Abstract
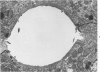
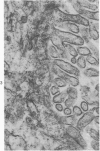
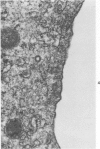
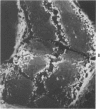
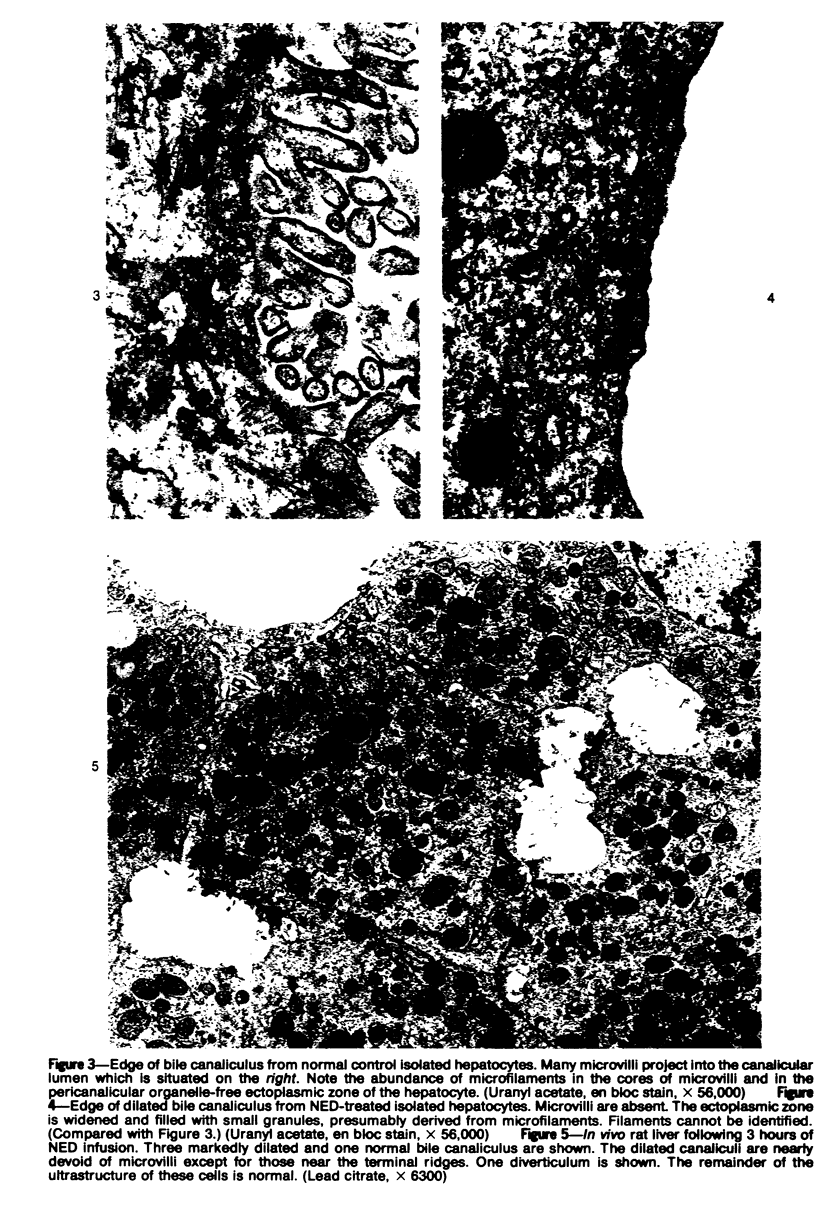
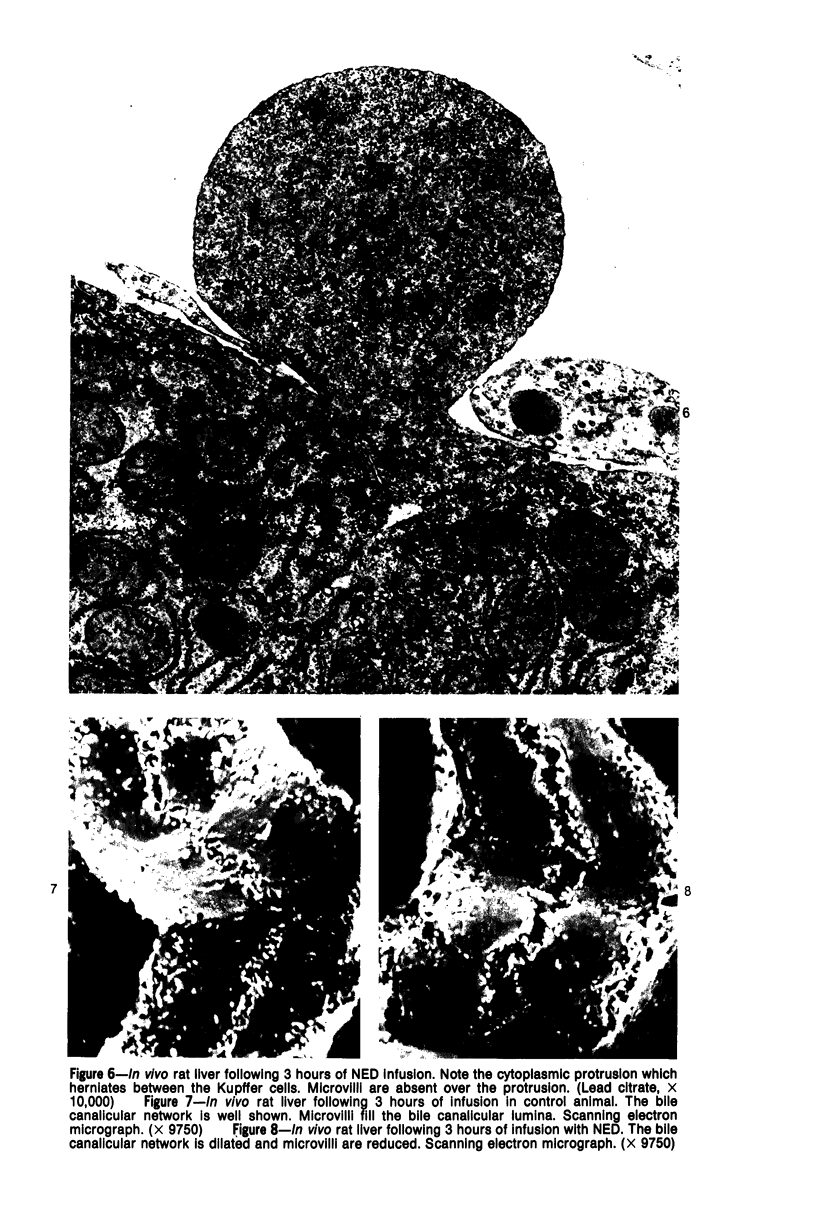
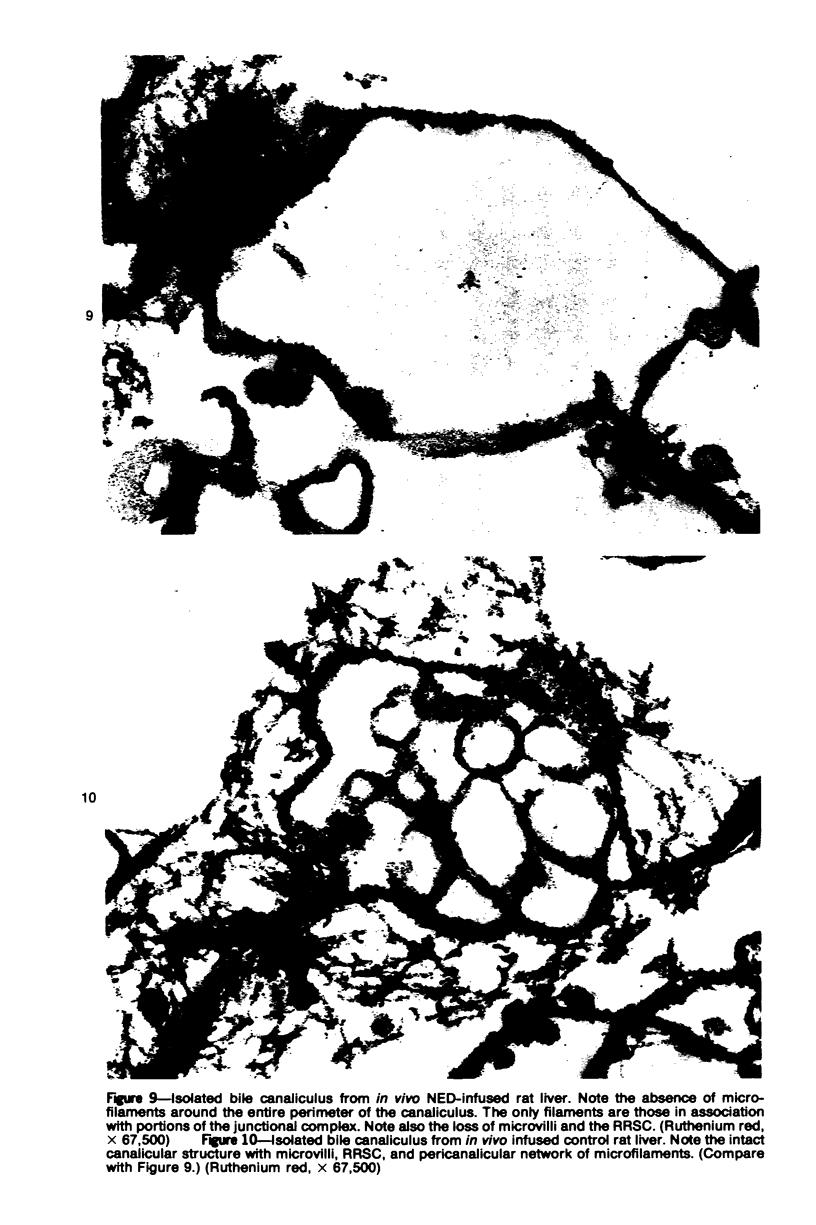
An experimental study of norethandrolone (NED)-induced intrahepatic cholestasis was made. NED was infused via a portal vein catheter into rat liver in vivo, and measurements were made of bile flow. Liver specimens were taken at intervals for light microscopy and for transmission and scanning electron microscopy. Bile-canalicular-rich membrane fractions were prepared. The effects of NED were also examined in isolated hepatocytes in suspension culture. NED infusion induced total cholestasis by 3 hours. Canalicular alterations commonly associated with cholestasis were found in in vivo infused liver and in isolated hepatocytes. Pericanalicular microfilament changes were also noted in both, with loss of filament structure and replacement by a granular zone. In isolated canalicular membrane fractions prepared from NED-treated animals, the normal investment of pericanalicular filaments was no longer present. Loss of the bile canalicular ruthenium red surface coat was also noted. In view of the identical findings in isolated hepatocytes and in in vivo liver, obstruction and mechanical factors can be excluded as possible causes. The results raise the possibility that the mechanism of NED-induced cholestasis may be related to disaggregation and/or detachment of microfilaments from the canalicular membranes.
Full text
PDF





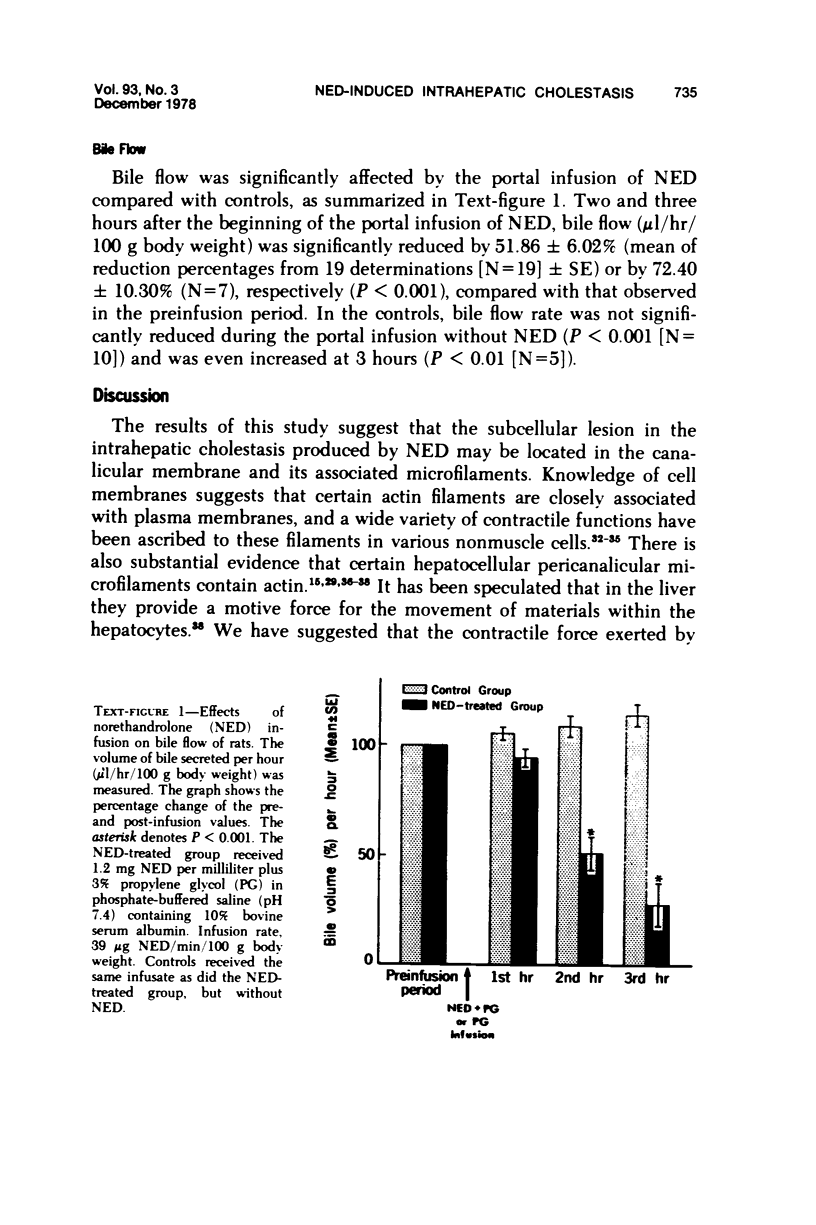





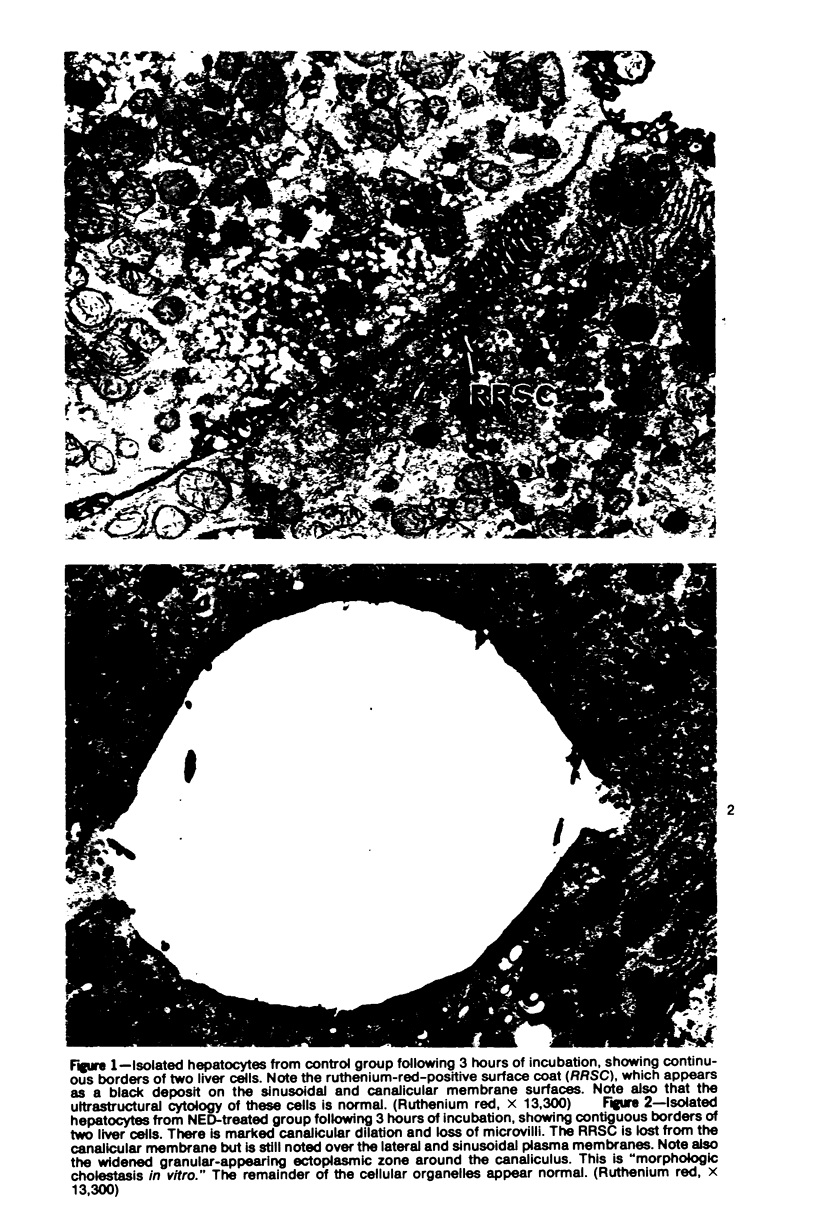
