Abstract
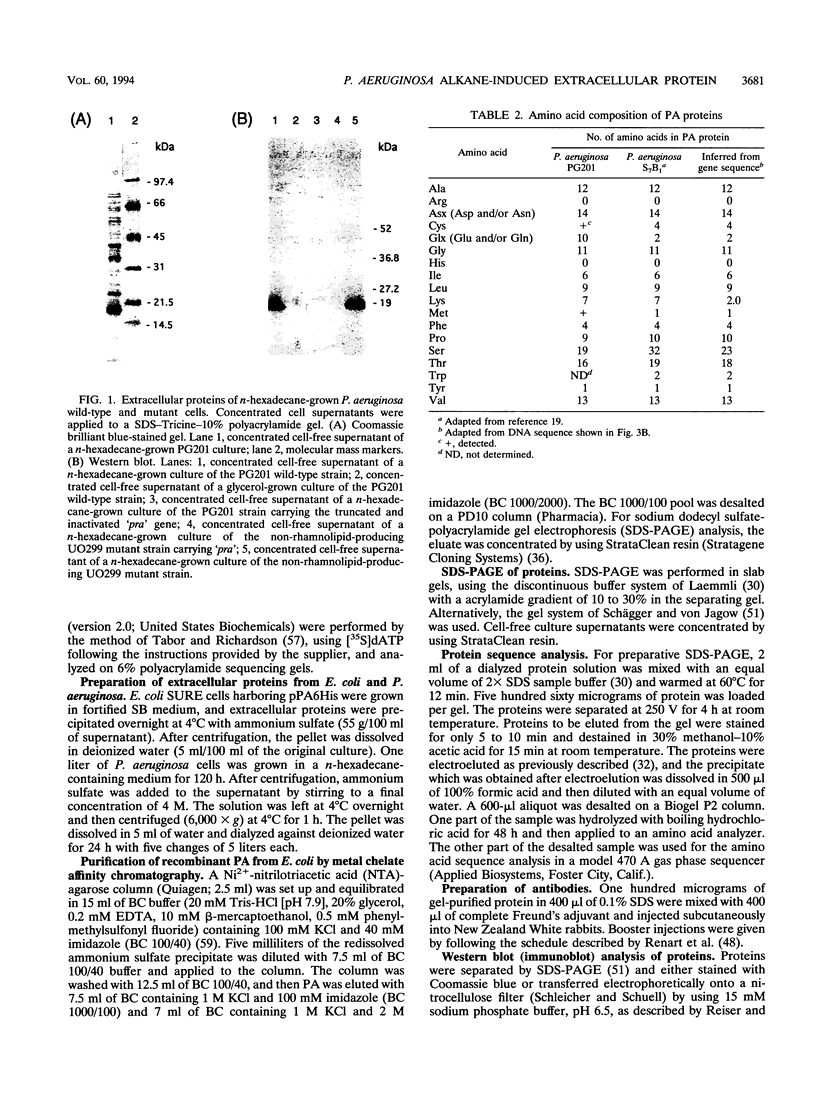
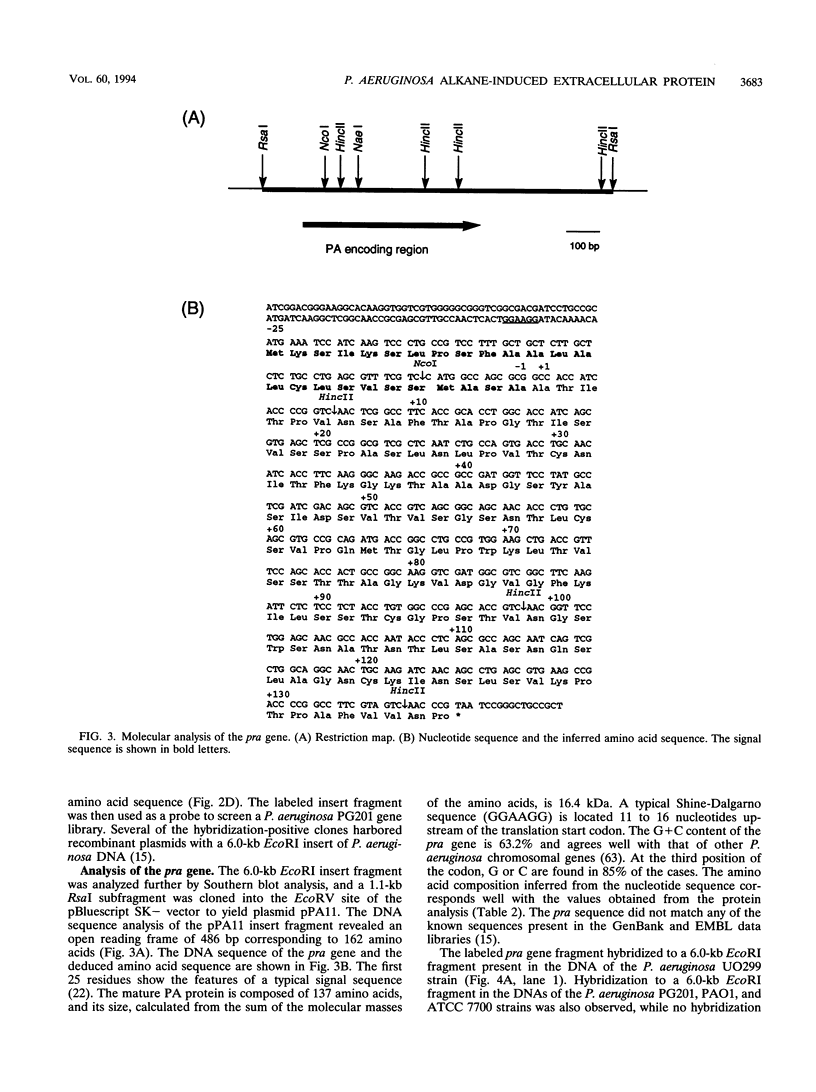
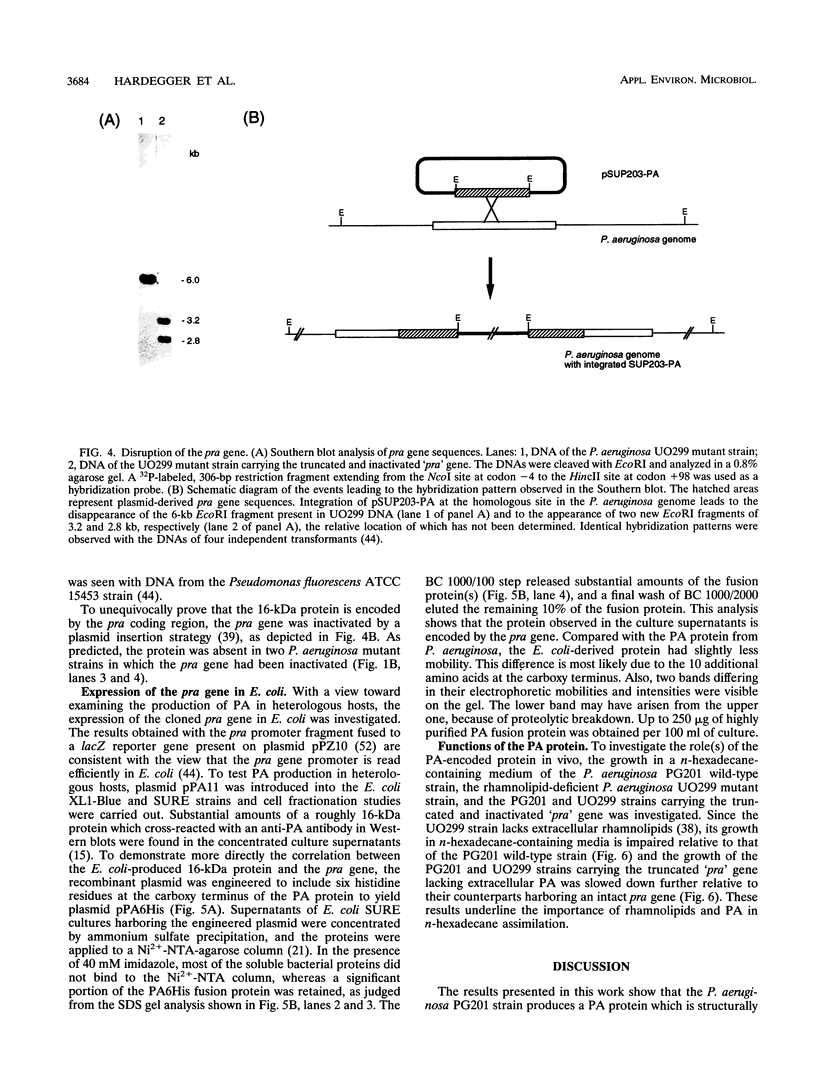
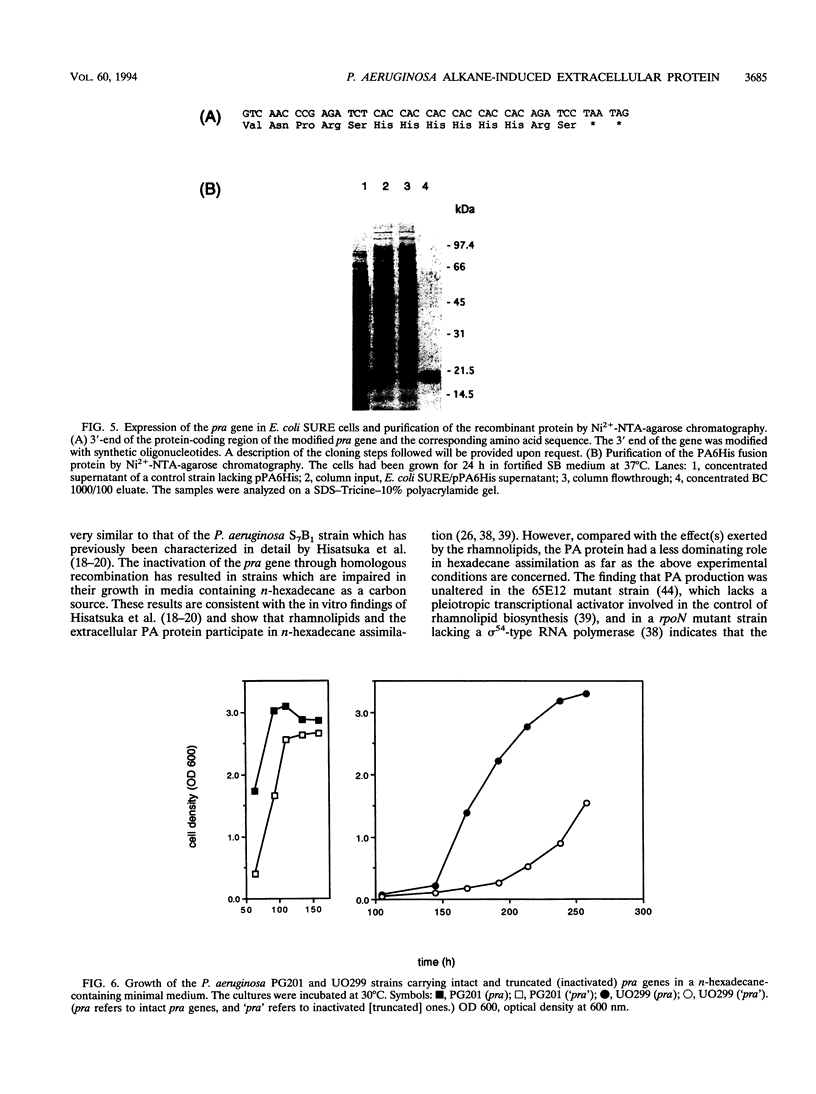
Pseudomonas aeruginosa PG201 produces a 16-kDa extracellular protein in media containing n-hexadecane as a carbon source but not in media containing glycerol or glucose. This protein was purified, and the N-terminal amino acid sequence was determined. The amino acid composition of the protein was found to be very similar to that of the so-called protein-like activator for n-alkane oxidation (PA) from P. aeruginosa S7B1. This extracellular protein was previously characterized (K. Hisatsuka, T. Nakahara, Y. Minoda, and K. Yamada, Agric. Biol. Chem. 41:445-450, 1977) and found to stimulate the growth of P. aeruginosa on n-hexadecane and to possess emulsifying activity. To study the role(s) of the PA protein and to make it accessible for possible future applications, we have cloned the PA-encoding (pra) gene and determined its nucleotide sequence. This analysis revealed a protein-coding region of 162 amino acids, with the first 25 residues being reminiscent of those of a typical bacterial signal sequence. The pra gene was inactivated by insertional mutagenesis, and the resulting strain was found to lack extracellular PA protein and to be retarded in its growth in n-hexadecane-containing media. These results are consistent with the growth stimulatory role of the PA protein. The pra gene was expressed in Escherichia coli, and substantial amounts of the recombinant protein were found in the extracellular growth medium. The recombinant protein was purified by metal chelate affinity chromatography. The ability to produce secreted PA protein by E. coli provides a simple and safe means to analyze its function(s) in alkane assimilation in the future.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BURGER M. M., GLASER L., BURTON R. M. THE ENZYMATIC SYNTHESIS OF A RHAMNOSE-CONTAINING GLYCOLIPID BY EXTRACTS OF PSEUDOMONAS AERUGINOSA. J Biol Chem. 1963 Aug;238:2595–2602. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyer H. W., Roulland-Dussoix D. A complementation analysis of the restriction and modification of DNA in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1969 May 14;41(3):459–472. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90288-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung C. T., Miller R. H. A rapid and convenient method for the preparation and storage of competent bacterial cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Apr 25;16(8):3580–3580. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.8.3580. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ditta G., Stanfield S., Corbin D., Helinski D. R. Broad host range DNA cloning system for gram-negative bacteria: construction of a gene bank of Rhizobium meliloti. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7347–7351. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dower W. J., Miller J. F., Ragsdale C. W. High efficiency transformation of E. coli by high voltage electroporation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jul 11;16(13):6127–6145. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.13.6127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. "A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity". Addendum. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):266–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiechter A. Biosurfactants: moving towards industrial application. Trends Biotechnol. 1992 Jun;10(6):208–217. doi: 10.1016/0167-7799(92)90215-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Georgiou G., Lin S. C., Sharma M. M. Surface-active compounds from microorganisms. Biotechnology (N Y) 1992 Jan;10(1):60–65. doi: 10.1038/nbt0192-60. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerra-Santos L., Käppeli O., Fiechter A. Pseudomonas aeruginosa biosurfactant production in continuous culture with glucose as carbon source. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Aug;48(2):301–305. doi: 10.1128/aem.48.2.301-305.