Abstract
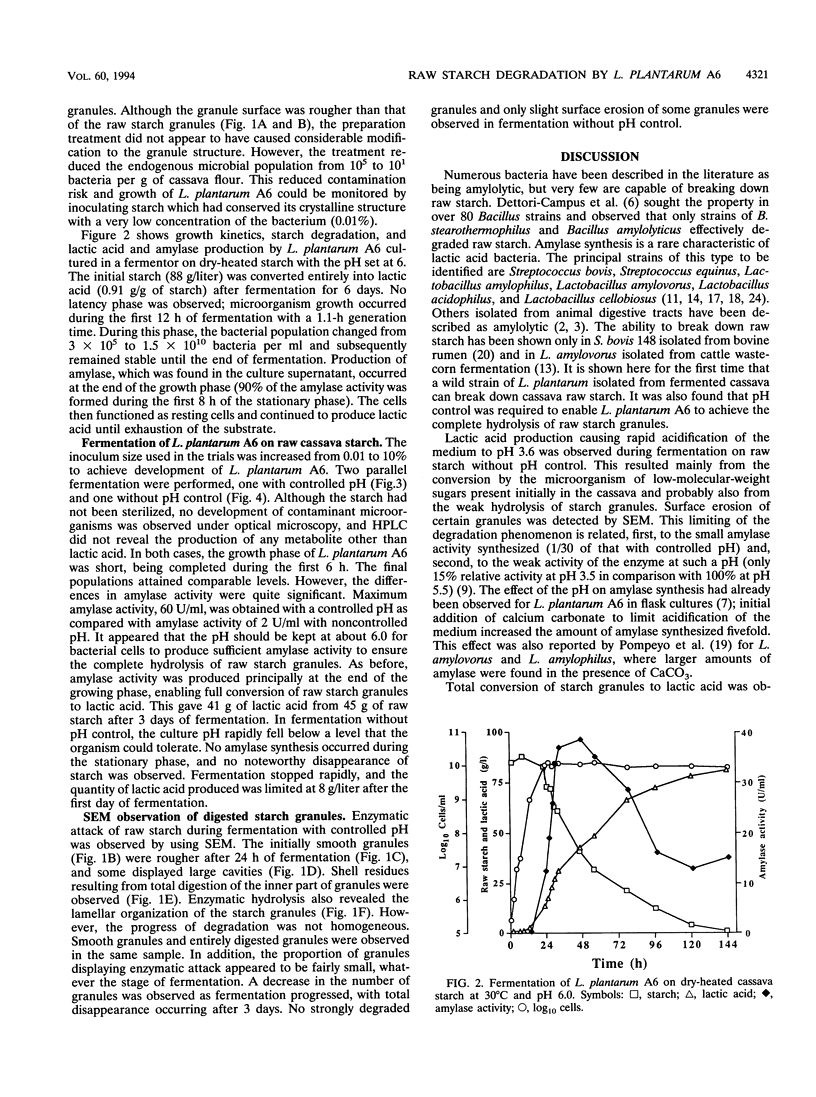
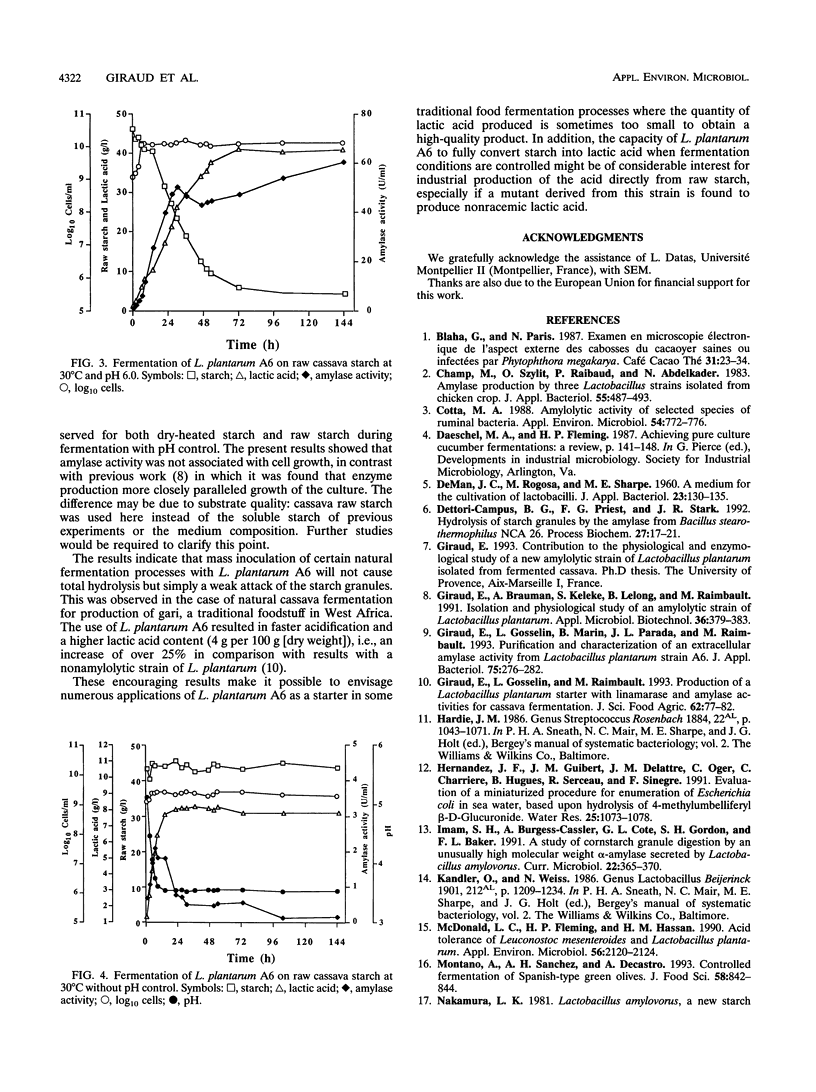
Lactobacillus plantarum A6, isolated from fermented cassava, can break down cassava raw starch that has not been subjected to preliminary physicochemical treatment. When the pH was kept at 6, the microorganism cultured in a bioreactor excreted a high α-amylase activity (60 U/ml). Synthesis of the enzyme occurred during the stationary phase and resulted in full hydrolysis of the cassava starch granules. This gave 41 g of lactic acid from 45 g of raw starch after 3 days of fermentation. Enzymatic attack was evident under scanning electron microscopy in the rougher appearance of the surface of starch granules and in the presence of large cavities in some of them. In contrast, when the pH was not regulated, only a small amount of α-amylase activity was produced (2 U/ml) and no decrease in the starch content of the medium was observed. However, under scanning electron microscopy, some granules displayed a rougher surface, which might have been the result of weak enzymatic attack.
