Abstract
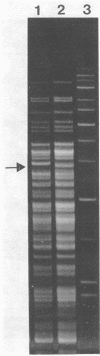
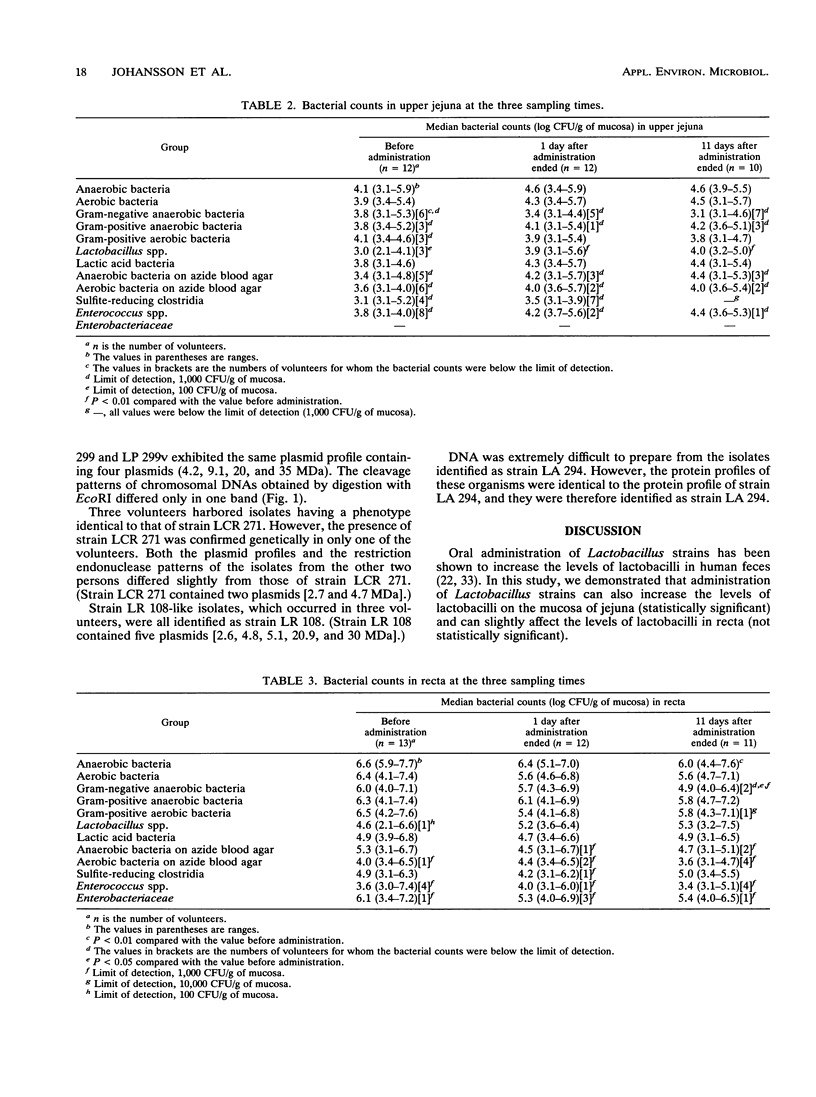
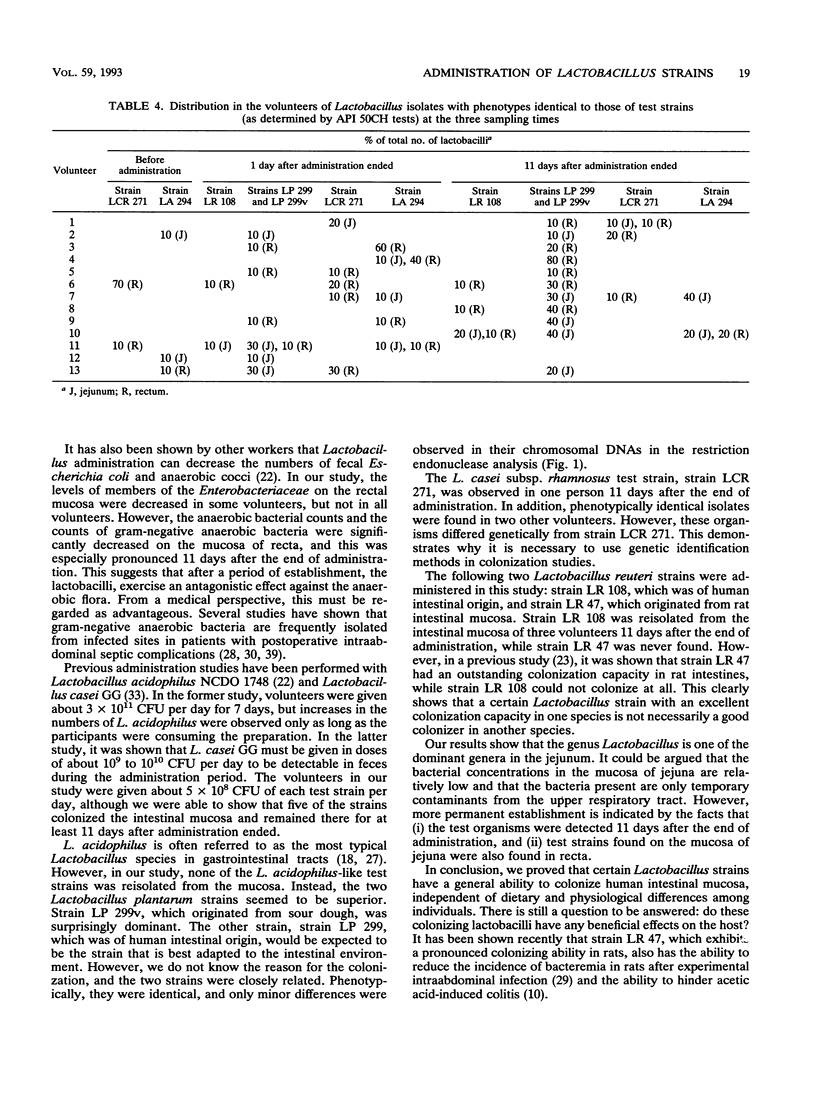
In vivo colonization by different Lactobacillus strains on human intestinal mucosa of healthy volunteers was studied together with the effect of Lactobacillus administration on different groups of indigenous bacteria. A total of 19 test strains were administered in fermented oatmeal soup containing 5 x 10(6) CFU of each strain per ml by using a dose of 100 ml of soup per day for 10 days. Biopsies were taken from both the upper jejunum and the rectum 1 day before administration was started and 1 and 11 days after administration was terminated. The administration significantly increased the Lactobacillus counts on the jejunum mucosa, and high levels remained 11 days after administration was terminated. The levels of streptococci increased by 10- to 100-fold in two persons, and the levels of sulfite-reducing clostridia in the jejunum decreased by 10- to 100-fold in three of the volunteers 1 day after administration was terminated. In recta, the anaerobic bacterium counts and the gram-negative anaerobic bacterium counts decreased significantly by the end of administration. Furthermore, a decrease in the number of members of the Enterobacteriaceae by 1,000-fold was observed on the rectal mucosa of two persons. Randomly picked Lactobacillus isolates were identified phenotypically by API 50CH tests and genotypically by the plasmid profiles of strains and by restriction endonuclease analysis of chromosomal DNAs.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alverdy J. C., Aoys E., Moss G. S. Total parenteral nutrition promotes bacterial translocation from the gut. Surgery. 1988 Aug;104(2):185–190. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arabi Y., Dimock F., Burdon D. W., Alexander-Williams J., Keighley M. R. Influence of neomycin and metronidazole on colonic microflora of volunteers. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1979 Sep;5(5):531–537. doi: 10.1093/jac/5.5.531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartlett J. G., Chang T. W., Gurwith M., Gorbach S. L., Onderdonk A. B. Antibiotic-associated pseudomembranous colitis due to toxin-producing clostridia. N Engl J Med. 1978 Mar 9;298(10):531–534. