Abstract
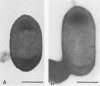
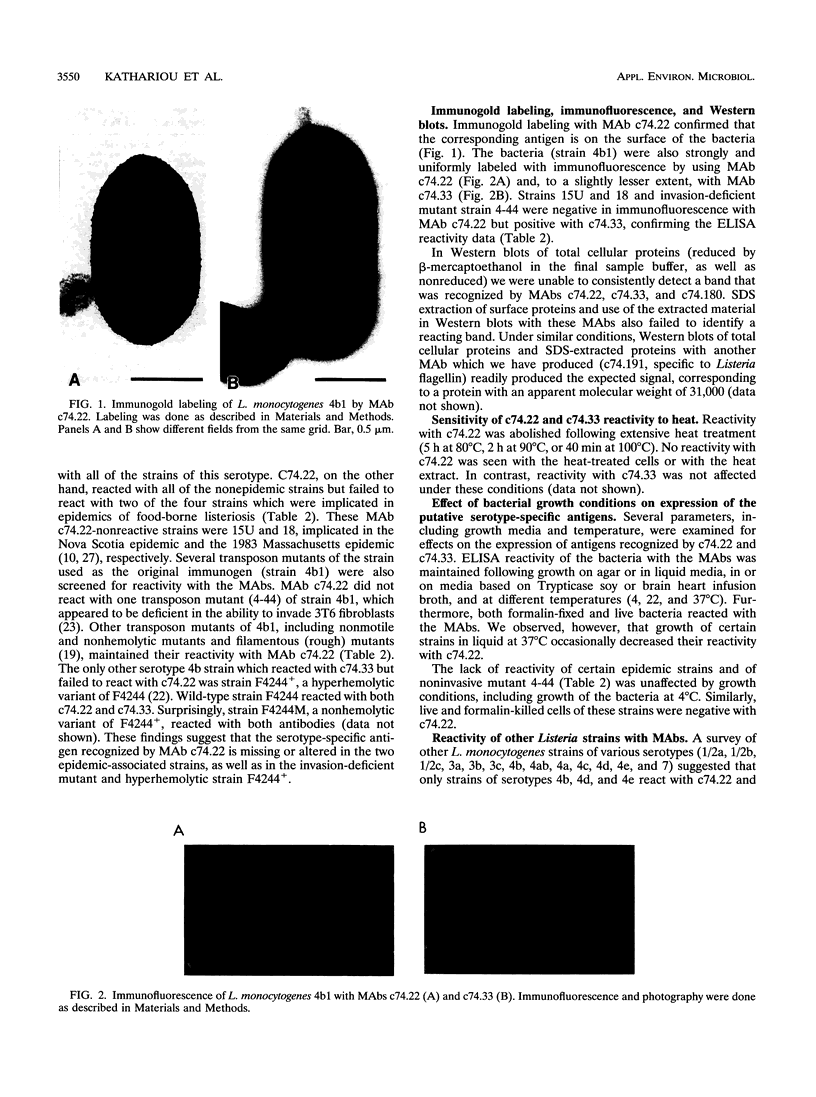
Strains of Listeria monocytogenes serotype 4b account for a large fraction of sporadic listeriosis cases, as well as all major food-borne epidemics attributed to this pathogen. We have identified a set of three monoclonal antibodies which showed a high degree of specificity for strains of L. monocytogenes serotype 4b. Two of these antibodies (c74.33 and c74.180, isotypes immunoglobulin M [IgM] and IgG3, respectively) recognized all serotype 4b strains, whereas antibody c74.22 (isotype IgG1) failed to recognize certain epidemic-associated strains. The corresponding antigens were located on the surface of the bacteria and were expressed following bacterial growth in different media and over a wide range of temperatures (4, 22, and 37 degrees C). Heating L. monocytogenes cells at 80,90, or 100 degrees C abolished reactivity for c74.22 but not for c74.33 MAb. These MAbs were negative for all of the non-Listeria strains tested, including representatives of several gram-negative and gram-positive species. The surface antigen recognized by c74.22 appeared to be associated with the ability of the bacteria to enter (invade) mammalian cells in culture.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benedict A. A., Alvarez A. M., Pollard L. W. Pathovar-Specific Antigens of Xanthomonas campestris pv. begoniae and X. campestris pv. pelargonii Detected with Monoclonal Antibodies. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Feb;56(2):572–574. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.2.572-574.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhunia A. K., Ball P. H., Fuad A. T., Kurz B. W., Emerson J. W., Johnson M. G. Development and characterization of a monoclonal antibody specific for Listeria monocytogenes and Listeria innocua. Infect Immun. 1991 Sep;59(9):3176–3184. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.9.3176-3184.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhunia A. K., Johnson M. G. Monoclonal antibody specific for Listeria monocytogenes associated with a 66-kilodalton cell surface antigen. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992 Jun;58(6):1924–1929. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.6.1924-1929.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bibb W. F., Gellin B. G., Weaver R., Schwartz B., Plikaytis B. D., Reeves M. W., Pinner R. W., Broome C. V. Analysis of clinical and food-borne isolates of Listeria monocytogenes in the United States by multilocus enzyme electrophoresis and application of the method to epidemiologic investigations. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Jul;56(7):2133–2141. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.7.2133-2141.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bibb W. F., Schwartz B., Gellin B. G., Plikaytis B. D., Weaver R. E. Analysis of Listeria monocytogenes by multilocus enzyme electrophoresis and application of the method to epidemiologic investigations. Int J Food Microbiol. 1989 Jun;8(3):233–239. doi: 10.1016/0168-1605(89)90018-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brosch R., Chen J., Luchansky J. B. Pulsed-field fingerprinting of listeriae: identification of genomic divisions for Listeria monocytogenes and their correlation with serovar. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1994 Jul;60(7):2584–2592. doi: 10.1128/aem.60.7.2584-2592.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butman B. T., Plank M. C., Durham R. J., Mattingly J. A. Monoclonal antibodies which identify a genus-specific Listeria antigen. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Jun;54(6):1564–1569. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.6.1564-1569.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dons L., Rasmussen O. F., Olsen J. E. Cloning and characterization of a gene encoding flagellin of Listeria monocytogenes. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Oct;6(20):2919–2929. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01751.