Abstract
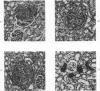
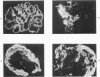
The sympathetic nervous system and catecholamines play a major role in fibrin deposition in organs in rabbits after endotoxin administration. Glomerular fibrin deposition is also a key factor in the pathogenesis of nephrotoxic nephritis in rabbits, but the role of the sympathetic nervous system in this type of fibrin deposition has not been defined. We investigated sympathetic nervous system involvement in nephrotoxic nephritis using a model of isolated chemical sympathectomy with 6-hydroxydopamine. Different quantities of pooled nephrotoxic serum were injected intravenously into control and sympathectomized rabbits to produce a known spectrum of pathology in normal rabbits. Animals were killed and their organs were analyzed to ascertain that sympathectomy had been accomplished. Biochemical, immunohistologic, and histopathologic evaluation of the animals, comparing controls and sympathectomized rabbits, revealed no differences in the degree of renal damage for a given quantity of nephrotoxic serum. We conclude that, in the rabbit model, the sympathetic nervous system plays no significant role in the pathogenesis of fibrin deposition and glomerular damage in nephrotoxic nephritis.
Full text
PDF



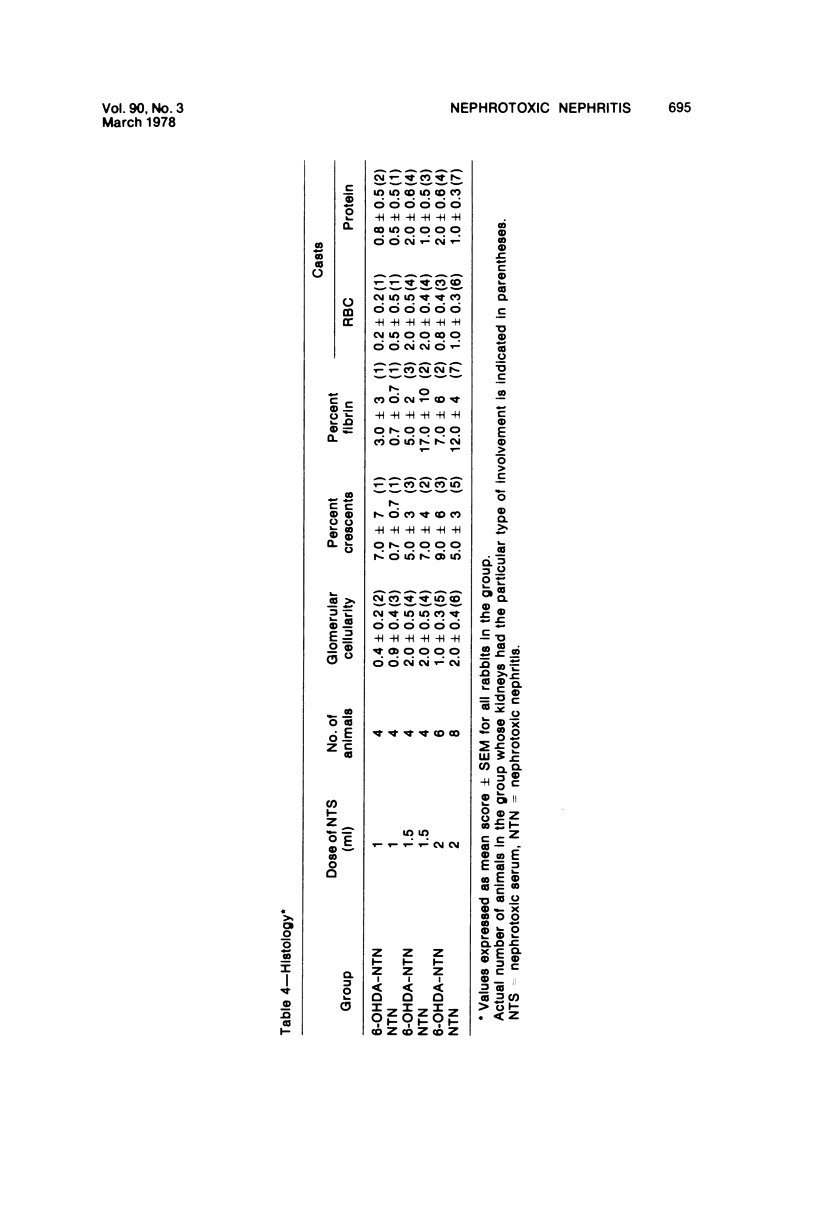



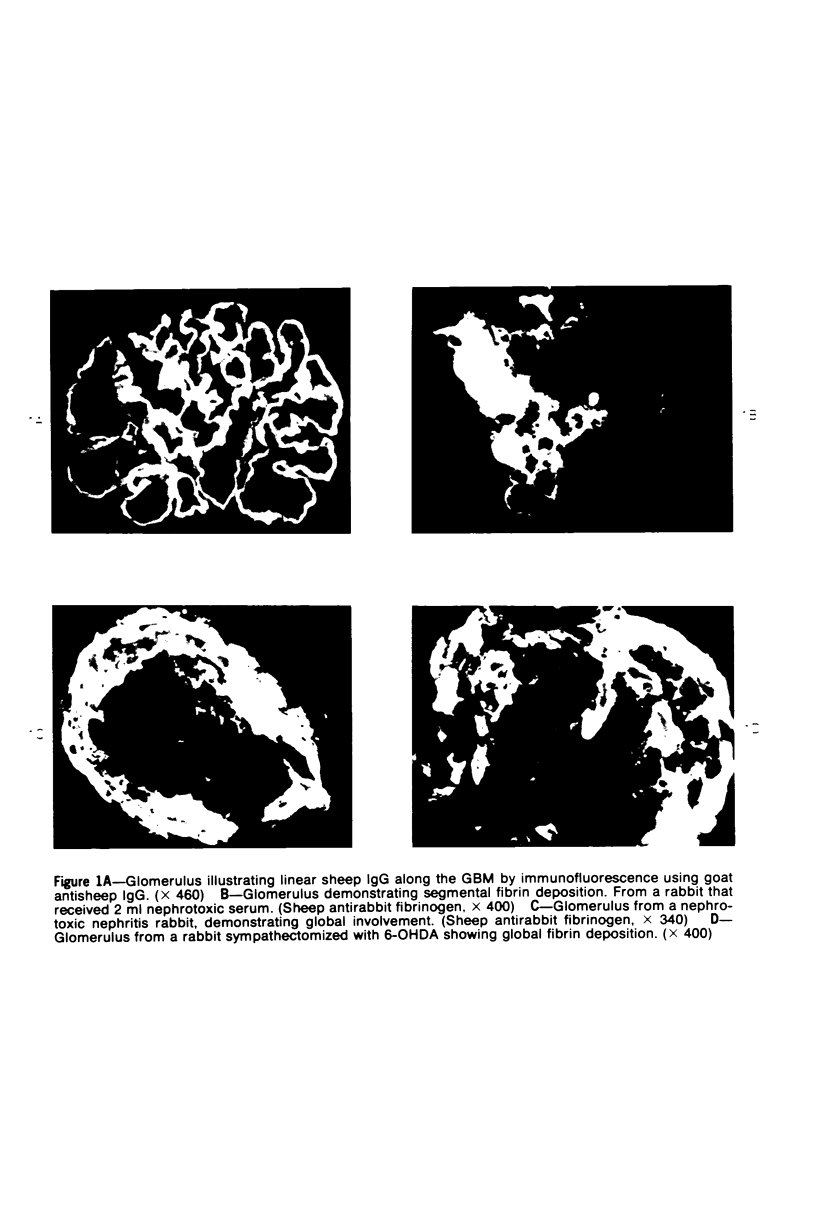
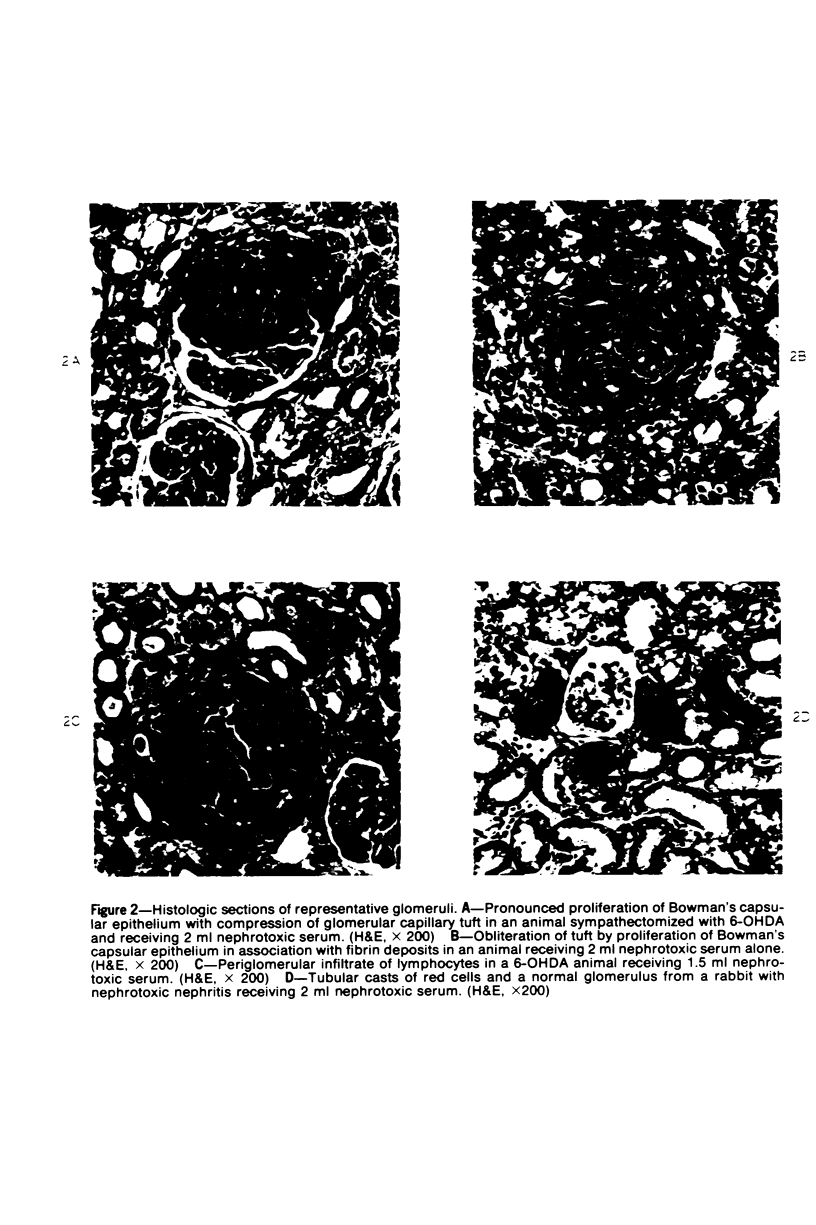
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beller F. K. The role of endotoxin in disseminated intravascular coagulation. Thromb Diath Haemorrh Suppl. 1969;36:125–149. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blantz R. C., Wilson C. B. Acute effects of antiglomerular basement membrane antibody on the process of glomerular filtration in the rat. J Clin Invest. 