Abstract
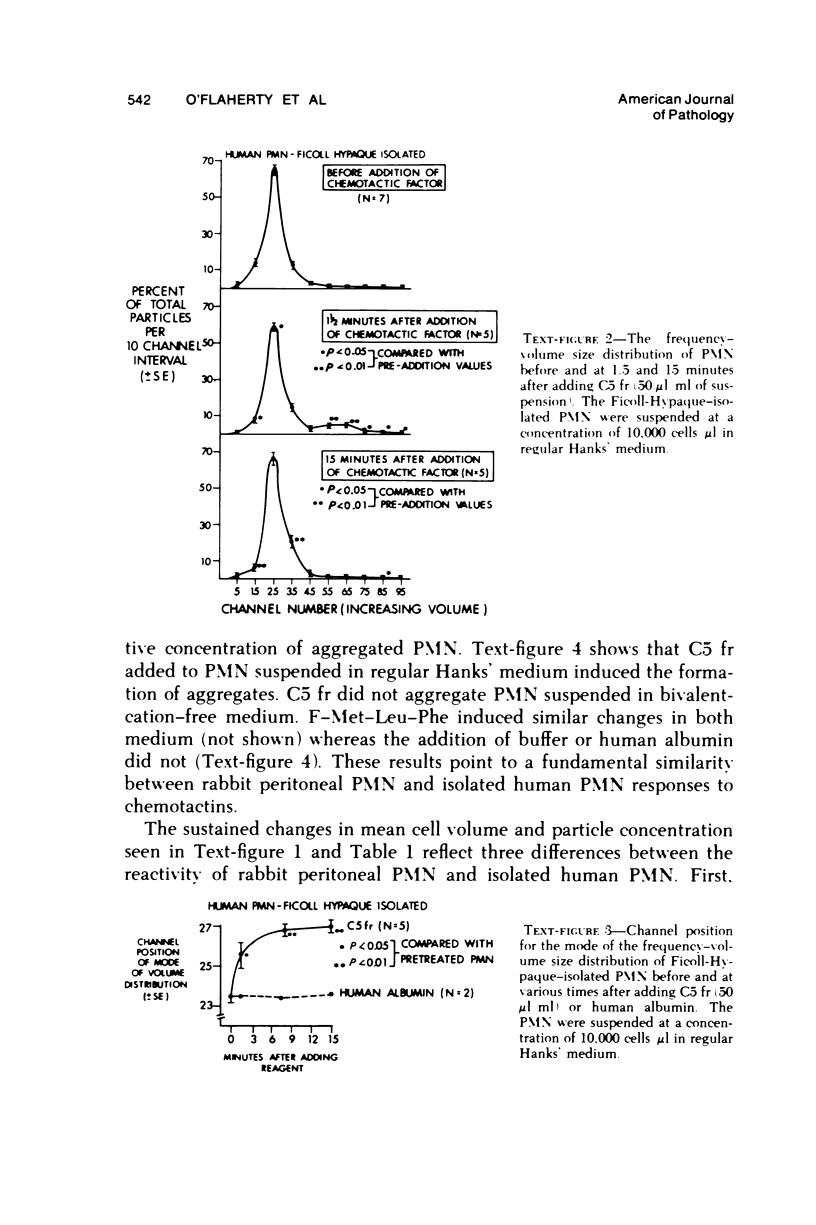
Chemotactic factors have been shown to induce aggregation and cellular swelling of rabbit polymorphonuclear neutrophils (PMN) obtained from the peritoneum. We examined the ability of the chemotactic fragment of C5 and the synthetic chemotactic tripeptide formyl-methionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine to induce these changes in various preparations of human leukocytes. We found that these factors did induce dextran-sedimented leukocytes and Ficoll-Hypaque-isolated PMN to aggregate and swell. Compared with rabbit peritoneal PMN, however, human PMN responded with more prominent swelling but with less prominent aggregation. Also unlike rabbit peritoneal PMN, human PMN adhered spontaneously to plastic surfaces; the chemotactic factors enhanced this adherence. Certain similarities between the responses of these two cell types were evident: in both rabbit peritoneal and isolated human peripheral PMN, the aggregates had a short life span in the fluid phase; in both, the number of aggregates formed was proportional to the log10 of the PMN concentration; and, in both, the chemotactic activity of the reagents paralleled their aggregating activity. In the system employed, lymphocytes were unresponsive to the chemotactic factors. Ficoll-Hypaque-isolated mononoclear cells (containing varying proportions of monocytes and lymphocytes) were responsive, indicating that human monocytes behave in a manner similar to the human PMN. The results suggest that chemotactic factors induce responsive cells to develop a hyperadherent cytoplasmic membrane. Aggregation and increased adhesiveness to plastic surfaces may reflect this induction.
