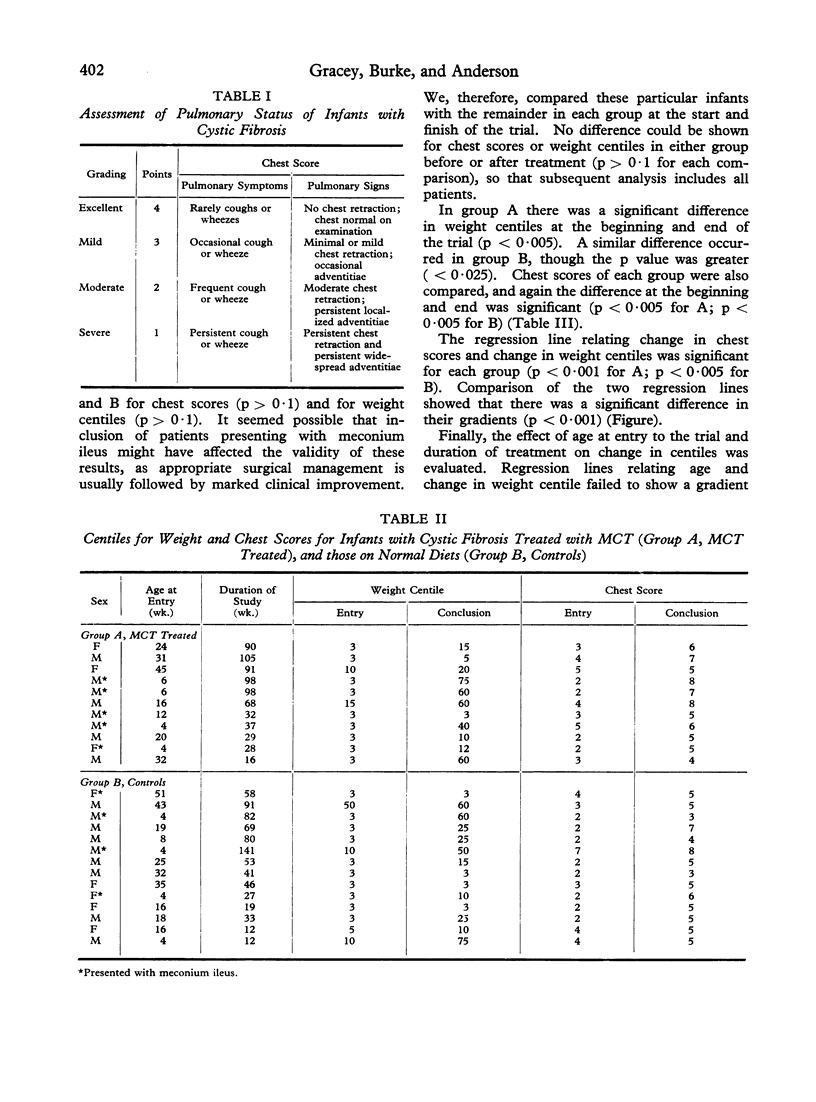
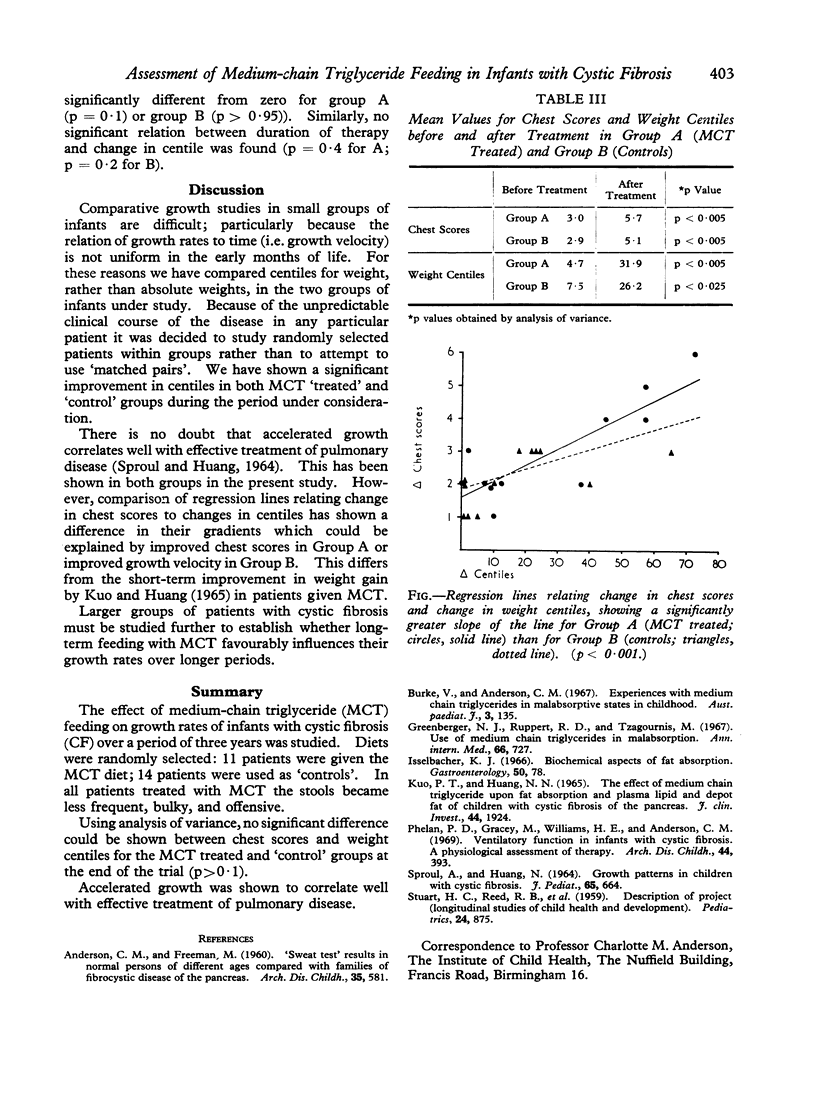
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANDERSON C. M., FREEMAN M. 'Sweat test' results in normal persons of different ages compared with families with fibrocystic disease of the pancreas. Arch Dis Child. 1960 Dec;35:581–587. doi: 10.1136/adc.35.184.581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberger N. J., Ruppert R. D., Tzagournis M. Use of medium chain triglycerides in malabsorption. Ann Intern Med. 1967 Apr;66(4):727–734. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-66-4-727. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isselbacher K. J. Biochemical aspects of fat absorption. Gastroenterology. 1966 Jan;50(1):78–82. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo P. T., Huang N. N. The effect of medium chain triglyceride upon fat absorption and plasma lipid and depot fat of children with cystic fibrosis of the pancreas. J Clin Invest. 1965 Nov;44(11):1924–1933. doi: 10.1172/JCI105298. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phelan P. D., Gracey M., Williams H. E., Anderson C. M. Ventilatory function in infants with cystic fibrosis. Physiological assessment of halation therapy. Arch Dis Child. 1969 Jun;44(235):393–400. doi: 10.1136/adc.44.235.393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SPROUL A., HUANG N. GROWTH PATTERNS IN CHILDREN WITH CYSTIC FIBROSIS. J Pediatr. 1964 Nov;65:664–676. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(64)80151-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STUART H. C., REED R. B. Longitudinal studies of child health and development--Series II. Description of project. Pediatrics. 1959 Nov;24:875–885. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


