Abstract
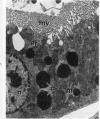
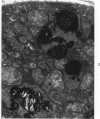
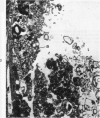
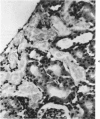
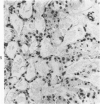
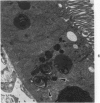
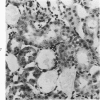
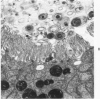
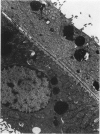
Fischer 344 rats were treated with tobramycin or gentamicin, 40 mg/kg/day, for up to 10 days or with tobramycin, 120 mg/kg/day, for up to 14 days. Serum creatinine and BUN at the time of sacrifice were determined, and kidney tissues were examined by light and electron microscopy. Rats receiving gentamicin demonstrated progressive renal proximal tubular necrosis which was nearly universal at the end of 10 days. Their BUN and creatinine levels rose progressively over the same period. Even at the higher dosage, tobramycin therapy resulted in only rare foci of proximal tubular necrosis and minimal elevation of BUN and creatinine. Although they occurred later and were substantially less severe, the ultrastructural changes induced by tobramycin were the same as those seen following gentamicin administration. These results indicate that the mechanism of tobramycin-induced renal injury is probably similar to that of gentamicin and that tobramycin is significantly less nephrotoxic in this experimental model.
Full text
PDF











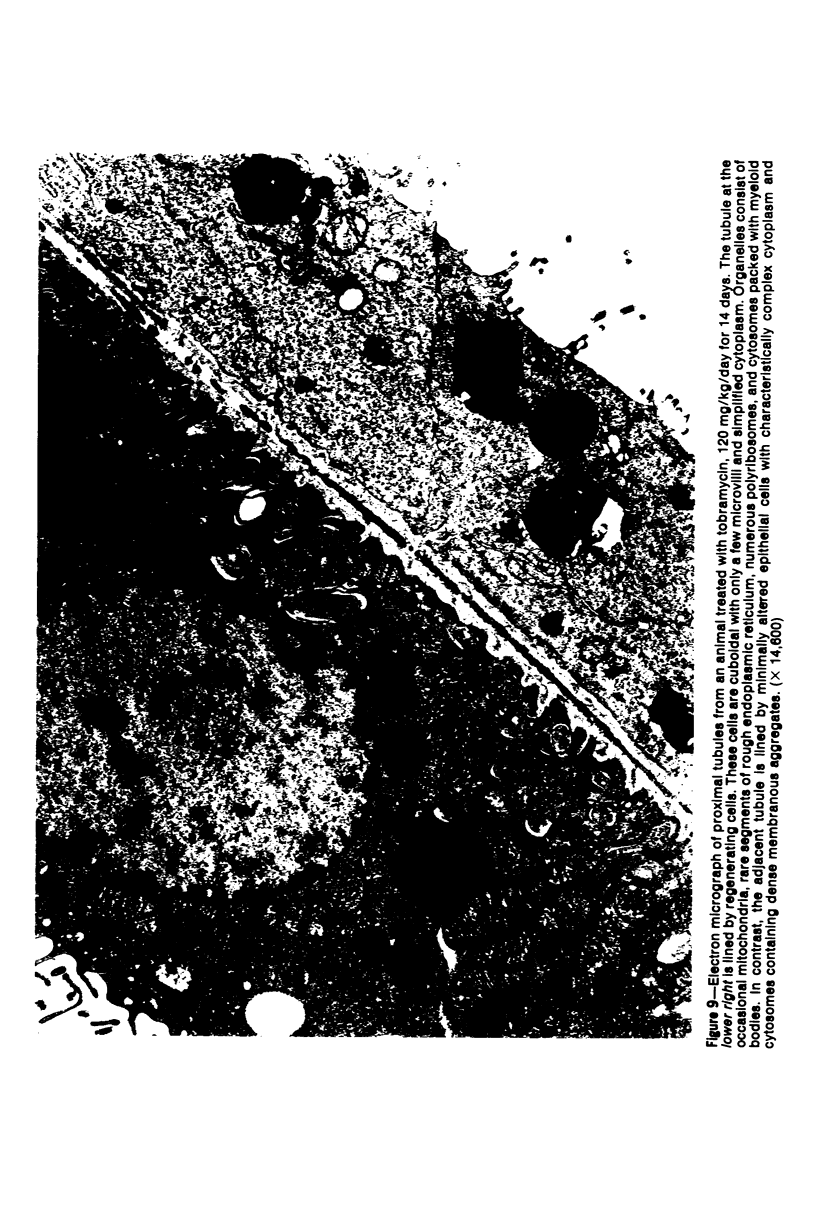
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BLACK J., CALESNICK B., WILLIAMS D., WEINSTEIN M. J. PHARMACOLOGY OF GENTAMICIN, A NEW BROAD-SPECTRUM ANTIBIOTIC. Antimicrob Agents Chemother (Bethesda) 1963;161:138–147. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bendush C. L., Weber R. Tobramycin sulfate: a summary of worldwide experience from clinical trials. J Infect Dis. 1976 Aug;134 (Suppl):S219–S234. doi: 10.1093/infdis/134.supplement_1.s219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brogden R. N., Pinder R. M., Sawyer P. R., Speight T. M., Avery G. S. Tobramycin: a review of its antibacterial and pharmacokinetic properties and therapeutic use. Drugs. 1976;12(3):166–200. doi: 10.2165/00003495-197612030-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuppage F. E., Setter K., Sullivan P., Reitzes E. J., Melnykovych A. O. Gentamicin nephrotoxicity. II. Physiological, biochemical and morphological effects of prolonged administration to rats. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol. 1977 Jun 24;24(2):121–138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HRUBAN Z., SPARGO B., SWIFT H., WISSLER R. W., KLEINFELD R. G. Focal cytoplasmic degradation. Am J Pathol. 1963 Jun;42:657–683. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houghton D. C., Hartnett M., Campbell-Boswell M., Porter G., Bennett W. A light and electron microscopic analysis of gentamicin nephrotoxicity in rats. Am J Pathol. 1976 Mar;82(3):589–612. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosek J. C., Mazze R. I., Cousins M. J. Nephrotoxicity of gentamicin. Lab Invest. 1974 Jan;30(1):48–57. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUFT J. H. Improvements in epoxy resin embedding methods. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1961 Feb;9:409–414. doi: 10.1083/jcb.9.2.409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker B. D., Gentry L. O. A randomized, comparative study of tobramycin and gentamicin in treatment of acute urinary tract infections. J Infect Dis. 1976 Aug;134 (Suppl):S146–S149. doi: 10.1093/infdis/134.supplement_1.s146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welles J. S., Emmerson J. L., Gibson W. R., Nickander R., Owen N. V., Anderson R. C. Preclinical toxicology studies with tobramycin. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1973 Jul;25(3):398–409. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(73)90313-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]