Abstract
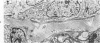
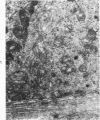
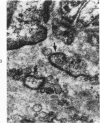
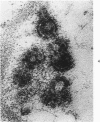
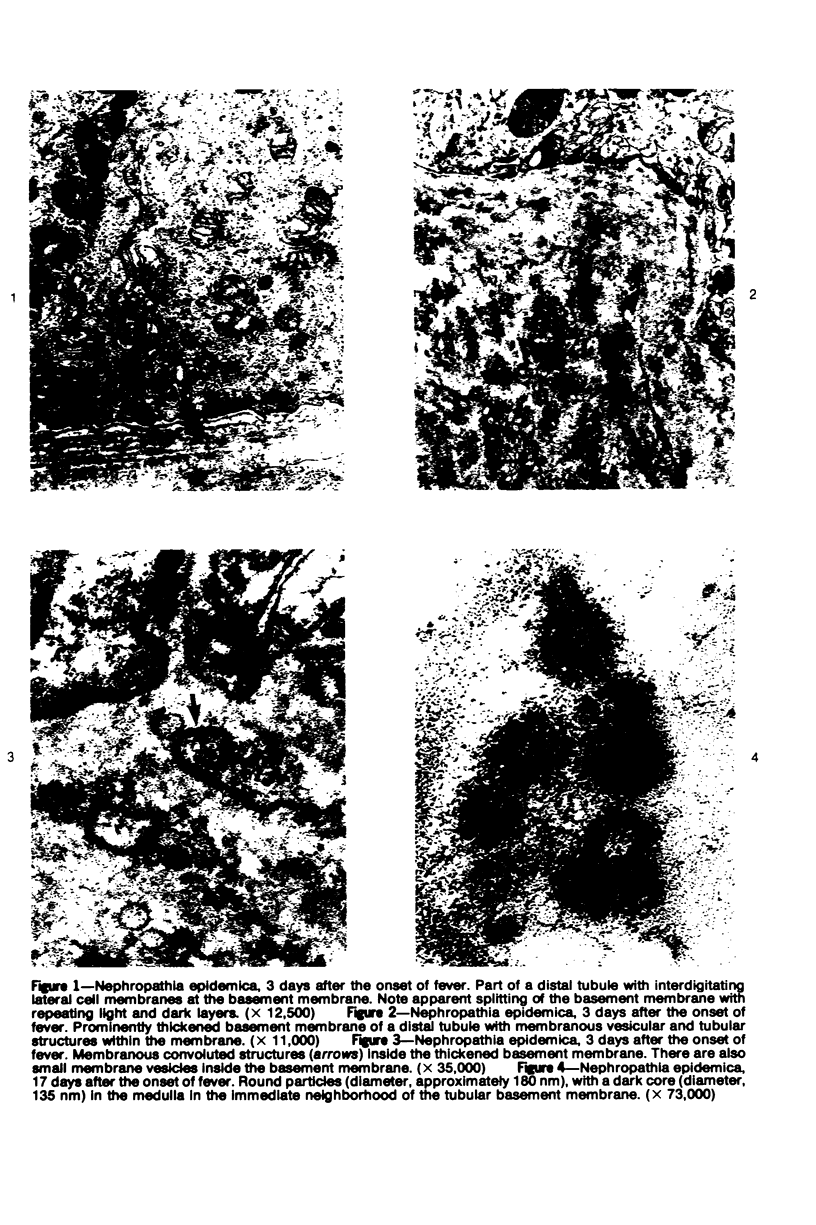
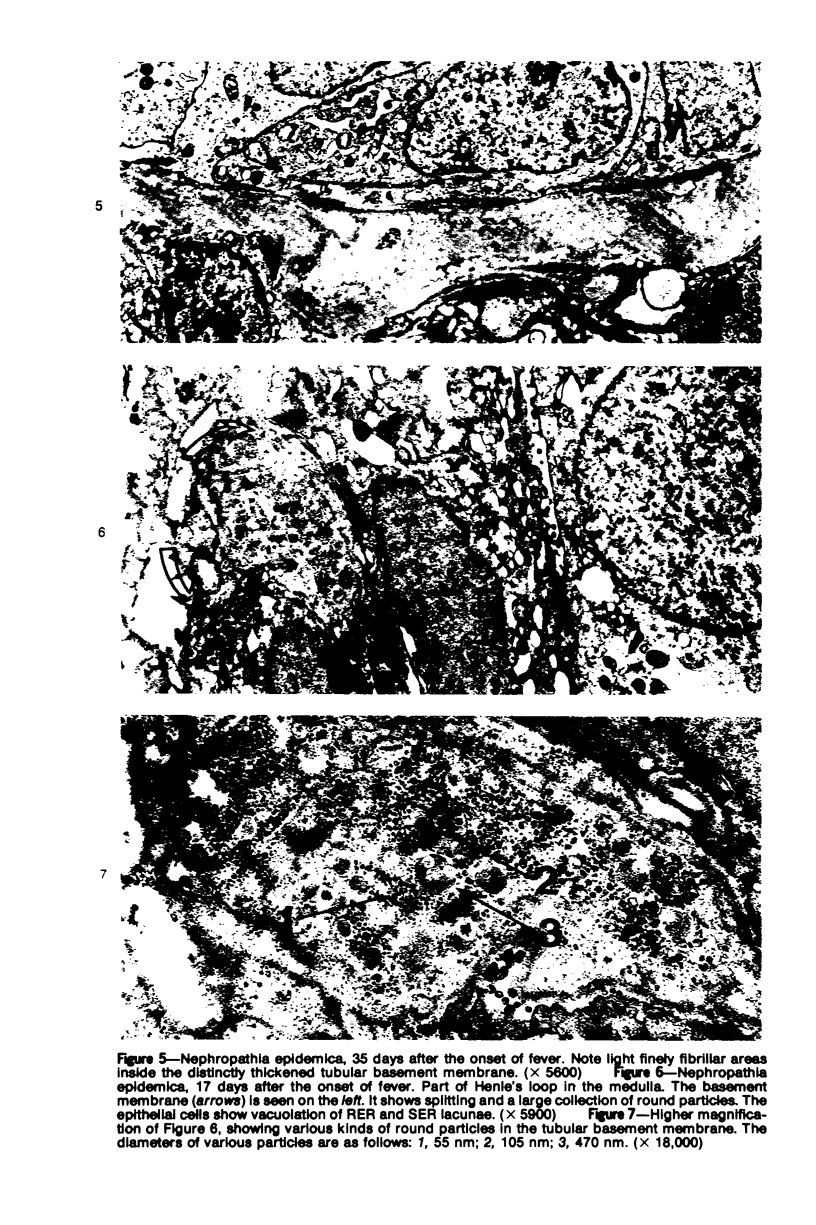
Tubular basement membranes in kidney biopsies from 18 patients with nephropathia epidemica were studied by electron microscopy. Both in the cortex and in the medulla there was splitting of the basement membrane. Thickened basement membrane around occasional tubules contained membrane vesicles, usually empty but also with a core and a diameter of approximately 180 nm. Membranous convoluted structures and light finely fibrillar areas in the basement membranes were seen. Splitting of the basement membrane was most prominent in the medulla, and the membrane was filled with round to oval particles 55 to 470 nm in diameter. Of the possible mechanisms of damage at the basement membrane level in this disease, the findings suggest liberation of antigen from the tubular cells and reaction of circulating antibodies with the antigen in the basement membrane.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bariety J., Callard P., Appay M. D., Grossetete J., Mandet C. Ultrastructural study of some frequent and poorly known intraglomerular structures. Adv Nephrol Necker Hosp. 1974;3:153–172. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bariety J., Callard P. Striated membranous structures in renal glomerular tufts. An electron microscopy study of 340 human renal biopsies. Lab Invest. 1975 May;32(5):636–641. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brentjens J. R., O'Connell D. W., Pawlowski I. B., Andres G. A. Extra-glomerular lesions associated with deposition of circulating antigen-antibody complexes in kidneys of rabbits with chronic serum sickness. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1974 Sep;3(1):112–126. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(74)90028-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brentjens J. R., Sepulveda M., Baliah T., Bentzel C., Erlanger B. F., Elwood C., Montes M., Hsu K. C., Andres G. A. Interstitial immune complex nephritis in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Kidney Int. 1975 May;7(5):342–350. doi: 10.1038/ki.1975.47. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Churg J., Grishman E. Ultrastructure of glomerular disease: a review. Kidney Int. 1975 Apr;7(4):254–261. doi: 10.1038/ki.1975.37. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Churg J., Grishman E. Ultrastructure of immune deposits in renal glomeruli. Ann Intern Med. 1972 Mar;76(3):479–486. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-76-3-479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collan Y., Lähdevirta J., Jokinen E. J. Electron Microscopy of Nephropathia Epidemica. Glomerular changes. Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histol. 1978 Feb 10;377(2):129–144. doi: 10.1007/BF00427001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GAJDUSEK D. C. Virus hemorrhagic fevers. Special reference to hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome (epidemic hemorrhagic fever). J Pediatr. 1962 Jun;60:841–857. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(62)80170-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jokinen E. J., Collan Y., Lähdevirta J. Renal immune complexes in epidemic nephropathy. Lancet. 1977 May 7;1(8019):1012–1013. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)92319-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jokinen E. J., Lähdevirta J., Collan Y. Nephropathia epidemica: immunohistochemical study of pathogenesis. Clin Nephrol. 1978 Jan;9(1):1–5. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klassen J., McCluskey R. T., Milgrom F. Nonglomerular renal disease produced in rabbits by immunization with homologous kidney. Am J Pathol. 1971 May;63(2):333–358. