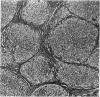
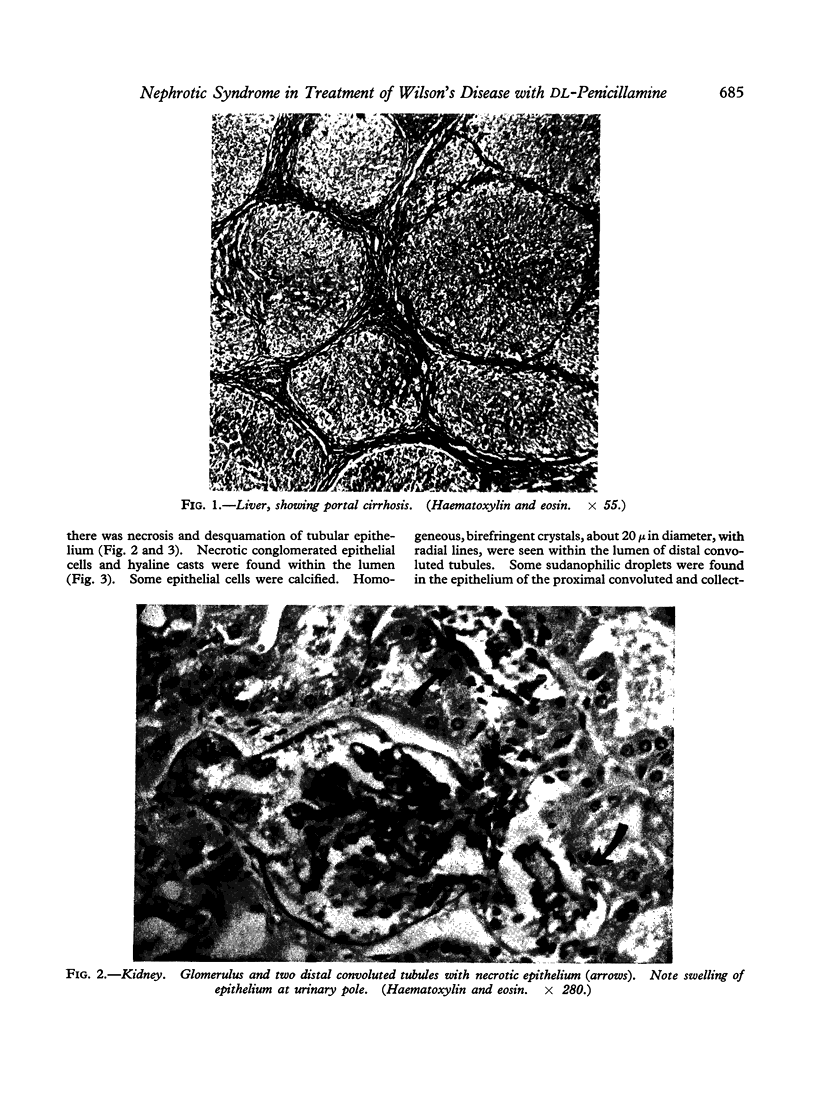
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ADAMS D. A., GOLDMAN R., MAXWELL M. H., LATTA H. NEPHROTIC SYNDROME ASSOCIATED WITH PENICILLAMINE THERAPY OF WILSON'S DISEASE. Am J Med. 1964 Feb;36:330–336. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(64)90096-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GILSANZ V., BARRERA A., ANAYA A. The renal biopsy in Wilson's disease. Arch Intern Med. 1960 May;105:758–761. doi: 10.1001/archinte.1960.00270170096012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KARK R. M. Some aspects of nutrition and the kidney. Am J Med. 1958 Nov;25(5):698–707. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(58)90007-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PLAYOUST M. R., DALE N. E. Metabolic balance studies in a patient with Wilson's disease and hypercalcuria. Metabolism. 1961 Apr;10:304–314. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STERNLIEB I., SCHEINBERG I. H. PENICILLAMINE THERAPY FOR HEPATOLENTICULAR DEGENERATION. JAMA. 1964 Sep 7;189:748–754. doi: 10.1001/jama.1964.03070100042008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel F. S. Nephrotoxic Properties of Copper under Experimental Conditions in Mice: With Special Reference to the Pathogenesis of the Renal Alterations in Wilson's Disease. Am J Pathol. 1960 Jun;36(6):699–711. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WALSHE J. M. Wilson's disease; new oral therapy. Lancet. 1956 Jan 7;270(6906):25–26. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(56)91859-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOLFF S. M. Copper deposition in the rat. Arch Pathol. 1960 Feb;69:217–223. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]