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boyer J. L., Reno D. Properties of (Na+ plus K+)-activated ATPase in rat liver plasma membranes enriched with bile canaliculi. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Aug 5;401(1):59–72. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(75)90341-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner B. M., Bohrer M. P., Baylis Ch, Deen W. M. Determinants of glomerular permselectivity: Insights derived from observations in vivo. Kidney Int. 1977 Oct;12(4):229–237. doi: 10.1038/ki.1977.107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUNNING M. F. Jaundice associated with norethandrolone (Nilevar) administration. J Am Med Assoc. 1958 Jul 5;167(10):1242–1243. doi: 10.1001/jama.1958.72990270011009d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Despopoulos A. Excretion of sulfobromophthalein by perfused rat liver as influenced by steroidal hormones. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1970 May;173(1):37–42. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erlinger S. Cholestasis: Pump failure, microvilli defect, or both? Lancet. 1978 Mar 11;1(8063):533–534. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)90555-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fahimi H. D. Perfusion and immersion fixation of rat liver with glutaraldehyde. Lab Invest. 1967 May;16(5):736–750. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher M. M., Bloxam D. L., Oda M., Phillips M. J., Yousef I. M. Characterization of rat liver cell plasma membranes. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1975 Oct;150(1):177–184. doi: 10.3181/00379727-150-38998. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- French S. W., Davies P. L. Ultrastructural localization of actin-like filaments in rat hepatocytes. Gastroenterology. 1975 Apr;68(4 Pt 1):765–774. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOLDFISCHER S., ARIAS I. M., ESSNER E., NOVIKOFF A. B. Cytochemical and electron microscopic studies of rat liver with reduced capacity to transport conjugated bilirubin. J Exp Med. 1962 Mar 1;115:467–474. doi: 10.1084/jem.115.3.467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godman G. C., Miranda A. F., Deitch A. D., Tanenbaum S. W. Action of cytochalasin D on cells of established lines. III. Zeiosis and movements at the cell surface. J Cell Biol. 1975 Mar;64(3):644–667. doi: 10.1083/jcb.64.3.644. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregory D. H., Vlahcevic Z. R., Schatzki P., Swell L. Mechanism of secretion of biliary lipids. I. Role of bile canalicular and microsomal membranes in the synthesis and transport of biliary lecithin and cholesterol. J Clin Invest. 1975 Jan;55(1):105–114. doi: 10.1172/JCI107900. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARGREAVES T., LATHE G. H. INHIBITORY ASPECTS OF BILE SECRETION. Nature. 1963 Dec 21;200:1172–1176. doi: 10.1038/2001172a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEANEY R. P., WHEDON G. D. Impairment of hepatic bromsulphalein clearance by two 17-substituted testosterones. J Lab Clin Med. 1958 Aug;52(2):169–175. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hargreaves T. Cholestatic drugs and bilirubin metabolism. Nature. 1965 Apr 10;206(980):154–156. doi: 10.1038/206154a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holborow E. J., Trenchev P. S., Dorling J., Webb J. Demostration of smooth muscle contractile protein antigens in liver and epithelial cells. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1975 Jun 30;254:489–504. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1975.tb29196.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeejeebhoy K. N., Ho J., Greenberg G. R., Phillips M. J., Bruce-Robertson A., Sodtke U. Albumin, fibrinogen and transferrin synthesis in isolated rat hepatocyte suspensions. A model for the study of plasma protein synthesis. Biochem J. 1975 Jan;146(1):141–155. doi: 10.1042/bj1460141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manasek F. J., Burnside B., Stroman J. The sensitivity of developing cardiac myofibrils to cytochalasin-B (electron microscopy-polarized light-Z-bands-heartbeat). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Feb;69(2):308–312. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.2.308. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyal K., Mayr W. W., Richardson A. L. Acute cholestasis induced by lithocholic acid in the rat. A freeze-fracture replica and thin section study. Lab Invest. 1975 Apr;32(4):527–535. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mooseker M. S., Tilney L. G. Organization of an actin filament-membrane complex. Filament polarity and membrane attachment in the microvilli of intestinal epithelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1975 Dec;67(3):725–743. doi: 10.1083/jcb.67.3.725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicolson G. L. Transmembrane control of the receptors on normal and tumor cells. I. Cytoplasmic influence over surface components. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Apr 13;457(1):57–108. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(76)90014-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oda M., Phillips M. J. Bile canalicular membrane pathology in cytochalasin B-induced cholestasis. Lab Invest. 1977 Oct;37(4):350–356. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oda M., Price V. M., Fisher M. M., Phillips M. J. Ultrastructure of bile canaliculi, with special reference to the surface coat and the pericanalicular web. Lab Invest. 1974 Oct;31(4):314–323. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orci L., Gabbay K. H., Malaisse W. J. Pancreatic beta-cell web: its possible role in insulin secretion. Science. 1972 Mar 10;175(4026):1128–1130. doi: 10.1126/science.175.4026.1128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orlandi F., Jezequel A. M. On the pathogenesis of the cholestasis induced by 17.alkylated steroids: ultrastructural and functional changes of the liver cells during the treatment. Rev Int Hepatol. 