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laguens R., Segal A. Experimental autologous immune-complex nephritis: an electron microscope and immunohistochemical study. Exp Mol Pathol. 1969 Aug;11(1):89–98. doi: 10.1016/0014-4800(69)90073-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee H. W., Lee P. W., Johnson K. M. Isolation of the etiologic agent of Korean Hemorrhagic fever. J Infect Dis. 1978 Mar;137(3):298–308. doi: 10.1093/infdis/137.3.298. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lähdevirta J. Nephropathia epidemica in Finland. A clinical histological and epidemiological study. Ann Clin Res. 1971;3:1–54. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madrazo A. A., Churg J. Radiation nephritis. Chronic changes following moderate doses of radiation. Lab Invest. 1976 Mar;34(3):283–290. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagle R. B., Kohnen P. W., Bulger R. E., Striker G. E., Benditt E. P. Ultrastructure of human renal obsolescent glomeruli. Lab Invest. 1969 Dec;21(6):519–526. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nyström K. Incidence and prevalence of endemic benign (epidemic) nephropathy in AC county, Sweden, in relation to population density and prevalence of small rodents. Acta Med Scand Suppl. 1977;609:1–92. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugisaki T., Klassen J., Milgrom F., Andres G. A., McCluskey R. T. Immunopathologic study of an autoimmune tubular and interstitial renal disease in brown Norway rats. Lab Invest. 1973 Jun;28(6):658–671. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tisher C. C., Bulger R. E., Trump B. F. Human renal ultrastructure. 3. The distal tubule in healthy individuals. Lab Invest. 1968 Jun;18(6):655–668. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tisher C. C., Bulger R. E., Trump B. F. Human renal ultrastructure. I. Proximal tubule of healthy individuals. Lab Invest. 1966 Aug;15(8):1357–1394. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]