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197803092981003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chassy B. M., Gibson E., Giuffrida A. Evidence for extrachromosomal elements in Lactobacillus. J Bacteriol. 1976 Sep;127(3):1576–1578. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.3.1576-1578.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins E. B., Aramaki K. Production of Hydrogen peroxide by Lactobacillus acidophilus. J Dairy Sci. 1980 Mar;63(3):353–357. doi: 10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(80)82938-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enfors S. O., Molin G., Ternström A. Effect of packaging under carbon dioxide, nitrogen or air on the microbial flora of pork stored at 4 degrees C. J Appl Bacteriol. 1979 Oct;47(2):197–208. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1979.tb01746.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gotz V., Romankiewicz J. A., Moss J., Murray H. W. Prophylaxis against ampicillin-associated diarrhea with a lactobacillus preparation. Am J Hosp Pharm. 1979 Jun;36(6):754–757. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heimdahl A., Nord C. E. Effect of phenoxymethylpenicillin and clindamycin on the oral, throat and faecal microflora of man. Scand J Infect Dis. 1979;11(3):233–242. doi: 10.3109/inf.1979.11.issue-3.11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heys S. D., Park K. G., Garlick P. J., Eremin O. Nutrition and malignant disease: implications for surgical practice. Br J Surg. 1992 Jul;79(7):614–623. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800790707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lidbeck A., Edlund C., Gustafsson J. A., Kager L., Nord C. E. Impact of Lactobacillus acidophilus on the normal intestinal microflora after administration of two antimicrobial agents. Infection. 1988;16(6):329–336. doi: 10.1007/BF01644541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lidbeck A., Gustafsson J. A., Nord C. E. Impact of Lactobacillus acidophilus supplements on the human oropharyngeal and intestinal microflora. Scand J Infect Dis. 1987;19(5):531–537. doi: 10.3109/00365548709032419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molin G., Andersson R., Ahrné S., Lönner C., Marklinder I., Johansson M. L., Jeppsson B., Bengmark S. Effect of fermented oatmeal soup on the cholesterol level and the Lactobacillus colonization of rat intestinal mucosa. