Abstract
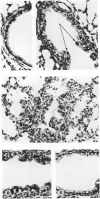
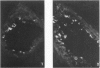
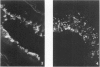
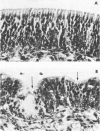
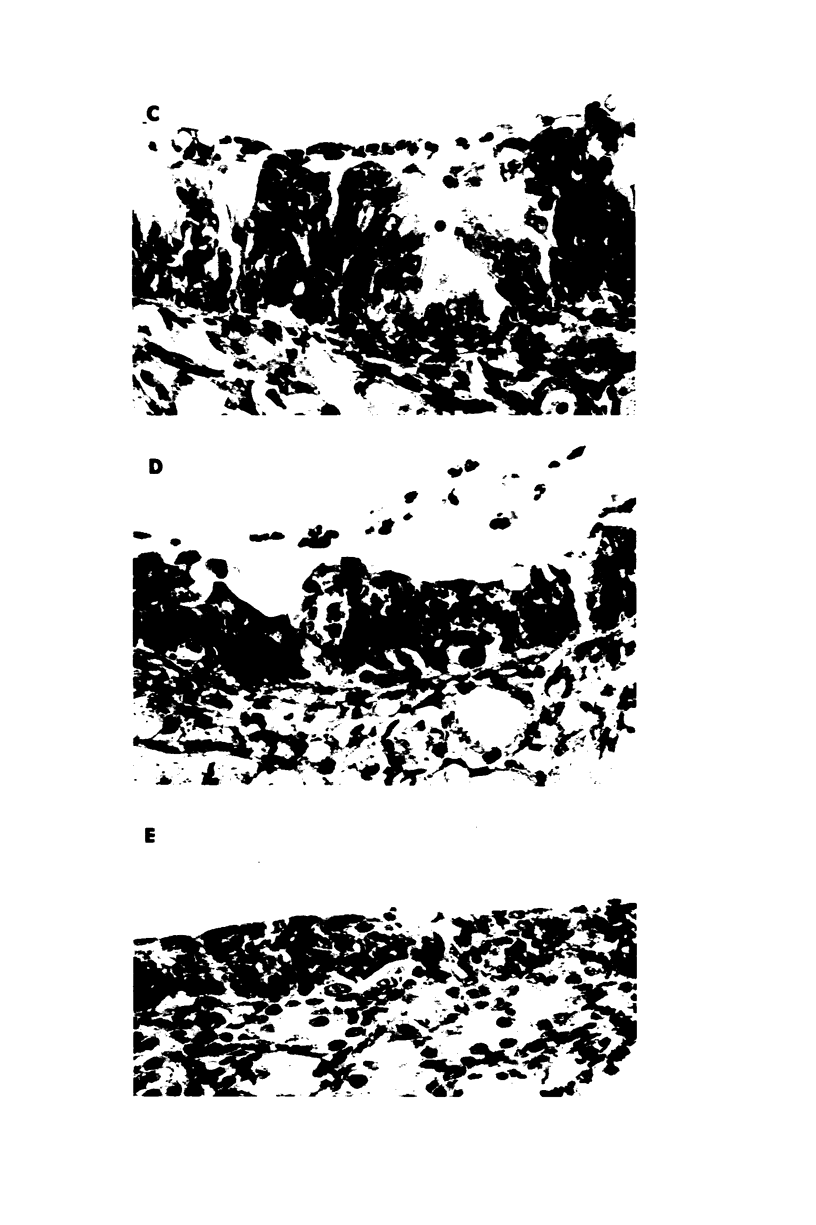