1966;16(2):331–333. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popper H., Schaffner F. Pathophysiology of cholestasis. Hum Pathol. 1970 Mar;1(1):1–24. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(70)80002-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rennke H. G., Cotran R. S., Venkatachalam M. A. Role of molecular charge in glomerular permeability. Tracer studies with cationized ferritins. J Cell Biol. 1975 Dec;67(3):638–646. doi: 10.1083/jcb.67.3.638. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ronchi G., Desmet V. J. Histochemical study of gamma glutamyl transpeptidase (GGT) in experimental intrahepatic and extrahepatic cholestasis. Beitr Pathol. 1973 Dec;150(3):316–321. doi: 10.1016/s0005-8165(73)80061-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHAFFNER F., POPPER H., PEREZ V. Changes in bile canaliculi produced by norethandrolone: electron microscopic study of human and rat liver. J Lab Clin Med. 1960 Oct;56:623–628. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaffner F., Popper H. Cholestasis is the result of hypoactive hypertrophic smooth endoplasmic reticulum in the hepatocyte. Lancet. 1969 Aug 16;2(7616):355–359. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(69)92704-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaffner F. Some observations concerning the molecular biology of cholestasis. Helv Med Acta. 1973 Sep;37(2):183–192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherlock S. Biliary secretory failure in man. The problem of cholestasis. Ann Intern Med. 1966 Sep;65(3):397–408. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-65-3-397. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon F. R., Arias I. M. Alteration of bile canalicular enzymes in cholestasis. A possible cause of bile secretory failure. J Clin Invest. 