Full text
PDF
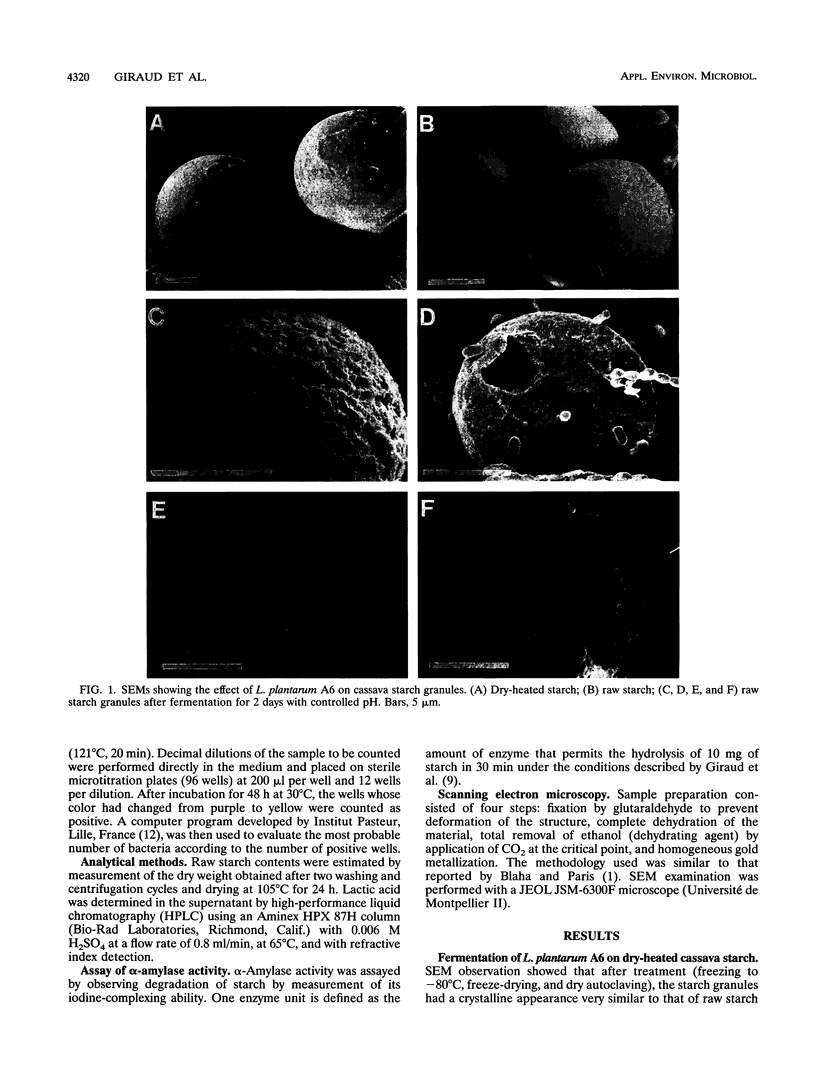

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Champ M., Szylit O., Raibaud P., Aït-Abdelkader N. Amylase production by three Lactobacillus strains isolated from chicken crop. J Appl Bacteriol. 1983 Dec;55(3):487–493. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1983.tb01689.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotta M. A. Amylolytic activity of selected species of ruminal bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Mar;54(3):772–776. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.3.772-776.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald L. C., Fleming H. P., Hassan H. M. Acid Tolerance of Leuconostoc mesenteroides and Lactobacillus plantarum. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Jul;56(7):2120–2124. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.7.2120-2124.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satoh E., Niimura Y., Uchimura T., Kozaki M., Komagata K. Molecular cloning and expression of two alpha-amylase genes from Streptococcus bovis 148 in Escherichia coli. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1993 Nov;59(11):3669–3673. doi: 10.1128/aem.59.11.3669-3673.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheirlinck T., Mahillon J., Joos H., Dhaese P., Michiels F. Integration and expression of alpha-amylase and endoglucanase genes in the Lactobacillus plantarum chromosome. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Sep;55(9):2130–2137. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.9.2130-2137.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]