., Müller D., Käckell Y., Katz M., Meyermann R. Isolation of infectious measles virus in measles encephalitis. Lancet. 1972 Dec 2;2(7788):1172–1175. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)92595-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]