Abstract
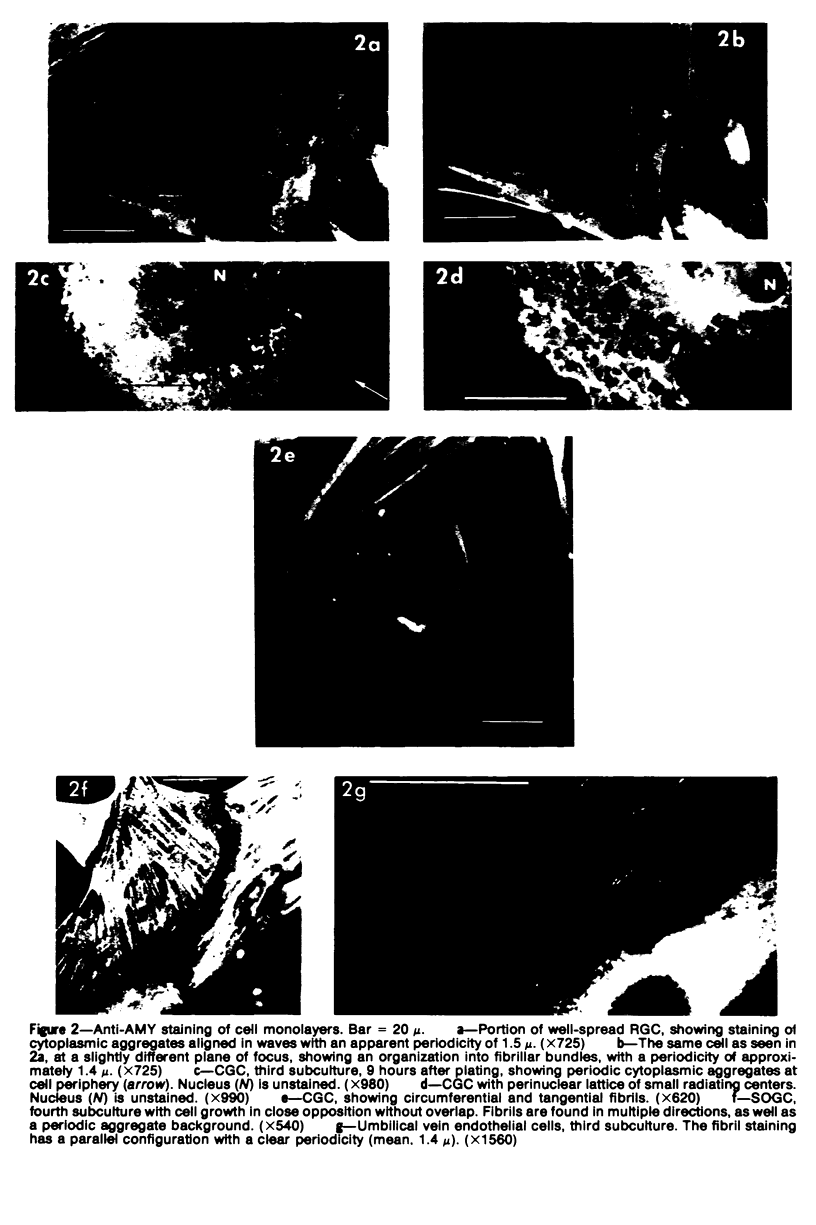
In this paper, we describe three cell types from the explanted human glomerulus: the circular glomerular cell (CGC), the rhomboid glomerular cell (RGC), and the small ovoid glomerular cell (SOGC). These cells were compared with subcultured human umbilical vein endothelial and smooth muscle cells, uterine smooth muscle cells, and skin fibroblasts. Immunochemical comparisons utilized antiserums to antigens in the human glomerulus: antiglomerular basement membrane, antifibroblast surface antigen (FSA) (reactive extensively with the mesangium), antiactomyosin (AMY) localizing more restrictively in the mesangium, and antihemophilic factor (AHF) localizing to the endothelium. No cultured glomerular cells bore the AHF marker of endothelial cells. The epithelioid CGC excrete most GBM antigen as an orderly palisade of granules from the cell surface. FSA is rapidly lost from the cell surface. RGC have a typical multilayered smooth muscle morphology and have a most prominent complex AMY pattern of periodic aggregates and fibrils. FSA adheres to the cell surface. SOGC form an initial nonoverlapped monolayer resembling endothelial cells but elongate and form multilayers after confluency. The AMY fibril pattern of SOGC is distinctively multidirectional. The translation of in vitro characteristics into in vivo identification must be interpreted cautiously: CGC may derive from glomerular epithelial cells; RGC may derive from mesangial cells; and SOGC may represent a more rapidly proliferating, less differentiated form of the epithelial cell or another, unidentified, glomerular cell type.
