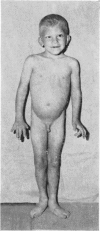
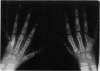
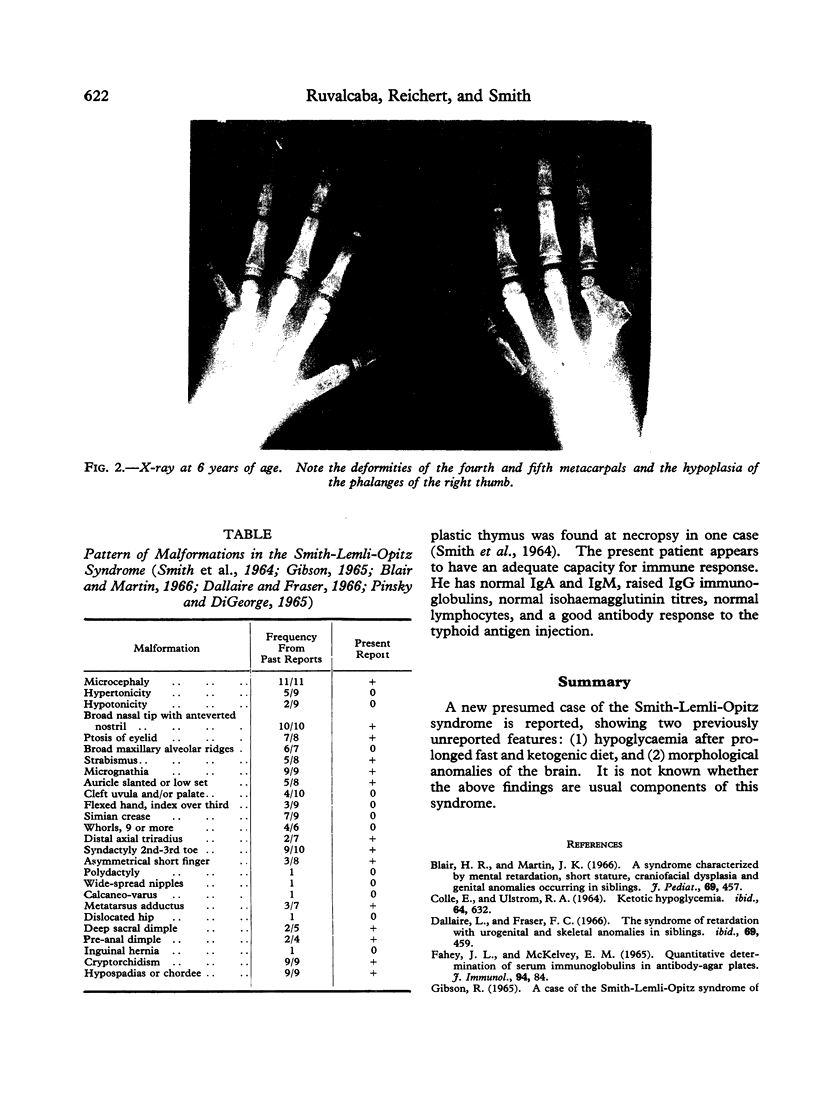
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blair H. R., Martin J. K. A syndrome characterized by mental retardation, short stature, craniofacial dysplasia, and genital anomalies occurring in siblings. J Pediatr. 1966 Sep;69(3):457–459. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(66)80094-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COLLE E., ULSTROM R. A. KETOTIC HYPOGLYCEMIA. J Pediatr. 1964 May;64:632–651. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(64)80611-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dallaire L., Fraser F. C. The syndrome of retardation with urogenital and skeletal anomalies in siblings. J Pediatr. 1966 Sep;69(3):459–460. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(66)80095-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FAHEY J. L., MCKELVEY E. M. QUANTITATIVE DETERMINATION OF SERUM IMMUNOGLOBULINS IN ANTIBODY-AGAR PLATES. J Immunol. 1965 Jan;94:84–90. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIBSON R. A CASE OF THE SMITH-LEMLI-OPITZ SYNDROME OF MULTIPLE CONGENITAL ANOMALIES IN ASSOCIATION WITH DYSPLASIA EPIPHYSIALIS PUNCTATA. Can Med Assoc J. 1965 Mar 13;92:574–575. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PINSKY L., DIGEORGE A. M. A FAMILIAL SYNDROME OF FACIAL AND SKELETAL ANOMALIES ASSOCIATED WITH GENITAL ABNORMALITY IN THE MALE AND NORAML GENITALS IN THE FEMALE: ANOTHER CAUSE OF MALE PSEUDOHERMAPHRODITISM. J Pediatr. 1965 Jun;66:1049–1054. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(65)80091-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH D. W., LEMLI L., OPITZ J. M. A NEWLY RECOGNIZED SYNDROME OF MULTIPLE CONGENITAL ANOMALIES. J Pediatr. 1964 Feb;64:210–217. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(64)80264-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]