Abstract
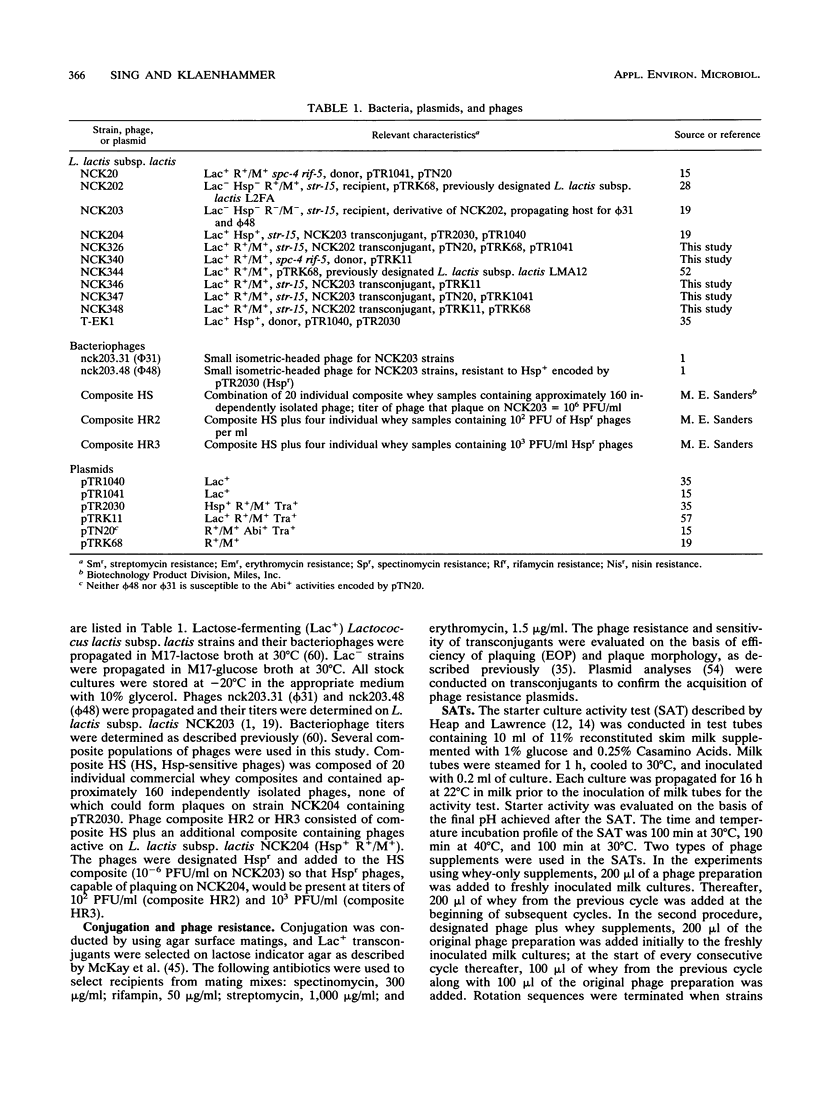