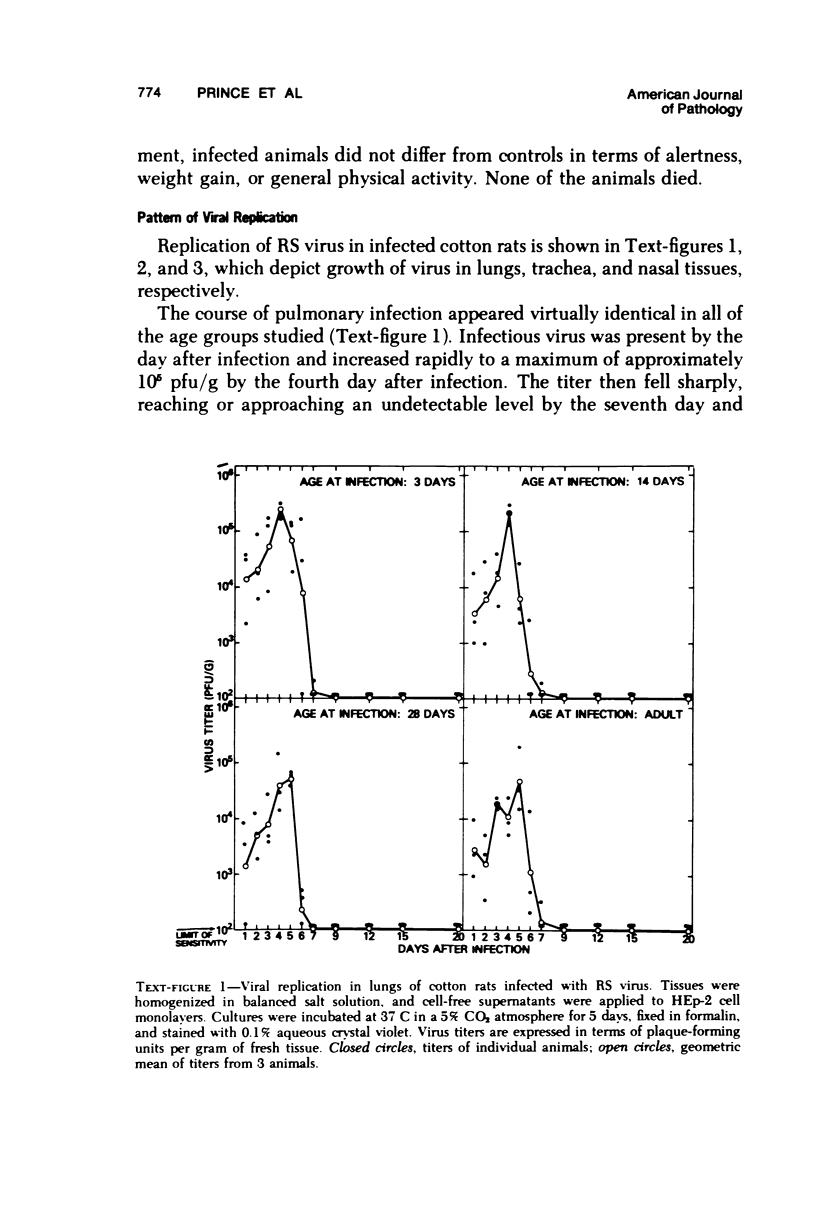
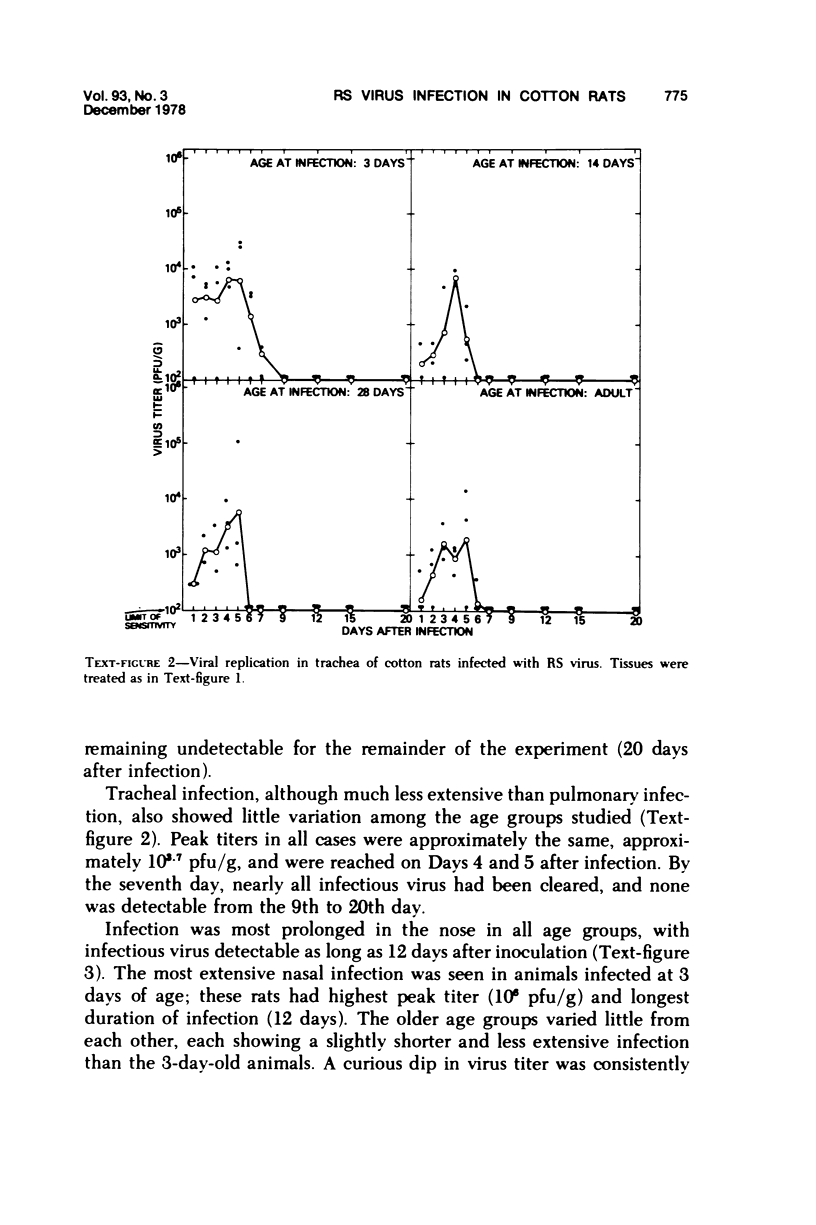
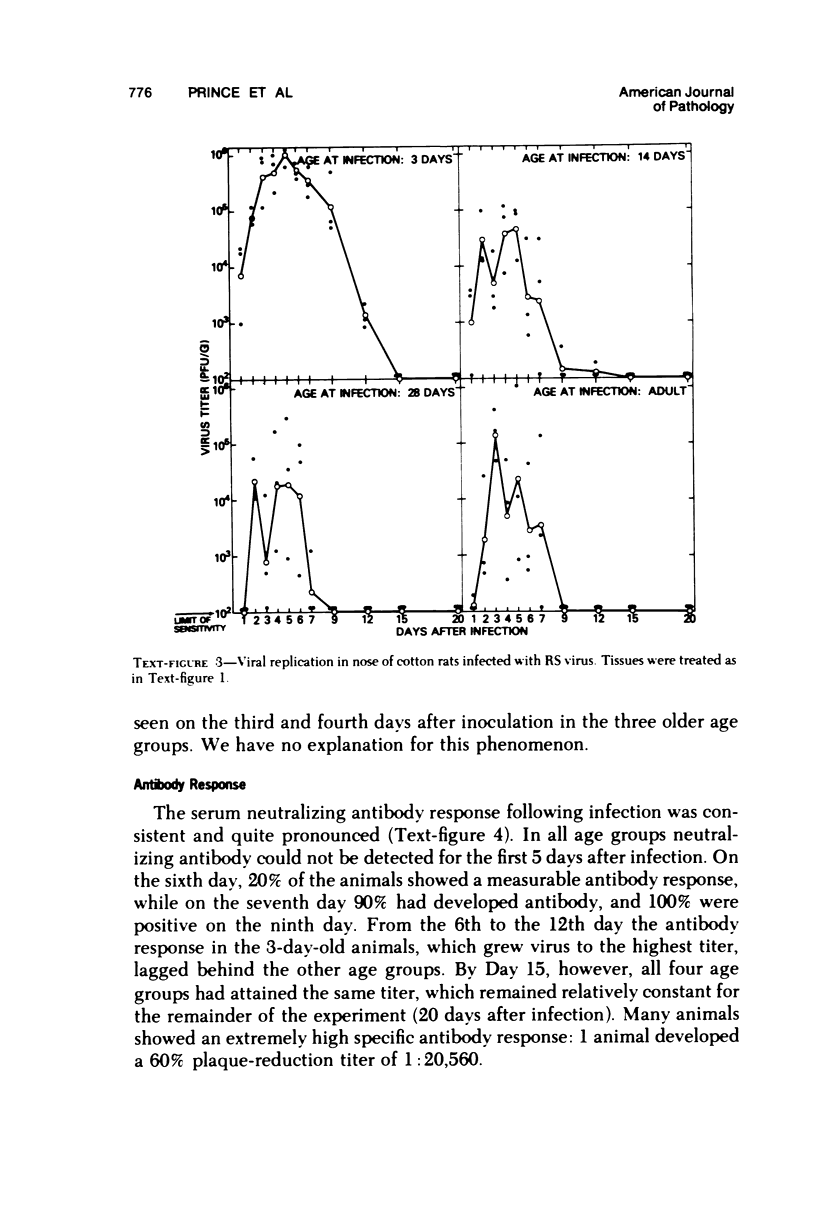
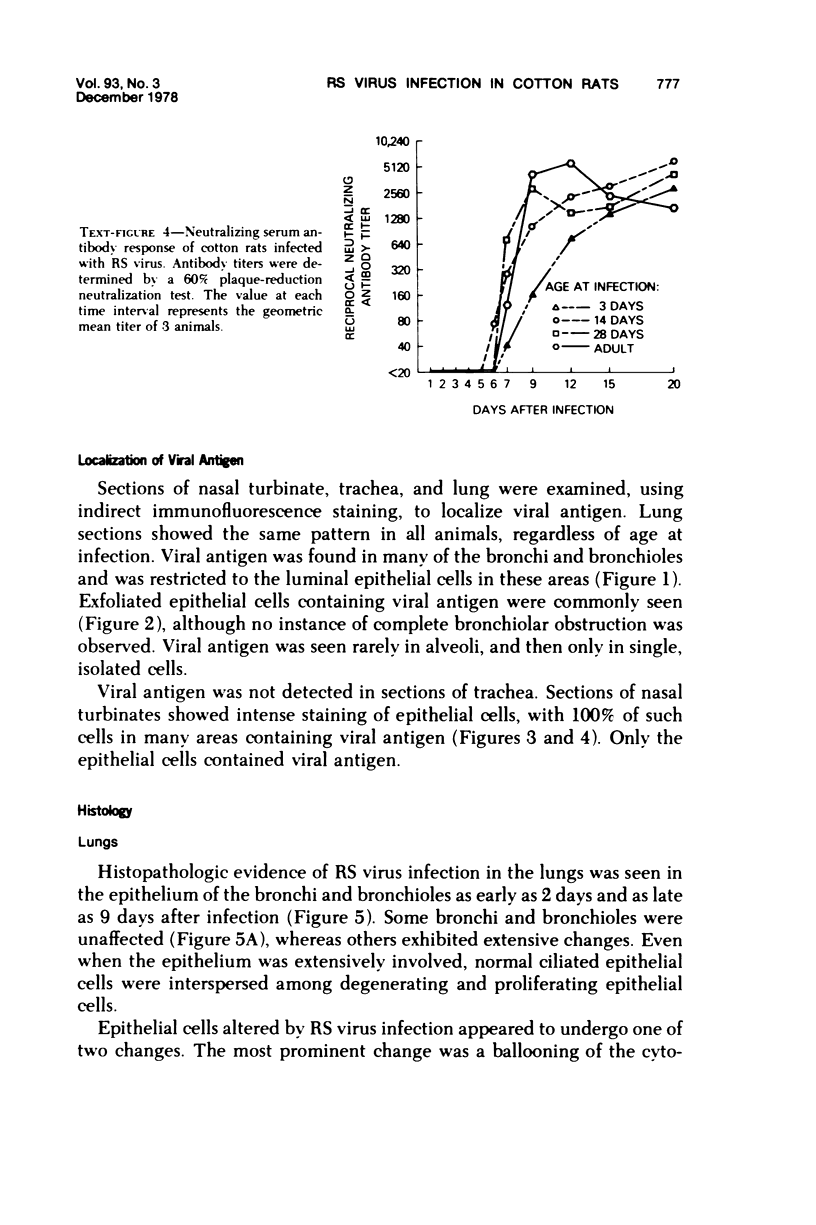
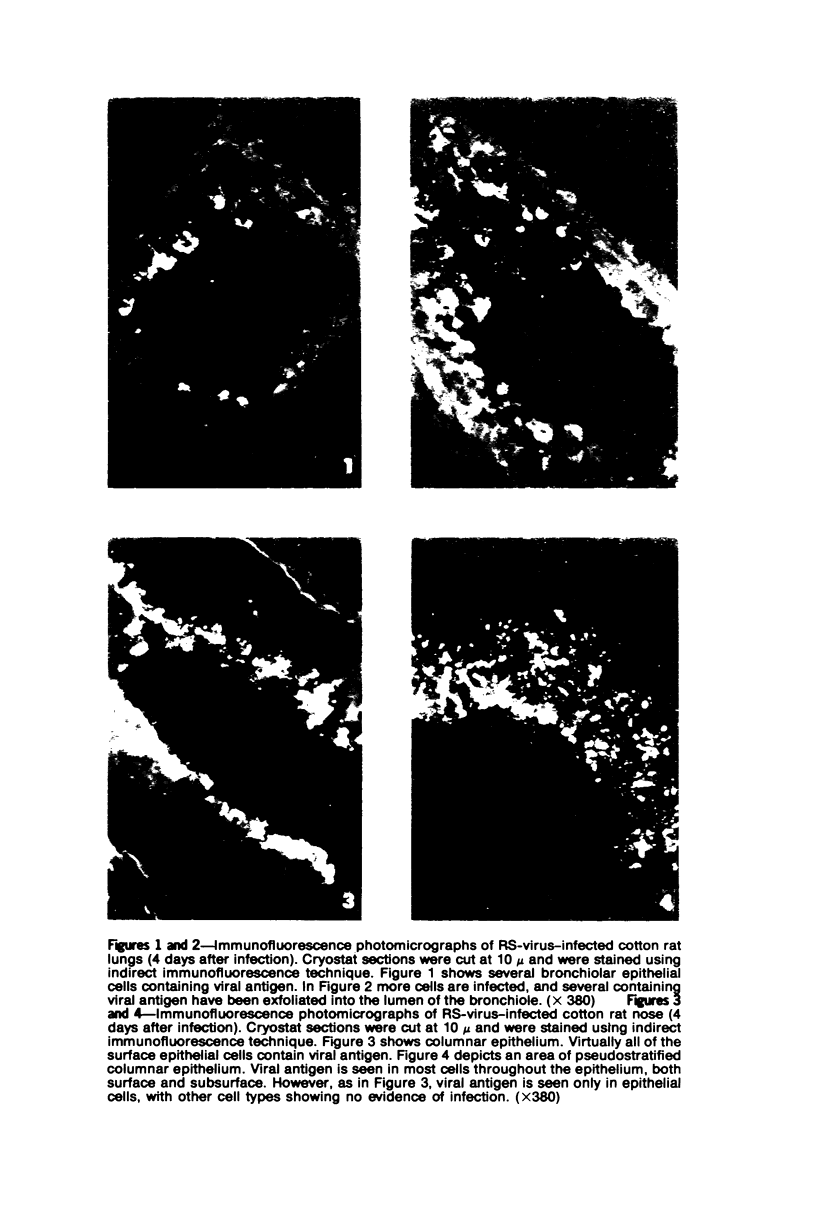
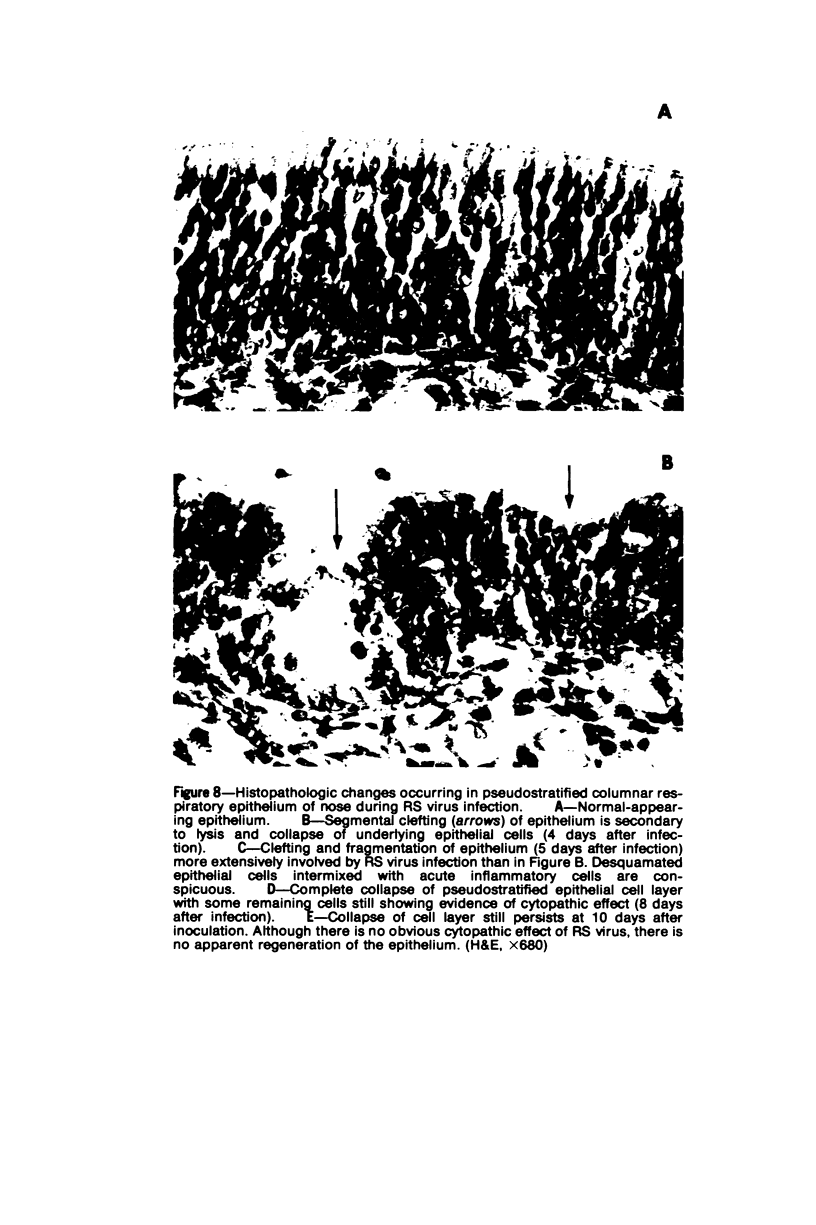
The cotton rat is susceptible to respiratory synctial virus infection in both the upper and lower portions of the respiratory tract. Virus replicates to high titer in the nose and lungs and to relatively low titer in the trachea. Immunofluorescence studies demonstrated viral antigen in the nasal epithelium and the bronchial and bronchiolar epithelium but not in the trachea or the alveolar cells of the lungs. Histopathologic changes included a desquamative, exudative rhinitis of moderate severity and a mild proliferative bronchiolitis. Serum neutralizing antibody developed in all animals by the ninth day after infection, reaching extremely high titer in several instances. Unlike the previously described response of experimentally infected infant ferrets, cotton rats are uniformly susceptible to pulmonary infection throughout life, thereby offering a model for long-term pulmonary studies heretofore not available.
