Full text
PDF
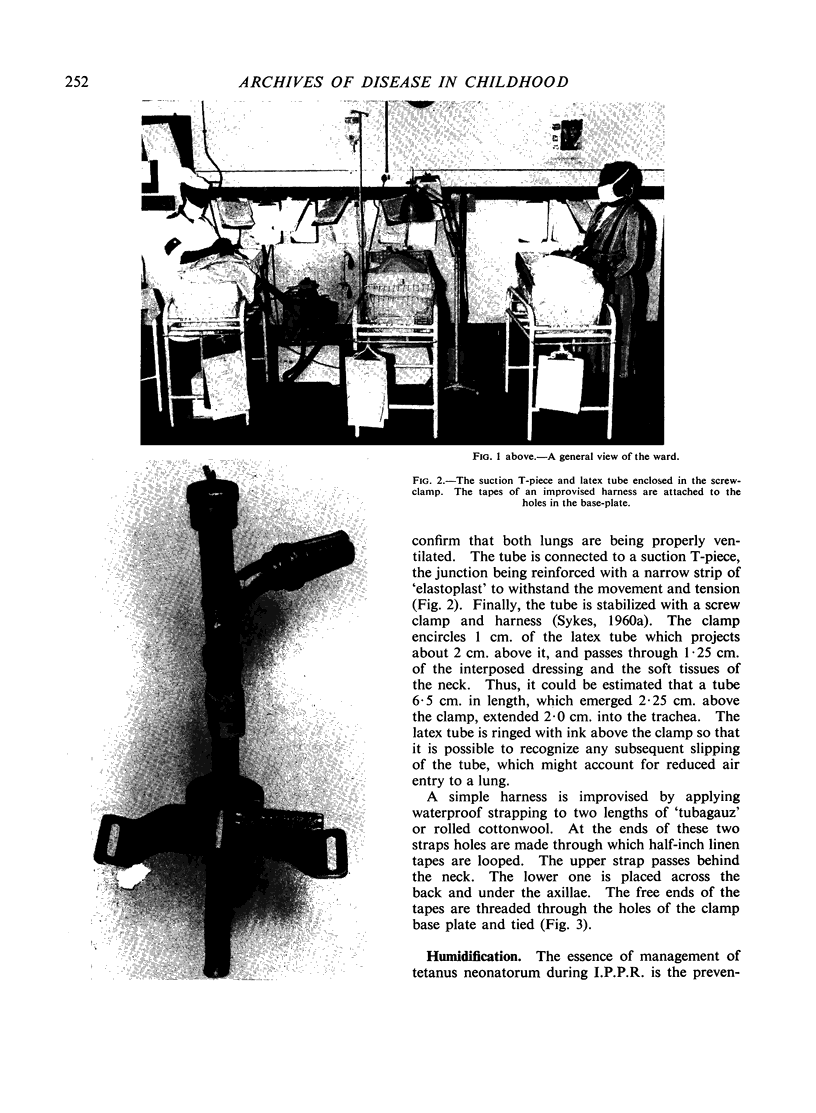







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ASTRUP P., GØTZCHE H., NEUKIRCH F. Laboratory investigations during treatment of patients with poliomyelitis and respiratory paralysis. Br Med J. 1954 Apr 3;1(4865):780–786. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.4865.780. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CAMPBELL E. J. Simplification of Haldane's apparatus for measuring carbon dioxide concentration in respired gases in clinical practice. Br Med J. 1960 Feb 13;1(5171):457–458. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5171.457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drury D. R., Henry J. P., Goodman J. THE EFFECTS OF CONTINUOUS PRESSURE BREATHING ON KIDNEY FUNCTION. J Clin Invest. 1947 Sep;26(5):945–951. doi: 10.1172/JCI101889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAY P. Pneumothorax complicating intermittent positive-pressure respiration. Lancet. 1954 Dec 4;267(6849):1156–1157. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(54)91990-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAWES W. E., HARRIES J. R. Intermittent positive-pressure respiration; an unusual complication in an infant. Lancet. 1956 May 26;270(6926):783–785. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(56)91247-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOVE A. H., RODDIE R. A., ROSENSWEIG J., SHANKS R. G. The effect of pressure changes in the respired air on the renal excretion of water and electrolytes. Clin Sci. 1957 May;16(2):281–296. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMYTHE P. M., BULL A. Treatment of tetanus neonatorum with intermittent positive-pressure respiration. Br Med J. 1959 Aug 1;2(5143):107–113. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5143.107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SYKES M. K. Intermittent positive pressure respiration in tetanus neonatorum. Anaesthesia. 1960 Oct;15:401–410. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2044.1960.tb13357.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WRIGHT R., SYKES M. K., JACKSON B. G., MANN N. M., ADAMS E. B. Intermittent positive-pressure respiration in tetanus neonatorum. Lancet. 1961 Sep 23;2(7204):678–680. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(61)92831-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]