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harvey S., Elashvili I., Valdes J. J., Kamely D., Chakrabarty A. M. Enhanced removal of Exxon Valdez spilled oil from Alaskan gravel by a microbial surfactant. Biotechnology (N Y) 1990 Mar;8(3):228–230. doi: 10.1038/nbt0390-228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkes R., Niday E., Gordon J. A dot-immunobinding assay for monoclonal and other antibodies. Anal Biochem. 1982 Jan 1;119(1):142–147. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90677-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holloway B. W. Genetics of Pseudomonas. Bacteriol Rev. 1969 Sep;33(3):419–443. doi: 10.1128/br.33.3.419-443.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jung V., Pestka S. B., Pestka S. Efficient cloning of PCR generated DNA containing terminal restriction endonuclease recognition sites. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Oct 25;18(20):6156–6156. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.20.6156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch A. K., Käppeli O., Fiechter A., Reiser J. Hydrocarbon assimilation and biosurfactant production in Pseudomonas aeruginosa mutants. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jul;173(13):4212–4219. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.13.4212-4219.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koronelli T. V., Komarova T. I., Denisov Iu V. Khimicheskii sostav i rol' peptidoglikolipida Pseudomonas aeruginosa v protsesse usvoeniia uglevodorodov. Mikrobiologiia. 1983 Sep-Oct;52(5):767–770. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koronelli T. V., Komarova T. I., Ignatchenko A. V. Rol' émul'girovaniia v protsesse pogloshcheniia uglevodorodov kletkami Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Mikrobiologiia. 1983 Jan-Feb;52(1):94–97. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacElwee C. G., Lee H., Trevors J. T. Production of extracellular emulsifying agent by Pseudomonas aeruginosa UG1. J Ind Microbiol. 