1973 Apr;52(4):765–775. doi: 10.1172/JCI107239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon F. R., Arias I. M. Alterations in liver plasma membranes and their possible role in cholestasis. Gastroenterology. 1972 Feb;62(2):342–345. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer S. J. The molecular organization of membranes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1974;43(0):805–833. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.43.070174.004105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spooner B. S., Wessells N. K. Effects of cytochalasin B upon microfilaments involved in morphogenesis of salivary epithelium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Jun;66(2):360–361. doi: 10.1073/pnas.66.2.360. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spooner B. S., Yamada K. M., Wessells N. K. Microfilaments and cell locomotion. J Cell Biol. 1971 Jun;49(3):595–613. doi: 10.1083/jcb.49.3.595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steck T. L. The organization of proteins in the human red blood cell membrane. A review. J Cell Biol. 1974 Jul;62(1):1–19. doi: 10.1083/jcb.62.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wrenn J. T., Wessells N. K. Cytochalasin B: effects upon microfilaments involved in morphogenesis of estrogen-induced glands of oviduct. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Jul;66(3):904–908. doi: 10.1073/pnas.66.3.904. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada K. M., Spooner B. S., Wessells N. K. Axon growth: roles of microfilaments and microtubules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Aug;66(4):1206–1212. doi: 10.1073/pnas.66.4.1206. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yousef I. M., Bloxam D. L., Phillips M. J., Fisher M. M. Liver cell plasma membrane lipids and the origin of biliary phospholipid. Can J Biochem. 1975 Sep;53(9):989–997. doi: 10.1139/o75-135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]