Full text
PDF



















Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Becker C. G. Demonstration of actomyosin in mesangial cells of the renal glomerulus. Am J Pathol. 1972 Jan;66(1):97–110. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernik M. B. Contractile activity of human glomeruli in culture. Nephron. 1969;6(1):1–10. doi: 10.1159/000179708. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke J. M., Balian G., Ross R., Bornstein P. Synthesis of types I and III procollagen and collagen by monkey aortic smooth muscle cells in vitro. Biochemistry. 1977 Jul 12;16(14):3243–3249. doi: 10.1021/bi00633a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burkholder P. M., Oberley T. D., Barber T. A., Beacom A., Koehler C. Immune adherence in renal glomeruli. Complement receptor sites on glomerular capillary epithelial cells. Am J Pathol. 1977 Mar;86(3):635–654. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caldwell P. R., Seegal B. C., Hsu K. C., Das M., Soffer R. L. Angiotensin-converting enzyme: vascular endothelial localization. Science. 1976 Mar 12;191(4231):1050–1051. doi: 10.1126/science.175444. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camazine S. M., Ryan G. B., Unanue E. R., Karnovsky M. J. Isolation of phagocytic cells from the rat renal glomerulus. Lab Invest. 1976 Oct;35(4):315–326. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniels J. R., Chu G. H. Basement membrane collagen of renal glomerulus. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 10;250(9):3531–3537. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faulk W. P., Conochie L. B., Temple A., Papamichail M. Immunobiology of membrane-bound collagen on mouse fibroblasts. Nature. 1975 Jul 10;256(5513):123–125. doi: 10.1038/256123a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fish A. J., Michael A. F., Vernier R. L., Brown D. M. Human glomerular cells in tissue culture. Lab Invest. 1975 Sep;33(3):330–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujiwara K., Pollard T. D. Fluorescent antibody localization of myosin in the cytoplasm, cleavage furrow, and mitotic spindle of human cells. J Cell Biol. 1976 Dec;71(3):848–875. doi: 10.1083/jcb.71.3.848. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gimbrone M. A., Jr, Cotran R. S., Folkman J. Human vascular endothelial cells in culture. Growth and DNA synthesis. J Cell Biol. 1974 Mar;60(3):673–684. doi: 10.1083/jcb.60.3.673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoyer L. W., De los Santos R. P., Hoyer J. R. Antihemophilic factor antigen. Localization in endothelial cells by immunofluorescent microscopy. J Clin Invest. 1973 Nov;52(11):2737–2744. doi: 10.1172/JCI107469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe E. A., Nachman R. L., Becker C. G., Minick C. R. Culture of human endothelial cells derived from umbilical veins. Identification by morphologic and immunologic criteria. J Clin Invest. 1973 Nov;52(11):2745–2756. doi: 10.1172/JCI107470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson A. R., Erdös E. G. Metabolism of vasoactive peptides by human endothelial cells in culture. Angiotensin I converting enzyme (kininase II) and angiotensinase. J Clin Invest. 1977 Apr;59(4):684–695. doi: 10.1172/JCI108687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kefalides N. A. Structure and biosynthesis of basement membranes. Int Rev Connect Tissue Res. 1973;6:63–104. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-363706-2.50008-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuusela P., Ruoslahti E., Engvall E., Vaheri A. Immunological interspecies cross-reactions of fibroblast surface antigen (fibronectin). Immunochemistry. 1976 Aug;13(8):639–642. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(76)90203-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LATTA H., MAUNSBACH A. B. Relations of the centrolobular region of the glomerulus to the juxtaglomerular apparatus. J Ultrastruct Res. 1962 Jun;6:562–578. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(62)80010-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linder E., Vaheri A., Ruoslahti E., Wartiovaara J. Distribution of fibroblast surface antigen in the developing chick embryo. J Exp Med. 1975 Jul 1;142(1):41–49. doi: 10.1084/jem.142.1.41. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macarak E. J., Howard B. V., Kefalides N. A. Biosynthesis of collagen and metabolism of lipids by endothelial cells in culture. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1976;275:104–113. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1976.tb43344.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marquardt H., Wilson C. B., Dixon F. J. Human glomerular basement membrane. Selective solubilization with chaotropes and chemical and immunologic characterization of its components. Biochemistry. 1973 Aug 14;12(17):3260–3266. doi: 10.1021/bi00741a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mauer S. M., Fish A. J., Blau E. B., Michael A. F. The glomerular mesangium. I. Kinetic studies of macromolecular uptake in normal and nephrotic rats. J Clin Invest. 1972 May;51(5):1092–1101. doi: 10.1172/JCI106901. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosesson M. W., Umfleet R. A. The cold-insoluble globulin of human plasma. I. Purification, primary characterization, and relationship to fibrinogen and other cold-insoluble fraction components. J Biol Chem. 1970 Nov 10;245(21):5728–5736. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowack H., Gay S., Wick G., Becker U., Timpl R. Preparation and use in immunohistology of antibodies specific for type I and type III collagen and procollagen. J Immunol Methods. 1976;12(1-2):117–124. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(76)90101-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollard T. D., Thomas S. M., Niederman R. Human platelet myosin. I. Purification by a rapid method applicable to other nonmuscle cells. Anal Biochem. 1974 Jul;60(1):258–266. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(74)90152-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quadracci L., Striker G. E. Growth and maintenance of glomerular cells in vitro. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1970 Dec;135(3):947–950. doi: 10.3181/00379727-135-35177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato T., Spiro R. G. Studies on the subunit composition of the renal glomerular basement membrane. J Biol Chem. 1976 Jul 10;251(13):4062–4070. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheinman J. I., Fish A. J., Brown D. M., Michael A. J. Human glomerular smooth muscle (mesangial) cells in culture. Lab Invest. 1976 Feb;34(2):150–158. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheinman J. I., Fish A. J., Kim Y., Michael A. F. C3b receptors on human glomeruli in vitro. Loss in culture. Am J Pathol. 1978 Jul;92(1):147–154. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheinman J. I., Fish A. J., Matas A. J., Michael A. F. The immunohistopathology of glomerular antigens. II. The glomerular basement membrane, actomyosin, and fibroblast surface antigens in normal, diseased, and transplanted human kidneys. Am J Pathol. 1978 Jan;90(1):71–88. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheinman J. I., Fish A. J., Michael A. F. The immunohistopathology of glomerular antigens. The glomerular basement membrane, collagen, and actomyosin antigens in normal and diseased kidneys. J Clin Invest. 1974 Nov;54(5):1144–1154. doi: 10.1172/JCI107858. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker F. The origin, turnover and removal of glomerular basement-membrane. J Pathol. 1973 Jul;110(3):233–244. doi: 10.1002/path.1711100306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward P. E., Schultz W., Reynolds R. C., Erdös E. G. Metabolism of kinins and angiotensins in the isolated glomerulus and brush border of rat kidney. Lab Invest. 1977 Jun;36(6):599–606. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wick G., Nowack H., Hahn E., Timpl R., Miller E. J. Visualization of type I and II collagens in tissue sections by immunohistologic techniques. J Immunol. 1976 Jul;117(1):298–303. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada K. M., Yamada S. S., Pastan I. Cell surface protein partially restores morphology, adhesiveness, and contact inhibition of movement to transformed fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Apr;73(4):1217–1221. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.4.1217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]