1976 Oct;58(4):899–911. doi: 10.1172/JCI108543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolton W. K., Benton F. R., Maclay J. G., Sturgill B. C. Spontaneous glomerular sclerosis in aging Sprague-Dawley rats. I. Lesions associated with mesangial IgM deposits. Am J Pathol. 1976 Nov;85(2):277–302. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bone J. M., Valdes A. J., Germuth F. G., Jr, Lubowitz H. Heparin therapy in anti-basement membrane nephritis. Kidney Int. 1975 Aug;8(2):72–79. doi: 10.1038/ki.1975.82. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Border W. A., Wilson C. B., Dixon F. J. Failure of heparin to affect two types of experimental glomerulonephritis in rabbits. Kidney Int. 1975 Sep;8(3):140–148. doi: 10.1038/ki.1975.93. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briggs J. D., Kwaan H. C., Potter E. V. The role of fibrinogen in renal disease. 3. Fibrinolytic and anticoagulant treatment of nephrotoxic serum nephritis in mice. J Lab Clin Med. 1969 Nov;74(5):715–724. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochrane C. G. Mediation of immunologic glomerular injury. Transplant Proc. 1969 Dec;1(4):949–958. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Couser W. G., Stilmant M. M., Jermanovich N. B. Complement-independent nephrotoxic nephritis in the guinea pig. Kidney Int. 1977 Mar;11(3):170–180. doi: 10.1038/ki.1977.25. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HALPERN B., MILLIEZ P., LAGRUE G., FRAY A., MORARD J. C. PROTECTIVE ACTION OF HEPARIN IN EXPERIMENTAL IMMUNE NEPHRITIS. Nature. 1965 Jan 16;205:257–259. doi: 10.1038/205257a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KLEINERMAN J. Effects of heparin on experimental nephritis in rabbits. Lab Invest. 