Full text
PDF












Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Craddock P. R., Fehr J., Brigham K. L., Kronenberg R. S., Jacob H. S. Complement and leukocyte-mediated pulmonary dysfunction in hemodialysis. N Engl J Med. 1977 Apr 7;296(14):769–774. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197704072961401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craddock P. R., Fehr J., Dalmasso A. P., Brighan K. L., Jacob H. S. Hemodialysis leukopenia. Pulmonary vascular leukostasis resulting from complement activation by dialyzer cellophane membranes. J Clin Invest. 1977 May;59(5):879–888. doi: 10.1172/JCI108710. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craddock P. R., Hammerschmidt D., White J. G., Dalmosso A. P., Jacob H. S. Complement (C5-a)-induced granulocyte aggregation in vitro. A possible mechanism of complement-mediated leukostasis and leukopenia. J Clin Invest. 1977 Jul;60(1):260–264. doi: 10.1172/JCI108763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- English D., Andersen B. R. Single-step separation of red blood cells. Granulocytes and mononuclear leukocytes on discontinuous density gradients of Ficoll-Hypaque. J Immunol Methods. 1974 Aug;5(3):249–252. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(74)90109-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallin J. I., Rosenthal A. S. The regulatory role of divalent cations in human granulocyte chemotaxis. Evidence for an association between calcium exchanges and microtubule assembly. J Cell Biol. 1974 Sep;62(3):594–609. doi: 10.1083/jcb.62.3.594. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCall C. E., De Chatelet L. R., Brown D., Lachmann P. New biological activity following intravascular activation of the complement cascade. Nature. 1974 Jun 28;249(460):841–843. doi: 10.1038/249841a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Flaherty J. T., Craddock P. R., Jacob H. S. Mechanism of anti-complementary activity of corticosteroids in vivo: possible relevance in endotoxin shock. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1977 Feb;154(2):206–209. doi: 10.3181/00379727-154-39638. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Flaherty J. T., Kreutzer D. L., Showell H. J., Ward P. A. Influence of inhibitors of cellular function on chemotactic factor-induced neutrophil aggregation. J Immunol. 1977 Nov;119(5):1751–1756. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Flaherty J. T., Kreutzer D. L., Ward P. A. Neutrophil aggregation and swelling induced by chemotactic agents. J Immunol. 1977 Jul;119(1):232–239. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Flaherty J. T., Showell H. J., Ward P. A. Neutropenia induced by systemic infusion of chemotactic factors. J Immunol. 1977 May;118(5):1586–1589. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Showell H. J., Freer R. J., Zigmond S. H., Schiffmann E., Aswanikumar S., Corcoran B., Becker E. L. The structure-activity relations of synthetic peptides as chemotactic factors and inducers of lysosomal secretion for neutrophils. J Exp Med. 1976 May 1;143(5):1154–1169. doi: 10.1084/jem.143.5.1154. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson M. J., Becker E. L. Measurement of chemotaxis of human polymorphonuclear leukocytes in filters by counting the number of cells in a single plane and comparison with leading front method. J Immunol Methods. 1976;13(2):191–197. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(76)90158-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WARD P. A., COCHRANE C. G., MUELLER-EBERHARD H. J. THE ROLE OF SERUM COMPLEMENT IN CHEMOTAXIS OF LEUKOCYTES IN VITRO. J Exp Med. 1965 Aug 1;122:327–346. doi: 10.1084/jem.122.2.327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams L. T., Snyderman R., Pike M. C., Lefkowitz R. J. Specific receptor sites for chemotactic peptides on human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Mar;74(3):1204–1208. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.3.1204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zigmond S. H., Hirsch J. G. Leukocyte locomotion and chemotaxis. New methods for evaluation, and demonstration of a cell-derived chemotactic factor. J Exp Med. 1973 Feb 1;137(2):387–410. doi: 10.1084/jem.137.2.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



