Abstract
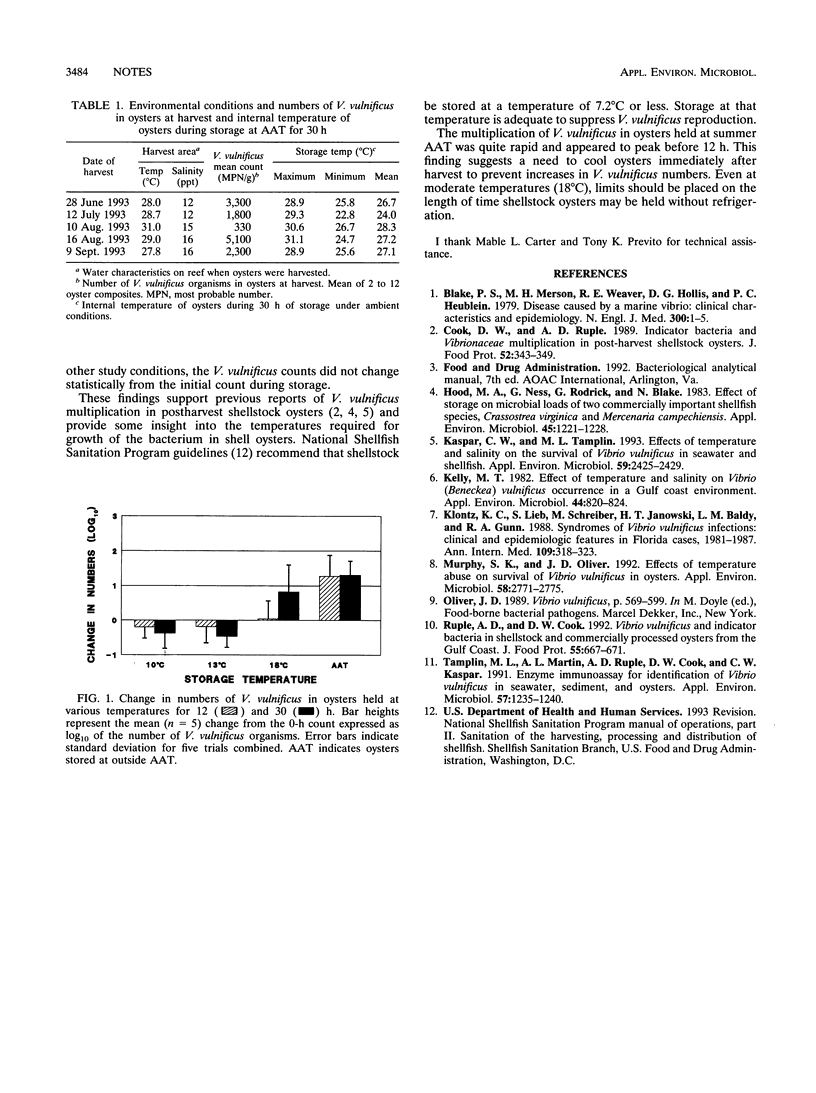
After harvest, shellstock oysters stored under controlled temperatures of 10, 13, and 18 degrees C and at ambient outside air temperature (23 to 34 degrees C) were sampled after 12 and 30 h for Vibrio vulnificus. At 13 degrees C and below, V. vulnificus failed to multiply in the oysters. In oysters held at 18 degrees C for 30 h and under ambient conditions for 12 and 30 h, V. vulnificus numbers were statistically greater (P < 0.05) than those in oysters at harvest. These data indicate that endogenous V. vulnificus can multiply in unchilled shellstock oysters.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blake P. A., Merson M. H., Weaver R. E., Hollis D. G., Heublein P. C. Disease caused by a marine Vibrio. Clinical characteristics and epidemiology. N Engl J Med. 1979 Jan 4;300(1):1–5. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197901043000101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hood M. A., Ness G. E., Rodrick G. E., Blake N. J. Effects of storage on microbial loads of two commercially important shellfish species, Crassostrea virginica and Mercenaria campechiensis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Apr;45(4):1221–1228. doi: 10.1128/aem.45.4.1221-1228.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaspar C. W., Tamplin M. L. Effects of temperature and salinity on the survival of Vibrio vulnificus in seawater and shellfish. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1993 Aug;59(8):2425–2429. doi: 10.1128/aem.59.8.2425-2429.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly M. T. Effect of temperature and salinity on Vibrio (Beneckea) vulnificus occurrence in a Gulf Coast environment. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Oct;44(4):820–824. doi: 10.1128/aem.44.4.820-824.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klontz K. C., Lieb S., Schreiber M., Janowski H. T., Baldy L. M., Gunn R. A. Syndromes of Vibrio vulnificus infections. Clinical and epidemiologic features in Florida cases, 1981-1987. Ann Intern Med. 1988 Aug 15;109(4):318–323. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-109-4-318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy S. K., Oliver J. D. Effects of temperature abuse on survival of Vibrio vulnificus in oysters. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992 Sep;58(9):2771–2775. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.9.2771-2775.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamplin M. L., Martin A. L., Ruple A. D., Cook D. W., Kaspar C. W. Enzyme immunoassay for identification of Vibrio vulnificus in seawater, sediment, and oysters. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Apr;57(4):1235–1240. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.4.1235-1240.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



