Abstract
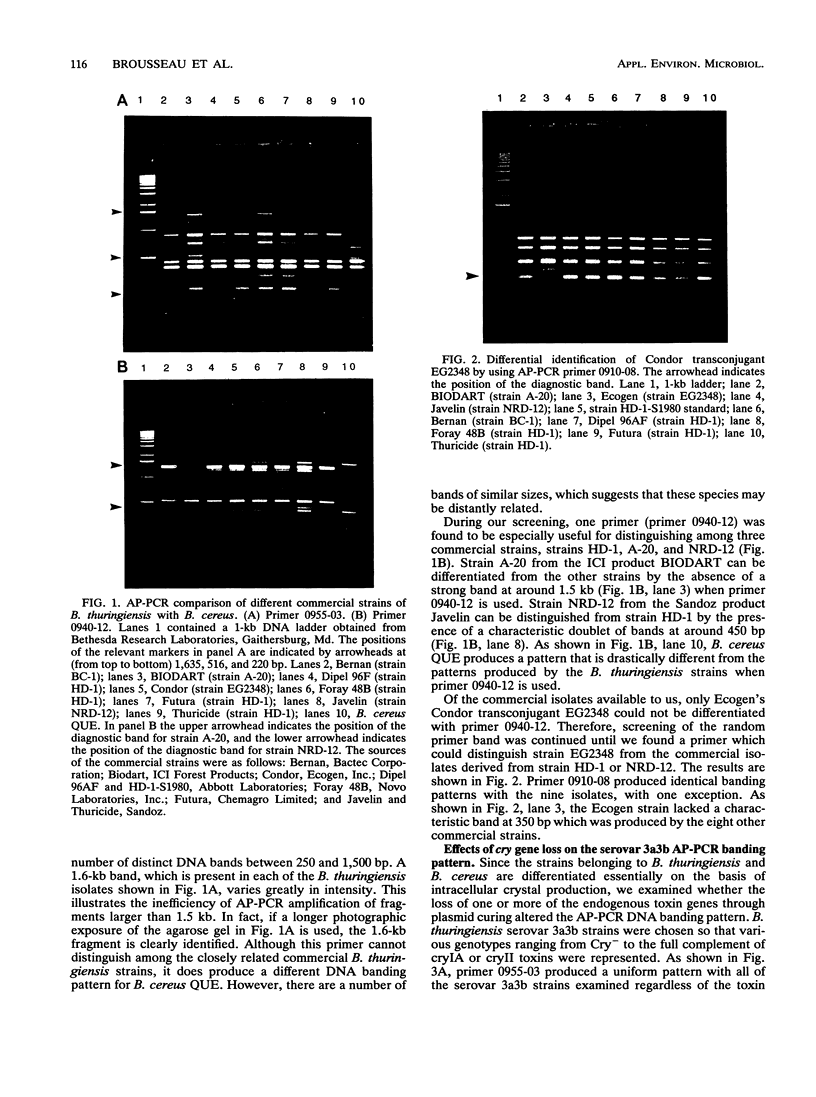
Arbitrary primer polymerase chain reaction technology has been applied to the identification of commercial strains of Bacillus thuringiensis by using total DNAs extracted from single bacterial colonies as templates. Characteristic DNA banding patterns can be readily and reproducibly obtained by agarose gel electrophoresis. This method has been used to distinguish commercial products containing B. thuringiensis serovar kurstaki (3a3b). When a single primer was used this method was capable of producing discriminating DNA fingerprints for 33 known serovars. Differentiation from the closely related species Bacillus cereus is also readily achieved. This technique should prove to be a powerful tool for identification and discrimination of individual B. thuringiensis strains.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ash C., Farrow J. A., Dorsch M., Stackebrandt E., Collins M. D. Comparative analysis of Bacillus anthracis, Bacillus cereus, and related species on the basis of reverse transcriptase sequencing of 16S rRNA. Int J Syst Bacteriol. 1991 Jul;41(3):343–346. doi: 10.1099/00207713-41-3-343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Battisti L., Green B. D., Thorne C. B. Mating system for transfer of plasmids among Bacillus anthracis, Bacillus cereus, and Bacillus thuringiensis. J Bacteriol. 1985 May;162(2):543–550. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.2.543-550.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caetano-Anollés G., Bassam B. J., Gresshoff P. M. DNA amplification fingerprinting using very short arbitrary oligonucleotide primers. Biotechnology (N Y) 1991 Jun;9(6):553–557. doi: 10.1038/nbt0691-553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gawron-Burke C., Baum J. A. Genetic manipulation of Bacillus thuringiensis insecticidal crystal protein genes in bacteria. Genet Eng (N Y) 1991;13:237–263. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-3760-1_11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- González J. M., Jr, Brown B. J., Carlton B. C. Transfer of Bacillus thuringiensis plasmids coding for delta-endotoxin among strains of B. thuringiensis and B. cereus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(22):6951–6955. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.22.6951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- González J. M., Jr, Carlton B. C. Patterns of plasmid DNA in crystalliferous and acrystalliferous strains of Bacillus thuringiensis. Plasmid. 1980 Jan;3(1):92–98. doi: 10.1016/s0147-619x(80)90038-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green M., Heumann M., Sokolow R., Foster L. R., Bryant R., Skeels M. Public health implications of the microbial pesticide Bacillus thuringiensis: an epidemiological study, Oregon, 1985-86. Am J Public Health. 