Full text
PDF














Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aherne W., Bird T., Court S. D., Gardner P. S., McQuillin J. Pathological changes in virus infections of the lower respiratory tract in children. J Clin Pathol. 1970 Feb;23(1):7–18. doi: 10.1136/jcp.23.1.7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chin J., Magoffin R. L., Shearer L. A., Schieble J. H., Lennette E. H. Field evaluation of a respiratory syncytial virus vaccine and a trivalent parainfluenza virus vaccine in a pediatric population. Am J Epidemiol. 1969 Apr;89(4):449–463. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a120957. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coates H. V., Alling D. W., Chanock R. M. An antigenic analysis of respiratory syncytial virus isolates by a plaque reduction neutralization test. Am J Epidemiol. 1966 Mar;83(2):299–313. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a120586. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fulginiti V. A., Eller J. J., Sieber O. F., Joyner J. W., Minamitani M., Meiklejohn G. Respiratory virus immunization. I. A field trial of two inactivated respiratory virus vaccines; an aqueous trivalent parainfluenza virus vaccine and an alum-precipitated respiratory syncytial virus vaccine. Am J Epidemiol. 1969 Apr;89(4):435–448. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a120956. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KRAVETZ H. M., KNIGHT V., CHANOCK R. M., MORRIS J. A., JOHNSON K. M., RIFKIND D., UTZ J. P. Respiratory syncytial virus. III. Production of illness and clinical observations in adult volunteers. JAMA. 1961 May 27;176:657–663. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapikian A. Z., Mitchell R. H., Chanock R. M., Shvedoff R. A., Stewart C. E. An epidemiologic study of altered clinical reactivity to respiratory syncytial (RS) virus infection in children previously vaccinated with an inactivated RS virus vaccine. Am J Epidemiol. 1969 Apr;89(4):405–421. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a120954. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter D. D., Porter H. G., Deerhake B. B. Immunofluorescence assay for antigen and antibody in lactic dehydrogenase virus infection of mice. J Immunol. 1969 Feb;102(2):431–436. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prince G. A., Porter D. D. Cryostat microtomy of lung tissue in an expanded state. Stain Technol. 1975 Jan;50(1):43–45. doi: 10.3109/10520297509117030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prince G. A., Porter D. D. The pathogenesis of respiratory syncytial virus infection in infant ferrets. Am J Pathol. 1976 Feb;82(2):339–352. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RODRIGUEZ J., DEINHARDT F. Preparation of a semipermanent mounting medium for fluorescent antibody studies. Virology. 1960 Oct;12:316–317. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(60)90205-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHULZE I. T., SCHLESINGER R. W. Plaque assay of dengue and other group B arthropod-borne viruses under methyl cellulose overlay media. Virology. 1963 Jan;19:40–48. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(63)90022-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]