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1992 Apr;61(3):167–173. doi: 10.1007/BF00584223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molin G., Johansson M. L., Ståhl M., Ahrné S., Andersson R., Jeppsson B., Bengmark S. Systematics of the Lactobacillus population on rat intestinal mucosa with special reference to Lactobacillus reuteri. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1992 Apr;61(3):175–183. doi: 10.1007/BF00584224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore W. E., Holdeman L. V. Human fecal flora: the normal flora of 20 Japanese-Hawaiians. Appl Microbiol. 1974 May;27(5):961–979. doi: 10.1128/am.27.5.961-979.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nichols R. L. Infections following gastrointestinal surgery: intra-abdominal abscess. Surg Clin North Am. 1980 Feb;60(1):197–212. doi: 10.1016/s0039-6109(16)42044-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Offenbartl K., Bengmark S. Intraabdominal infections and gut origin sepsis. World J Surg. 1990 Mar-Apr;14(2):191–195. doi: 10.1007/BF01664872. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savage D. C. Microbial ecology of the gastrointestinal tract. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1977;31:107–133. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.31.100177.000543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siitonen S., Vapaatalo H., Salminen S., Gordin A., Saxelin M., Wikberg R., Kirkkola A. L. Effect of Lactobacillus GG yoghurt in prevention of antibiotic associated diarrhoea. Ann Med. 1990 Feb;22(1):57–59. doi: 10.3109/07853899009147243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilmore D. W., Smith R. J., O'Dwyer S. T., Jacobs D. O., Ziegler T. R., Wang X. D. The gut: a central organ after surgical stress. Surgery. 1988 Nov;104(5):917–923. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zoppi G., Deganello A., Benoni G., Saccomani F. Oral bacteriotherapy in clinical practice. I. The use of different preparations in infants treated with antibiotics. Eur J Pediatr. 1982 Sep;139(1):18–21. doi: 10.1007/BF00442072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]