Abstract
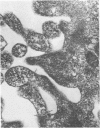
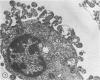
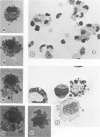
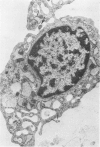
Using a newly described dissociation and isolation technique, Type 1 alveolar lining cells were obtained from adult rabbit lung within a heterogeneous population. Identification of many lung cell types in this mixed population was by a) comparison of isolated cells with in situ lung cells in lung sections using identical parallel staining, b) stepwise ultrastructural examination of cells during all stages of lung dissociation so that intercellular associations were monitored throughout, and c) Type 1 cell surface changes following collagenase treatment. This phenomenon was studied with both electron and light microscopy, the latter employing tetrachrome staining of basophilic blebs as well as characteristic staining of nucleus and cytoplasm. Following their isolation, most Type 1 cells lost their surface blebs and assumed a “relaxed” state. In this condition, Type 1 cells were exposed to cytochalasin D (CD) for various times and at several concentrations. Surface knobs, having all the characteristics of zeiotic knobs produced in a number of cultured cell lines by exposure to CD, were produced in isolated Type 1 epithelial cells within 45 minutes. The reaction to CD was temperature-dependent, proceeding maximally at 37 C with inhibition at lower temperatures and was inhibited by antimetabolites such as dinitrophenol and 2-deoxyglucose in the presence of CD. As with established cell lines, formation of zeiotic knobs at the isolated Type 1 cell surface appeared closely related to microfilamentous nets located beneath the plasmalemma. The density of this net appeared to vary as isolated Type 1 cells underwent expansion and contraction in response to CD. Zeiotic knobs were formed as the result of herniation of endoplasm through the cell cortex. The significance of such a labile cortical zone is considered in relation to the deformation changes Type 1 cells undergo during inflation-deflation of alveoli and the folding-unfolding of alveolar lining cells as a result of lung volume changes.
Full text
PDF


















Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AGOSTONI E., TAGLIETTI A., AGOSTONI A. F., SETNIKAR I. Mechanical aspects of the first breath. J Appl Physiol. 1958 Nov;13(3):344–348. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1958.13.3.344. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachofen M., Weibel E. R. Basic pattern of tissue repair in human lungs following unspecific injury. Chest. 1974 Apr;65(Suppl):14S–19S. doi: 10.1378/chest.65.4_supplement.14s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COSTERO I., POMERAT C. M. Cultivation of neurons from the adult human cerebral and cerebellar cortes. Am J Anat. 1951 Nov;89(3):405–467. doi: 10.1002/aja.1000890304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dominguez E. A., Liebow A. A., Bensch K. G. Studies on the pulmonary air-tissue barrier. I. Absorption of albumin by the alveolar wall. Lab Invest. 1967 Jun;16(6):905–911. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forrest J. B. The effect of changes in lung volume on the size and shape of alveoli. J Physiol. 1970 Oct;210(3):533–547. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gil J., Weibel E. R. Morphological study of pressure-volume hysteresis in rat lungs fixed by vascular perfusion. Respir Physiol. 1972 Jun;15(2):190–213. doi: 10.1016/0034-5687(72)90098-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glazier J. B., Hughes J. M., Maloney J. E., West J. B. Vertical gradient of alveolar size in lungs of dogs frozen intact. J Appl Physiol. 1967 Nov;23(5):694–705. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1967.23.5.694. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godman G. C., Miranda A. F., Deitch A. D., Tanenbaum S. W. Action of cytochalasin D on cells of established lines. III. Zeiosis and movements at the cell surface. J Cell Biol. 1975 Mar;64(3):644–667. doi: 10.1083/jcb.64.3.644. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraicer J., Herlant M., Duclos P. Changes in adenohypophyseal cytology and nucleic acid content in the rat 32 days after bilateral adrenalectomy and the chronic injection of cortisol. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1967 Nov;45(6):947–956. doi: 10.1139/y67-112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuno K., Staub N. C. Acute mechanical effects of lung volume changes on artificial microholes in alveolar walls. J Appl Physiol. 1968 Jan;24(1):83–92. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1968.24.1.83. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miranda A. F., Godman G. C., Deitch A. D., Tanenbaum S. W. Action of cytochalasin D on cells of established lines. I. Early events. J Cell Biol. 1974 May;61(2):481–500. doi: 10.1083/jcb.61.2.481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miranda A. F., Godman G. C., Tanenbaum S. W. Action of cytochalasin D on cells of established lines. II. Cortex and microfilaments. J Cell Biol. 1974 Aug;62(2):406–423. doi: 10.1083/jcb.62.2.406. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picciano P., Rosenbaum R. M. The type 1 alveolar lining cells of the mammalian lung. I. Isolation and enrichment from dissociated adult rabbit lung. Am J Pathol. 1978 Jan;90(1):99–122. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter K., Prescott D., Frye J. Changes in surface morphology of Chinese hamster ovary cells during the cell cycle. J Cell Biol. 1973 Jun;57(3):815–836. doi: 10.1083/jcb.57.3.815. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puck T. T., Waldren C. A., Hsie A. W. Membrane dynamics in the action of dibutyryl adenosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate and testosterone on mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jul;69(7):1943–1947. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.7.1943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose G. G. Zeiosis. I. Ejection of cell nuclei into zeiotic blebs. J R Microsc Soc. 1966 Dec;86(2):87–102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spooner B. S., Yamada K. M., Wessells N. K. Microfilaments and cell locomotion. J Cell Biol. 1971 Jun;49(3):595–613. doi: 10.1083/jcb.49.3.595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sträuli P., Lindenmann R., Haemmerli G. Mikrokinematographische und elektronenmikroskopische Beobachtungen an Zelloberflächen und Zellkontakten der menschlichen Carcinom-Zellkulturlinie HEp 2. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol. 1971;8(2):143–161. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trinkaus J. P. Modes of cell locomotion in vivo. Ciba Found Symp. 1973;14:233–249. doi: 10.1002/9780470719978.ch11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weibel E. R. The mystery of "non-nucleated plates" in the alveolar epithelium of the lung explained. Acta Anat (Basel) 1971;78(3):425–443. doi: 10.1159/000143605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto E., Wittner M., Rosenbaum R. M. Resistance and susceptibility to oxygen toxicity by cell types of the gas-blood barrier of the rat lung. Am J Pathol. 1970 Jun;59(3):409–436. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]