1954 Nov-Dec;3(6):495–508. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KRAKOWER C. A., GREENSPON S. A. Localization of the nephrotoxic antigen within the isolated renal glomerulus. AMA Arch Pathol. 1951 Jun;51(6):629–639. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi Y., Shigematsu H., Tada T. Nephritogenic properties of nephrotoxic guinea pig antibodies. II. Glomerular lesions induced by F(ab')2 fragments of nephrotoxic IgG1 antibody in rats. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol. 1973 Dec 31;15(1):35–44. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKAY D. G., SHAPIRO S. S. Alterations in the blood coagulation system induced by bacterial endotoxin. I. In vivo (generalized Shwartzman reaction). J Exp Med. 1958 Mar 1;107(3):353–367. doi: 10.1084/jem.107.3.353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naish P. F., Thomson N. M., Simpson I. J., Peters D. K. The role of polymorphonuclear leucocytes in the autologous phase of nephrotoxic nephritis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1975 Oct;22(1):102–111. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naish P., Penn G. B., Evans D. J., Peters D. K. The effect of defibrination on nephrotoxic serum nephritis in rabbits. Clin Sci. 1972 May;42(5):643–646. doi: 10.1042/cs0420643. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson I. J., Amos N., Evans D. J., Thomson N. M., Peters D. K. Guinea-pig nephrotoxic nephritis. I. The role of complement and polymorphonuclear leucocytes and the effect of antibody subclass and fragments in the heterologous phase. Clin Exp Immunol. 1975 Mar;19(3):499–511. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THOMAS L., GOOD R. A. Studies on the generalized Shwartzman reaction: I. General observations concerning the phenomenon. J Exp Med. 1952 Dec;96(6):605–624. doi: 10.1084/jem.96.6.605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomson N. M., Naish P. F., Simpson I. J., Peters D. K. The role of C3 in the autologous phase of nephrotoxic nephritis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1976 Jun;24(3):464–473. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- UNANUE E. R., DIXON F. J. EXPERIMENTAL GLOMERULONEPHRITIS. V. STUDIES ON THE INTERACTION OF NEPHROTOXIC ANTIBODIES WITH TISSUE OF THE RAT. J Exp Med. 1965 May 1;121:697–714. doi: 10.1084/jem.121.5.697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- UNANUE E. R., DIXON F. J. EXPERIMENTAL GLOMERULONEPHRITIS. VI. THE AUTOLOGOUS PHASE OF NEPHROTOXIC SERUM NEPHRITIS. J Exp Med. 1965 May 1;121:715–725. doi: 10.1084/jem.121.5.715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- UNANUE E., DIXON F. J. EXPERIMENTAL GLOMERULONEPHRITIS. IV. PARTICIPATION OF COMPLEMENT IN NEPHROTOXIC NEPHRITIS. J Exp Med. 1964 Jan 1;119:965–982. doi: 10.1084/jem.119.6.965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unanue E. R., Dixon F. J. Experimental glomerulonephritis: immunological events and pathogenetic mechanisms. Adv Immunol. 1967;6:1–90. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60521-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unanue E. R., Mardiney M. R., Jr, Dixon F. J. Nephrotoxic serum nephritis in complement intact and deficient mice. J Immunol. 1967 Mar;98(3):609–617. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VASSALLI P., MCCLUSKEY R. T. THE PATHOGENIC ROLE OF THE COAGULATION PROCESS IN RABBIT MASUGI NEPHRITIS. Am J Pathol. 1964 Oct;45:653–677. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]