1990 Jan;5(1):25–31. doi: 10.1007/BF01569603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ochsner U. A., Fiechter A., Reiser J. Isolation, characterization, and expression in Escherichia coli of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa rhlAB genes encoding a rhamnosyltransferase involved in rhamnolipid biosurfactant synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1994 Aug 5;269(31):19787–19795. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ochsner U. A., Koch A. K., Fiechter A., Reiser J. Isolation and characterization of a regulatory gene affecting rhamnolipid biosurfactant synthesis in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1994 Apr;176(7):2044–2054. doi: 10.1128/jb.176.7.2044-2054.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Power B. E., Ivancic N., Harley V. R., Webster R. G., Kortt A. A., Irving R. A., Hudson P. J. High-level temperature-induced synthesis of an antibody VH-domain in Escherichia coli using the PelB secretion signal. Gene. 1992 Apr 1;113(1):95–99. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(92)90674-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugsley A. P. The complete general secretory pathway in gram-negative bacteria. Microbiol Rev. 1993 Mar;57(1):50–108. doi: 10.1128/mr.57.1.50-108.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiser J., Stark G. R. Immunologic detection of specific proteins in cell extracts by fractionation in gels and transfer to paper. Methods Enzymol. 1983;96:205–215. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)96018-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renart J., Reiser J., Stark G. R. Transfer of proteins from gels to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper and detection with antisera: a method for studying antibody specificity and antigen structure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jul;76(7):3116–3120. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.7.3116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schweizer H. P. Improved broad-host-range lac-based plasmid vectors for the isolation and characterization of protein fusions in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Gene. 1991 Jul 15;103(1):87–92. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(91)90396-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schägger H., von Jagow G. Tricine-sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis for the separation of proteins in the range from 1 to 100 kDa. Anal Biochem. 1987 Nov 1;166(2):368–379. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(87)90587-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Short J. M., Fernandez J. M., Sorge J. A., Huse W. D. Lambda ZAP: a bacteriophage lambda expression vector with in vivo excision properties. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Aug 11;16(15):7583–7600. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.15.7583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor S., Richardson C. C. DNA sequence analysis with a modified bacteriophage T7 DNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(14):4767–4771. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.14.4767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Dyke M. W., Sirito M., Sawadogo M. Single-step purification of bacterially expressed polypeptides containing an oligo-histidine domain. Gene. 1992 Feb 1;111(1):99–104. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(92)90608-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter M. V., Porteous A., Seidler R. J. Measuring genetic stability in bacteria of potential use in genetic engineering. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Jan;53(1):105–109. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.1.105-109.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West S. E., Iglewski B. H. Codon usage in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Oct 11;16(19):9323–9335. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.19.9323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]






