Abstract
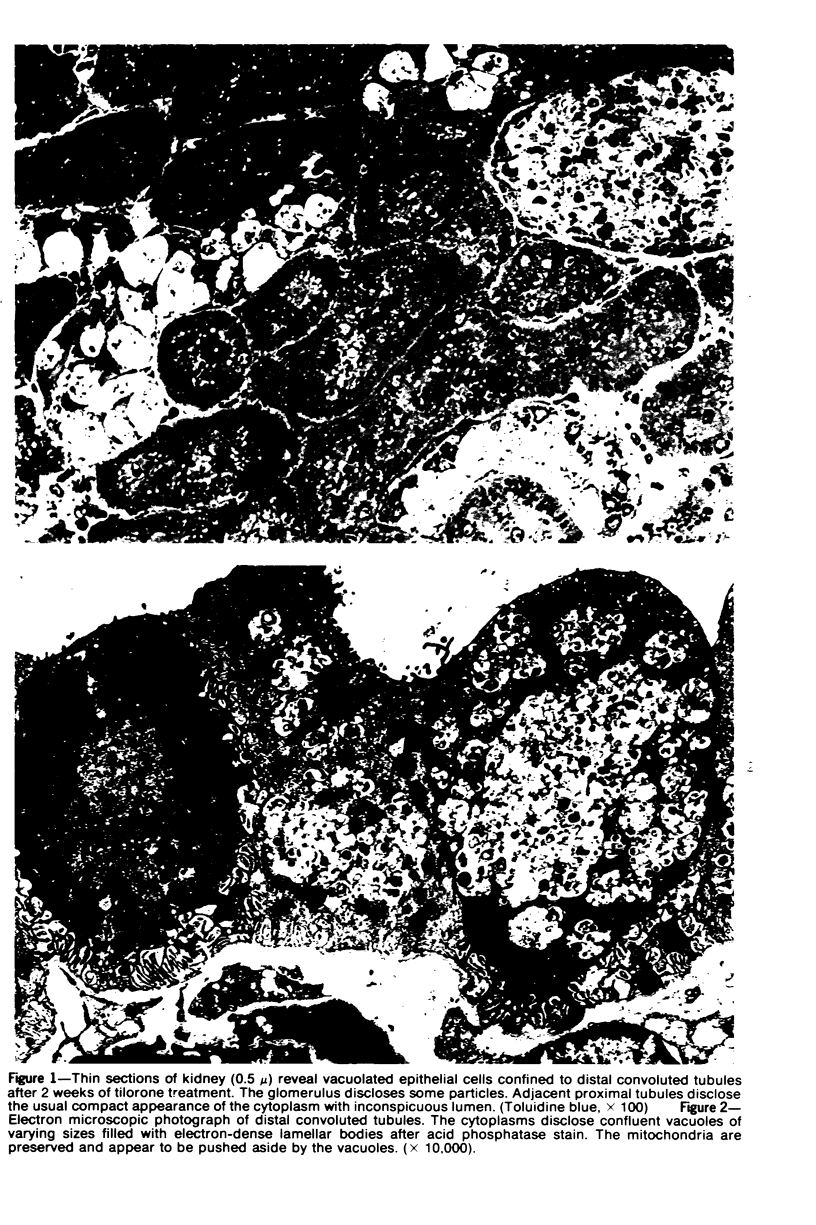
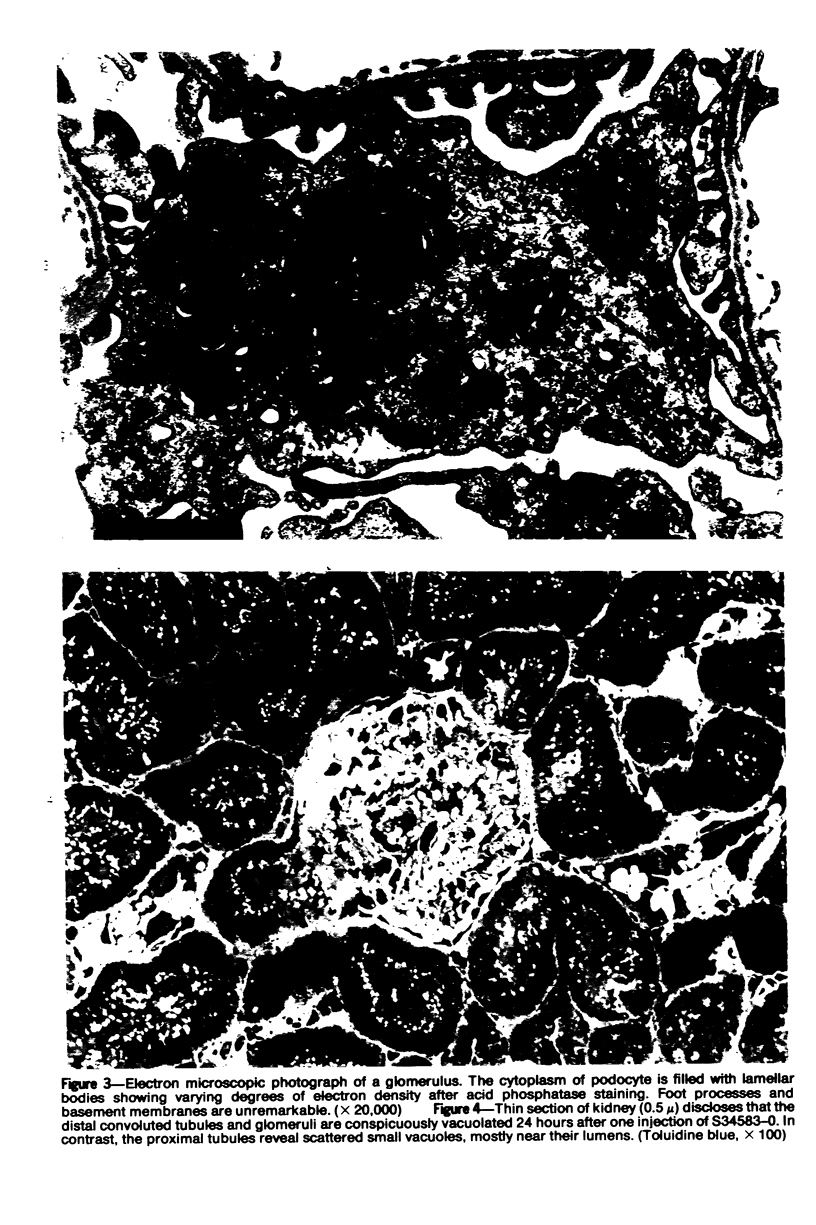
Tilorone, 2,7-bis-(diethylaminoethoxy)-fluoren-9-one hydrochloride, an interferon inducer, has been shown to cause hydropic degeneration in choroid plexus and distal convoluted tubules of kidney. Ultrastructural and histochemical studies of the renal lesion produced by tilorone and one of its analogs revealed striking accumulation of vacuoles and/or acid-phosphatase-positive lemellar bodies retricted to glomeruli, ascending limb of Henle's loop, and distal convoluted tubules.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ERICSSON J. L., TRUMP B. F. ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC STUDIES OF THE EPITHELIUM OF THE PROXIMAL TUBULE OF THE RAT KIDNEY. I. THE INTRACELLULAR LOCALIZATION OF ACID PHOSPHATASE. Lab Invest. 1964 Nov;13:1427–1456. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leeson G. A., Biedenbach S. A., Chan K. Y., Gibson J. P., Wright G. J. Decrease in the activity of the drug-metabolizing enzymes of rat liver following the administration of tilorone hydrochloride. Drug Metab Dispos. 1976 May-Jun;4(3):232–238. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine S., Gibson J. P., Megel H. Selective depletion of thymus dependent areas in lymphoid tissue by tilorone. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1974 May;146(1):245–248. doi: 10.3181/00379727-146-38079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine S., Sowinski R., Albrecht W. L. T-Lymphocyte depletion induced in rats by analogs of tilorone hydrochloride. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1977 Apr;40(1):137–145. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(77)90125-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine S., Sowinski R. T-Lymphocyte depletion and lesions of choroid plexus and kidney induced by tertiary amines in rats. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1977 Apr;40(1):147–159. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(77)90126-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lüllmann H., Lüllmann-Rauch R., Wassermann O. Drug-induced phospholipidosis. Ger Med. 1973 Winter;3(3-4):128–135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Megel H., Raychaudhuri A., Shemano I., Beaver T. H., Thomas L. L. The anti-inflammatory actions of tilorone hydrochloride. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1975 May;149(1):89–93. doi: 10.3181/00379727-149-38749. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SPARGO B. Kidney changes in hypokalemic alkalosis in the rat. J Lab Clin Med. 1954 May;43(5):802–814. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STOECKENIUS W. Some electron microscopical observations on liquid-crystalline phases in lipid-water systems. J Cell Biol. 1962 Feb;12:221–229. doi: 10.1083/jcb.12.2.221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toback F. G., Ordónez N. G., Bortz S. L., Spargo B. H. Zonal changes in renal structure and phospholipid metabolism in potassium-deficient rats. Lab Invest. 1976 Feb;34(2):115–124. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]