Abstract
Flow cytometry, combined with fluorescently labelled monoclonal antibodies, offers advantages of speed and sensitivity for the detection of specific pathogenic bacteria in foods. We investigated the detection of Salmonella typhimurium in eggs and milk. Using a sample clearing procedure, we determined that the detection limit was on the order of 10(3) cells per ml after a total analysis time of 40 min. After 6 h of nonselective enrichment, the detection limits were 10 cells per ml for milk and 1 cell per ml for eggs, even in the presence of a 10,000-fold excess of Escherichia coli cells.
Full text
PDF
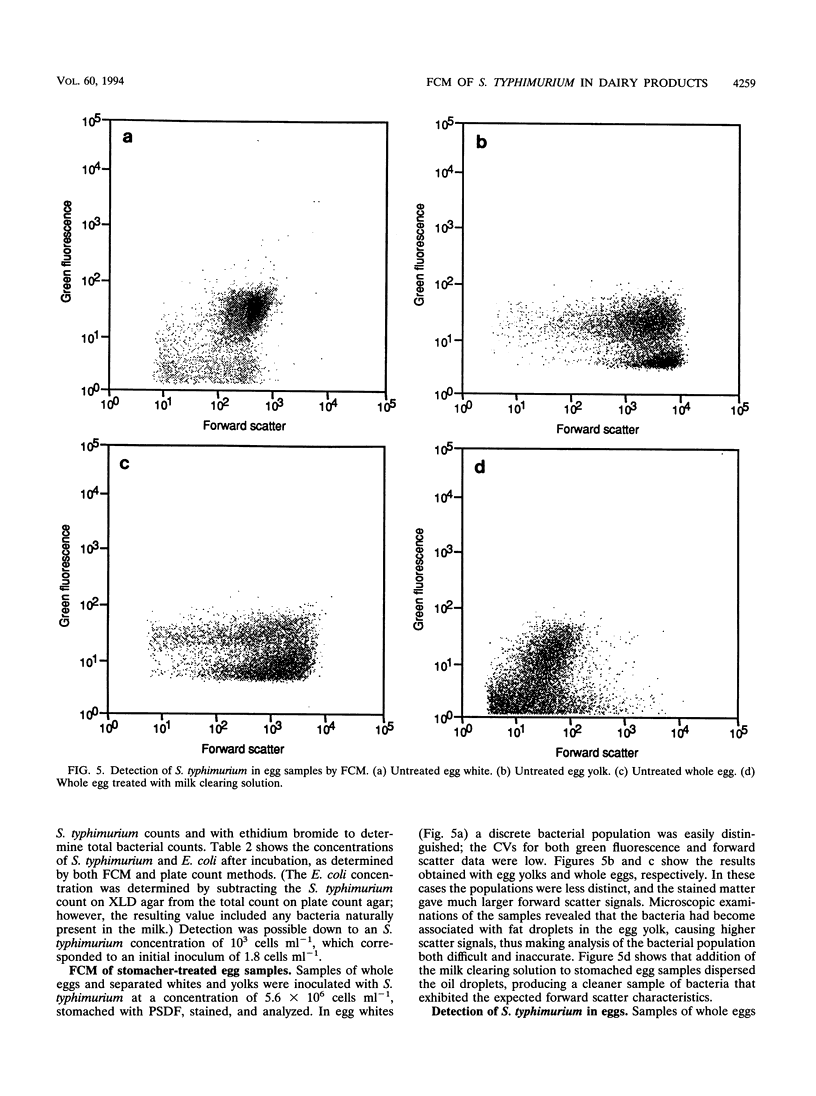
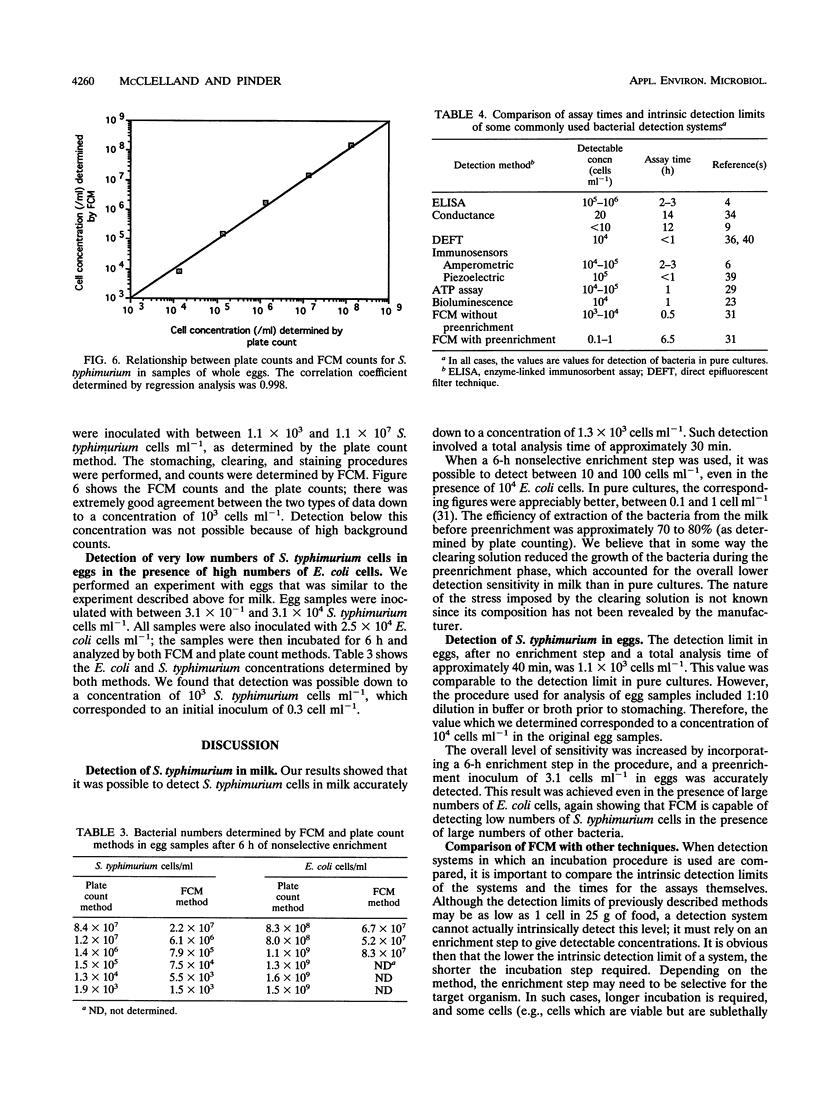


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allman R., Hann A. C., Manchee R., Lloyd D. Characterization of bacteria by multiparameter flow cytometry. J Appl Bacteriol. 1992 Nov;73(5):438–444. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1992.tb05001.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amann R. I., Binder B. J., Olson R. J., Chisholm S. W., Devereux R., Stahl D. A. Combination of 16S rRNA-targeted oligonucleotide probes with flow cytometry for analyzing mixed microbial populations. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Jun;56(6):1919–1925. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.6.1919-1925.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baird-Parker A. C. Foodborne salmonellosis. Lancet. 1990 Nov 17;336(8725):1231–1235. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)92844-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackburn C. W. Rapid and alternative methods for the detection of salmonellas in foods. J Appl Bacteriol. 1993 Sep;75(3):199–214. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1993.tb02767.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks J. L., Mirhabibollahi B., Kroll R. G. Experimental enzyme-linked amperometric immunosensors for the detection of salmonellas in foods. J Appl Bacteriol. 1992 Sep;73(3):189–196. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1992.tb02977.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Aoust J. Y., Sewell A. M., Warburton D. W. A comparison of standard cultural methods for the detection of foodborne Salmonella. Int J Food Microbiol. 1992 May;16(1):41–50. doi: 10.1016/0168-1605(92)90124-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diaper J. P., Tither K., Edwards C. Rapid assessment of bacterial viability by flow cytometry. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 1992 Nov;38(2):268–272. doi: 10.1007/BF00174481. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donnelly C. W., Baigent G. J. Method for flow cytometric detection of Listeria monocytogenes in milk. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Oct;52(4):689–695. doi: 10.1128/aem.52.4.689-695.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gast R. K., Beard C. W. Research to understand and control Salmonella enteritidis in chickens and eggs. Poult Sci. 1993 Jun;72(6):1157–1163. doi: 10.3382/ps.0721157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphrey T. J., Whitehead A., Gawler A. H., Henley A., Rowe B. Numbers of Salmonella enteritidis in the contents of naturally contaminated hens' eggs. Epidemiol Infect. 1991 Jun;106(3):489–496. doi: 10.1017/s0950268800067546. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kell D. B., Ryder H. M., Kaprelyants A. S., Westerhoff H. V. Quantifying heterogeneity: flow cytometry of bacterial cultures. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1991 Oct-Nov;60(3-4):145–158. doi: 10.1007/BF00430362. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kodikara C. P., Crew H. H., Stewart G. S. Near on-line detection of enteric bacteria using lux recombinant bacteriophage. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1991 Oct 15;67(3):261–265. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(91)90486-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee H. A., Wyatt G. M., Bramham S., Morgan M. R. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for Salmonella typhimurium in food: feasibility of 1-day Salmonella detection. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Jun;56(6):1541–1546. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.6.1541-1546.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maguire H., Cowden J., Jacob M., Rowe B., Roberts D., Bruce J., Mitchell E. An outbreak of Salmonella dublin infection in England and Wales associated with a soft unpasteurized cows' milk cheese. Epidemiol Infect. 1992 Dec;109(3):389–396. doi: 10.1017/s0950268800050378. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClelland R. G., Pinder A. C. Detection of low levels of specific Salmonella species by fluorescent antibodies and flow cytometry. J Appl Bacteriol. 1994 Oct;77(4):440–447. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1994.tb03447.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morton N. Despite intensive efforts, egg-related salmonellosis outbreaks continue. S D J Med. 1993 Jun;46(6):189–191. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettipher G. L., Rodrigues U. M. Rapid enumeration of microorganisms in foods by the direct epifluorescent filter technique. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Oct;44(4):809–813. doi: 10.1128/aem.44.4.809-813.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinder A. C., Purdy P. W., Poulter S. A., Clark D. C. Validation of flow cytometry for rapid enumeration of bacterial concentrations in pure cultures. J Appl Bacteriol. 