Abstract
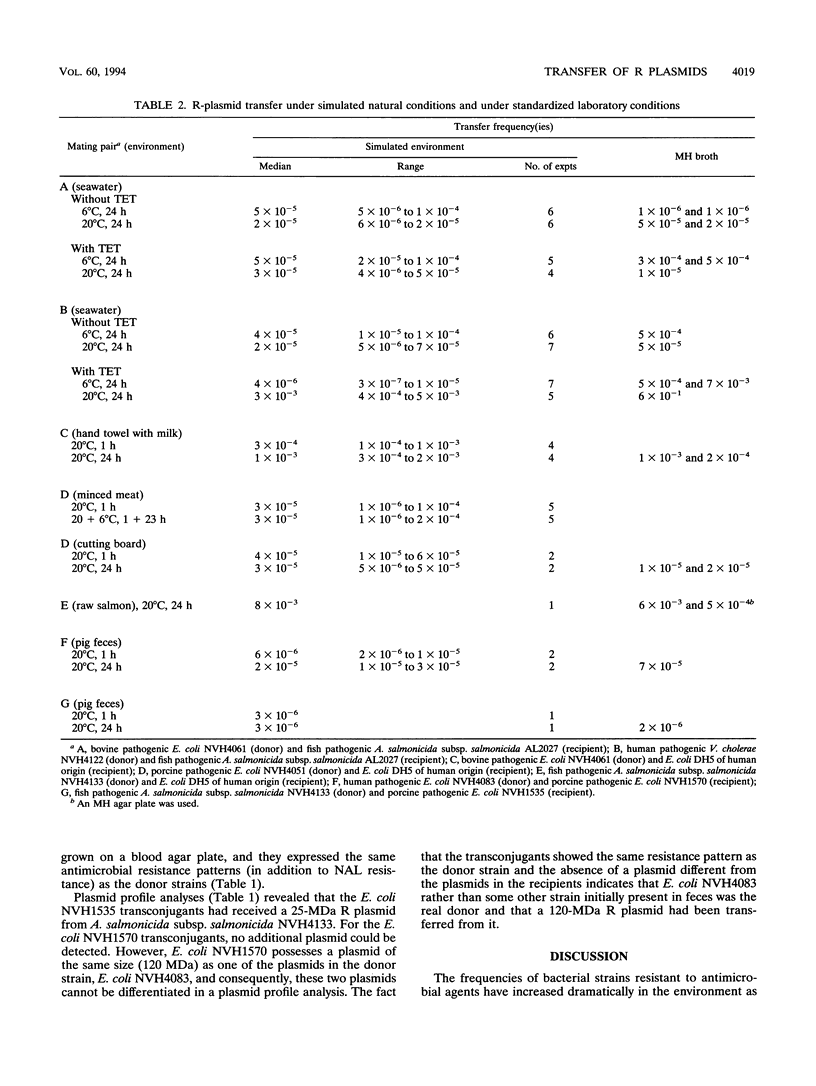
Plasmids harboring multiple antimicrobial-resistance determinants (R plasmids) were transferred in simulated natural microenvironments from various bacterial pathogens of human, animal, or fish origin to susceptible strains isolated from a different ecological niche. R plasmids in a strain of the human pathogen Vibrio cholerae O1 E1 Tor and a bovine Escherichia coli strain were conjugated to a susceptible strain of the fish pathogenic bacterium Aeromonas salmonicida subsp. salmonicida in marine water. Conjugations of R plasmids between a resistant bovine pathogenic E. coli strain and a susceptible E. coli strain of human origin were performed on a hand towel contaminated with milk from a cow with mastitis. A similar conjugation event between a resistant porcine pathogenic E. coli strain of human origin was studied in minced meat on a cutting board. Conjugation of R plasmids between a resistant strain of the fish pathogenic bacterium A. salmonicida subsp. salmonicida and a susceptible E. coli strain of human origin was performed in raw salmon on a cutting board. R plasmids in a strain of A. salmonicida subsp. salmonicida and a human pathogenic E. coli strain were conjugated to a susceptible porcine E. coli strain in porcine feces. Transfer of the different R plasmids was confirmed by plasmid profile analyses and determination of the resistance pattern of the transconjugants. The different R plasmids were transferred equally well under simulated natural conditions and under controlled laboratory conditions, with median conjugation frequencies ranging from 3 x 10(-6) to 8 x 10(-3). The present study demonstrates that conjugation and transfer of R plasmids is a phenomenon that belongs to the environment and can occur between bacterial strains of human, animal, and fish origins that are unrelated either evolutionarily or ecologically even in the absence of antibiotics. Consequently, the contamination of the environment with bacterial pathogens resistant to antimicrobial agents is a real threat not only as a source of disease but also as a source from which R plasmids can easily spread to other pathogens of diverse origins.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson J. D. Factors that may prevent transfer of anti-biotic resistance between gram-negative bacteria in the gut. J Med Microbiol. 1975 Feb;8(1):83–88. doi: 10.1099/00222615-8-1-83. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson J. D., Gillespie W. A., Richmond M. H. Chemotherapy and antibiotic-resistance transfer between Enterobacteria in the human gastro-intestinal tract. J Med Microbiol. 1973 Nov;6(4):461–473. doi: 10.1099/00222615-6-4-461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bale M. J., Day M. J., Fry J. C. Novel method for studying plasmid transfer in undisturbed river epilithon. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Nov;54(11):2756–2758. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.11.2756-2758.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baya A. M., Brayton P. R., Brown V. L., Grimes D. J., Russek-Cohen E., Colwell R. R. Coincident plasmids and antimicrobial resistance in marine bacteria isolated from polluted and unpolluted Atlantic Ocean samples. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Jun;51(6):1285–1292. doi: 10.1128/aem.51.6.1285-1292.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Datta N. Drug resistance and R factors in the bowel bacteria of London patients before and after admission to hospital. Br Med J. 1969 May 17;2(5654):407–411. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5654.407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez-Astorga A., Muela A., Cisterna R., Iriberri J., Barcina I. Biotic and abiotic factors affecting plasmid transfer in Escherichia coli strains. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992 Jan;58(1):392–398. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.1.392-398.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fontaine T. D., 3rd, Hoadley A. W. Transferable drug resistance associated with coliforms isolated from hospital and domestic sewage. Health Lab Sci. 1976 Oct;13(4):238–245. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frost L. S. Bacterial conjugation: everybody's doin' it. Can J Microbiol. 1992 Nov;38(11):1091–1096. doi: 10.1139/m92-179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gealt M. A., Chai M. D., Alpert K. B., Boyer J. C. Transfer of plasmids pBR322 and pBR325 in wastewater from laboratory strains of Escherichia coli to bacteria indigenous to the waste disposal system. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Apr;49(4):836–841. doi: 10.1128/aem.49.4.836-841.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman A. E., Hild E., Marshall K. C., Hermansson M. Conjugative Plasmid Transfer between Bacteria under Simulated Marine Oligotrophic Conditions. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1993 Apr;59(4):1035–1040. doi: 10.1128/aem.59.4.1035-1040.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grabow W. O., Prozesky O. W. Drug resistance of coliform bacteria in hospital and city sewage. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1973 Feb;3(2):175–180. doi: 10.1128/aac.3.2.175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D. Studies on transformation of Escherichia coli with plasmids. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 5;166(4):557–580. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80284-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jørgensen S. T. Relatedness of chloramphenicol resistance plasmids in epidemiologically unrelated strains of pathogenic Escherichia coli from man and animals. J Med Microbiol. 1983 May;16(2):165–173. doi: 10.1099/00222615-16-2-165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruse H., Kariuki S., Søli N., Olsvik O. Multiresistant Shigella species from African AIDS patients: antibacterial resistance patterns and application of the E-test for determination of minimum inhibitory concentration. Scand J Infect Dis. 1992;24(6):733–739. doi: 10.3109/00365549209062458. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy S. B., FitzGerald G. B., Macone A. B. Spread of antibiotic-resistant plasmids from chicken to chicken and from chicken to man. Nature. 1976 Mar 4;260(5546):40–42. doi: 10.1038/260040a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linton A. H. Flow of resistance genes in the environment and from animals to man. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1986 Oct;18 (Suppl 100):189–197. doi: 10.1093/jac/18.supplement_c.189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linton A. H., Timoney J. F., Hinton M. The ecology of chloramphenicol-resistance in Salmonella typhimurium and Escherichia coli in calves with endemic salmonella infection. J Appl Bacteriol. 1981 Feb;50(1):115–129. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1981.tb00876.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mach P. A., Grimes D. J. R-plasmid transfer in a wastewater treatment plant. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Dec;44(6):1395–1403. doi: 10.1128/aem.44.6.1395-1403.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maher D., Taylor D. E. Host range and transfer efficiency of incompatibility group HI plasmids. Can J Microbiol. 1993 Jun;39(6):581–587. doi: 10.1139/m93-084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazodier P., Davies J. Gene transfer between distantly related bacteria. Annu Rev Genet. 1991;25:147–171. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.25.120191.001051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McPherson P., Gealt M. A. Isolation of indigenous wastewater bacterial strains capable of mobilizing plasmid pBR325. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 May;51(5):904–909. doi: 10.1128/aem.51.5.904-909.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mee B. J., Nikoletti S. M. Plasmids encoding trimethoprim resistance in bacterial isolates from man and pigs. J Appl Bacteriol. 1983 Apr;54(2):225–235. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1983.tb02611.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Morchoe S. B., Ogunseitan O., Sayler G. S., Miller R. V. Conjugal transfer of R68.45 and FP5 between Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains in a freshwater environment. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Aug;54(8):1923–1929. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.8.1923-1929.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul J. H., Frischer M. E., Thurmond J. M. Gene transfer in marine water column and sediment microcosms by natural plasmid transformation. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 May;57(5):1509–1515. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.5.1509-1515.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Showsh S. A., Andrews R. E., Jr Tetracycline enhances Tn916-mediated conjugal transfer. Plasmid. 1992 Nov;28(3):213–224. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(92)90053-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. W. Incidence of river water of Escherichia coli containing R factors. Nature. 1970 Dec 26;228(5278):1286–1288. doi: 10.1038/2281286a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. W. Transfer of antibiotic resistance from animal and human strains of Escherichia coli to resident E. coli in the alimentary tract of man. Lancet. 1969 Jun 14;1(7607):1174–1176. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(69)92164-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talbot H. W., Jr, Yamamoto D. K., Smith M. W., Seidler R. J. Antibiotic resistance and its transfer among clinical and nonclinical Klebsiella strains in botanical environments. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Jan;39(1):97–104. doi: 10.1128/aem.39.1.97-104.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toranzo A. E., Combarro P., Lemos M. L., Barja J. L. Plasmid coding for transferable drug resistance in bacteria isolated from cultured rainbow trout. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Oct;48(4):872–877. doi: 10.1128/aem.48.4.872-877.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WATANABE T. Infective heredity of multiple drug resistance in bacteria. Bacteriol Rev. 1963 Mar;27:87–115. doi: 10.1128/br.27.1.87-115.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young H. K. Antimicrobial resistance spread in aquatic environments. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1993 May;31(5):627–635. doi: 10.1093/jac/31.5.627. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