1990 Jul;80(7):848–852. doi: 10.2105/ajph.80.7.848. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honda T., Shiba A., Seo S., Yamamoto J., Matsuyama J., Miwatani T. Identity of hemolysins produced by Bacillus thuringiensis and Bacillus cereus. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1991 Apr 15;63(2-3):205–209. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(91)90087-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaneko T., Nozaki R., Aizawa K. Deoxyribonucleic acid relatedness between Bacillus anthracis, Bacillus cereus and Bacillus thuringiensis. Microbiol Immunol. 1978;22(10):639–641. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1978.tb00414.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence D., Heitefuss S., Seifert H. S. Differentiation of Bacillus anthracis from Bacillus cereus by gas chromatographic whole-cell fatty acid analysis. J Clin Microbiol. 1991 Jul;29(7):1508–1512. doi: 10.1128/jcm.29.7.1508-1512.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samples J. R., Buettner H. Corneal ulcer caused by a biologic insecticide (Bacillus thuringiensis). Am J Ophthalmol. 1983 Feb;95(2):258–260. doi: 10.1016/0002-9394(83)90028-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samples J. R., Buettner H. Ocular infection caused by a biological insecticide. J Infect Dis. 1983 Sep;148(3):614–614. doi: 10.1093/infdis/148.3.614. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somerville H. J., Jones M. L. DNA competition studies within the Bacillus cereus group of bacilli. J Gen Microbiol. 1972 Nov;73(2):257–265. doi: 10.1099/00221287-73-2-257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welsh J., McClelland M. Fingerprinting genomes using PCR with arbitrary primers. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Dec 25;18(24):7213–7218. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.24.7213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. G., Kubelik A. R., Livak K. J., Rafalski J. A., Tingey S. V. DNA polymorphisms amplified by arbitrary primers are useful as genetic markers. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Nov 25;18(22):6531–6535. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.22.6531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zahner V., Momen H., Salles C. A., Rabinovitch L. A comparative study of enzyme variation in Bacillus cereus and Bacillus thuringiensis. J Appl Bacteriol. 1989 Sep;67(3):275–282. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1989.tb02496.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Frankenhuyzen K., Milne R., Brousseau R., Masson L. Comparative toxicity of the HD-1 and NRD-12 strains of Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. kurstaki to defoliating forest Lepidoptera. J Invertebr Pathol. 1992 Mar;59(2):149–154. doi: 10.1016/0022-2011(92)90025-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]