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farber J. M., Peterkin P. I. Listeria monocytogenes, a food-borne pathogen. Microbiol Rev. 1991 Sep;55(3):476–511. doi: 10.1128/mr.55.3.476-511.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiedler F. Biochemistry of the cell surface of Listeria strains: a locating general view. Infection. 1988;16 (Suppl 2):S92–S97. doi: 10.1007/BF01639729. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gellin B. G., Broome C. V. Listeriosis. JAMA. 1989 Mar 3;261(9):1313–1320. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graves L. M., Swaminathan B., Reeves M. W., Wenger J. Ribosomal DNA fingerprinting of Listeria monocytogenes using a digoxigenin-labeled DNA probe. Eur J Epidemiol. 1991 Jan;7(1):77–82. doi: 10.1007/BF00221345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayes P. S., Graves L. M., Ajello G. W., Swaminathan B., Weaver R. E., Wenger J. D., Schuchat A., Broome C. V. Comparison of cold enrichment and U.S. Department of Agriculture methods for isolating Listeria monocytogenes from naturally contaminated foods. The Listeria Study Group. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Aug;57(8):2109–2113. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.8.2109-2113.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kathariou S., Metz P., Hof H., Goebel W. Tn916-induced mutations in the hemolysin determinant affecting virulence of Listeria monocytogenes. J Bacteriol. 1987 Mar;169(3):1291–1297. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.3.1291-1297.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kathariou S., Pine L., George V., Carlone G. M., Holloway B. P. Nonhemolytic Listeria monocytogenes mutants that are also noninvasive for mammalian cells in culture: evidence for coordinate regulation of virulence. Infect Immun. 1990 Dec;58(12):3988–3995. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.12.3988-3995.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piffaretti J. C., Kressebuch H., Aeschbacher M., Bille J., Bannerman E., Musser J. M., Selander R. K., Rocourt J. Genetic characterization of clones of the bacterium Listeria monocytogenes causing epidemic disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(10):3818–3822. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.10.3818. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pine L., Kathariou S., Quinn F., George V., Wenger J. D., Weaver R. E. Cytopathogenic effects in enterocytelike Caco-2 cells differentiate virulent from avirulent Listeria strains. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 May;29(5):990–996. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.5.990-996.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasmussen O. F., Beck T., Olsen J. E., Dons L., Rossen L. Listeria monocytogenes isolates can be classified into two major types according to the sequence of the listeriolysin gene. Infect Immun. 1991 Nov;59(11):3945–3951. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.11.3945-3951.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuchat A., Swaminathan B., Broome C. V. Epidemiology of human listeriosis. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1991 Apr;4(2):169–183. doi: 10.1128/cmr.4.2.169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schönberg A., Teufel P., Weise E. Serovars of Listeria monocytogenes and Listeria innocua from food. Acta Microbiol Hung. 1989;36(2-3):249–253. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siragusa G. R., Johnson M. G. Monoclonal antibody specific for Listeria monocytogenes, Listeria innocua, and Listeria welshimeri. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Jun;56(6):1897–1904. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.6.1897-1904.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torensma R., Visser M. J., Aarsman C. J., Poppelier M. J., Fluit A. C., Verhoef J. Monoclonal antibodies that react with live Listeria spp. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1993 Aug;59(8):2713–2716. doi: 10.1128/aem.59.8.2713-2716.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]