1990 Jul;69(1):92–100. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1990.tb02916.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prusak-Sochaczewski E., Luong J. H., Guilbault G. G. Development of a piezoelectric immunosensor for the detection of Salmonella typhimurium. Enzyme Microb Technol. 1990 Mar;12(3):173–177. doi: 10.1016/0141-0229(90)90034-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. J., Boardman A., Shutt P. C. Detection of salmonellas in animal feeds by electrical conductance. J Appl Bacteriol. 1989 Dec;67(6):575–588. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1989.tb02530.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St Louis M. E., Morse D. L., Potter M. E., DeMelfi T. M., Guzewich J. J., Tauxe R. V., Blake P. A. The emergence of grade A eggs as a major source of Salmonella enteritidis infections. New implications for the control of salmonellosis. JAMA. 1988 Apr 8;259(14):2103–2107. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsen H. Y., Wang S. J., Roe B. A., Green S. S. DNA sequence of a Salmonella-specific DNA fragment and the use of oligonucleotide probes for Salmonella detection. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 1991 Jun;35(3):339–347. doi: 10.1007/BF00172723. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallner G., Amann R., Beisker W. Optimizing fluorescent in situ hybridization with rRNA-targeted oligonucleotide probes for flow cytometric identification of microorganisms. Cytometry. 1993;14(2):136–143. doi: 10.1002/cyto.990140205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Way J. S., Josephson K. L., Pillai S. D., Abbaszadegan M., Gerba C. P., Pepper I. L. Specific detection of Salmonella spp. by multiplex polymerase chain reaction. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1993 May;59(5):1473–1479. doi: 10.1128/aem.59.5.1473-1479.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wegmüller B., Lüthy J., Candrian U. Direct polymerase chain reaction detection of Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli in raw milk and dairy products. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1993 Jul;59(7):2161–2165. doi: 10.1128/aem.59.7.2161-2165.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyatt G. M., Langley M. N., Lee H. A., Morgan M. R. Further studies on the feasibility of one-day Salmonella detection by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1993 May;59(5):1383–1390. doi: 10.1128/aem.59.5.1383-1390.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el-Gazzar F. E., Marth E. H. Salmonellae, salmonellosis, and dairy foods: a review. J Dairy Sci. 1992 Sep;75(9):2327–2343. doi: 10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(92)77993-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]