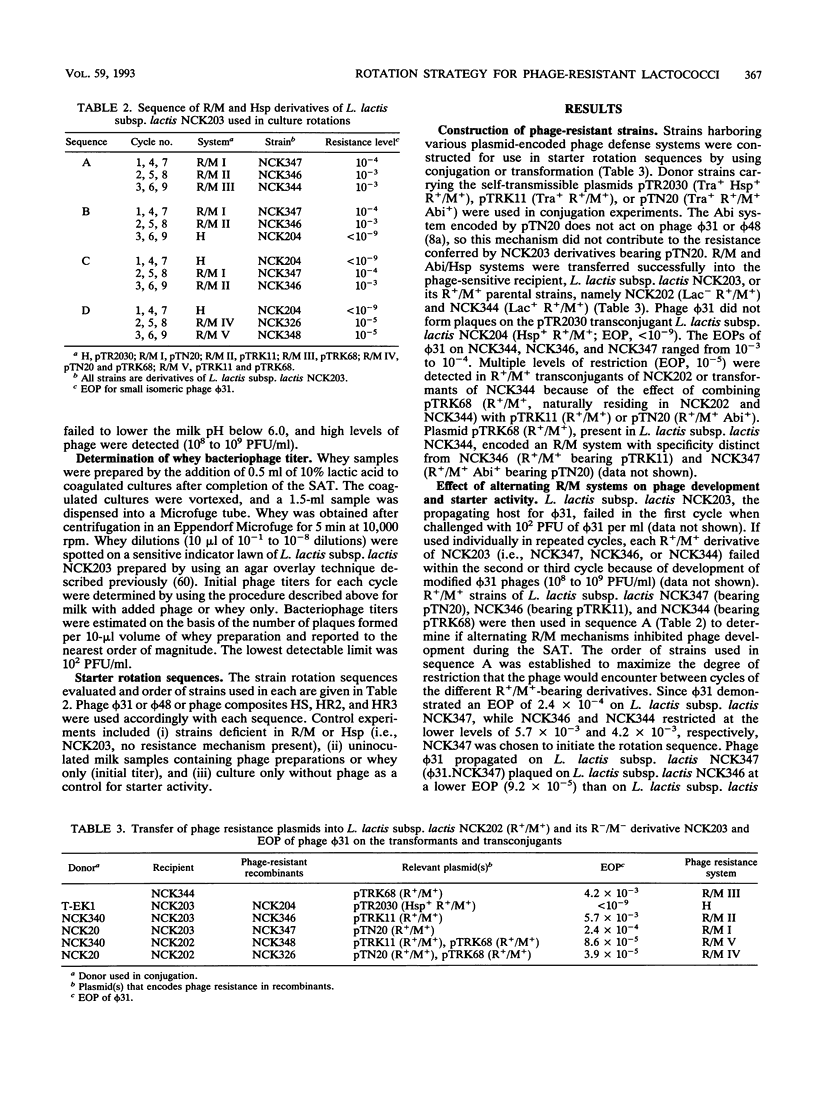
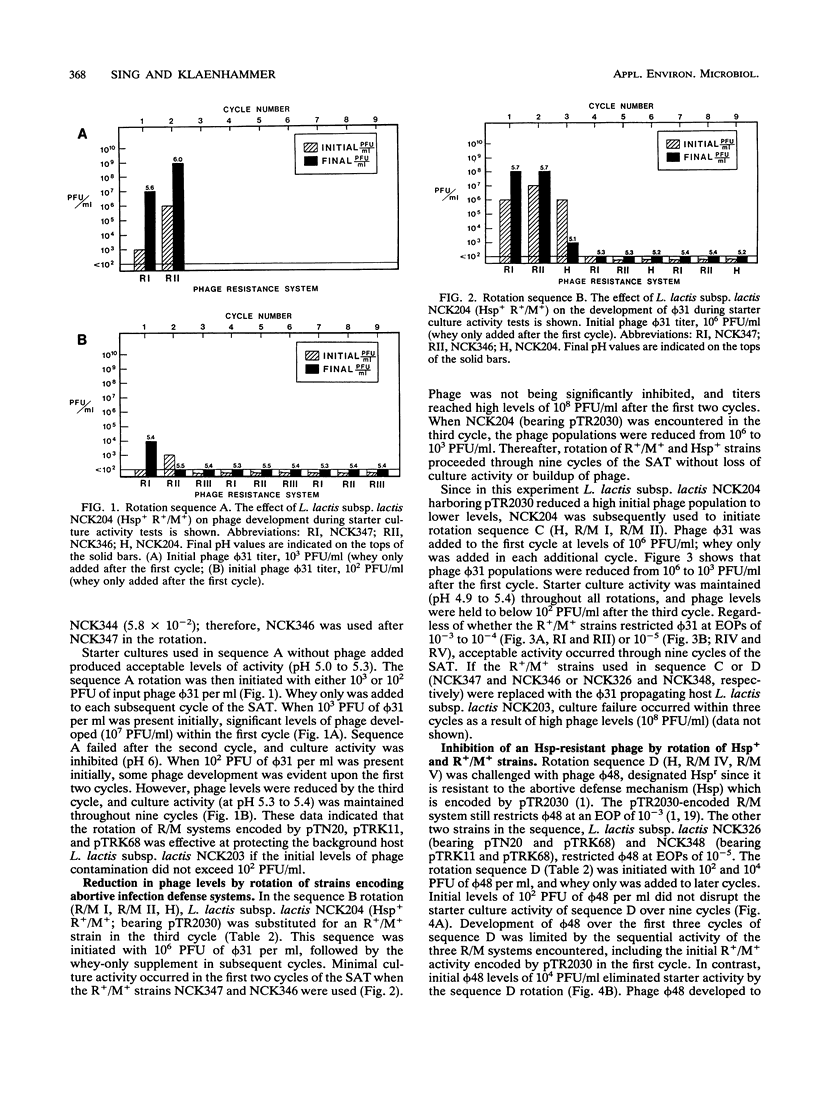
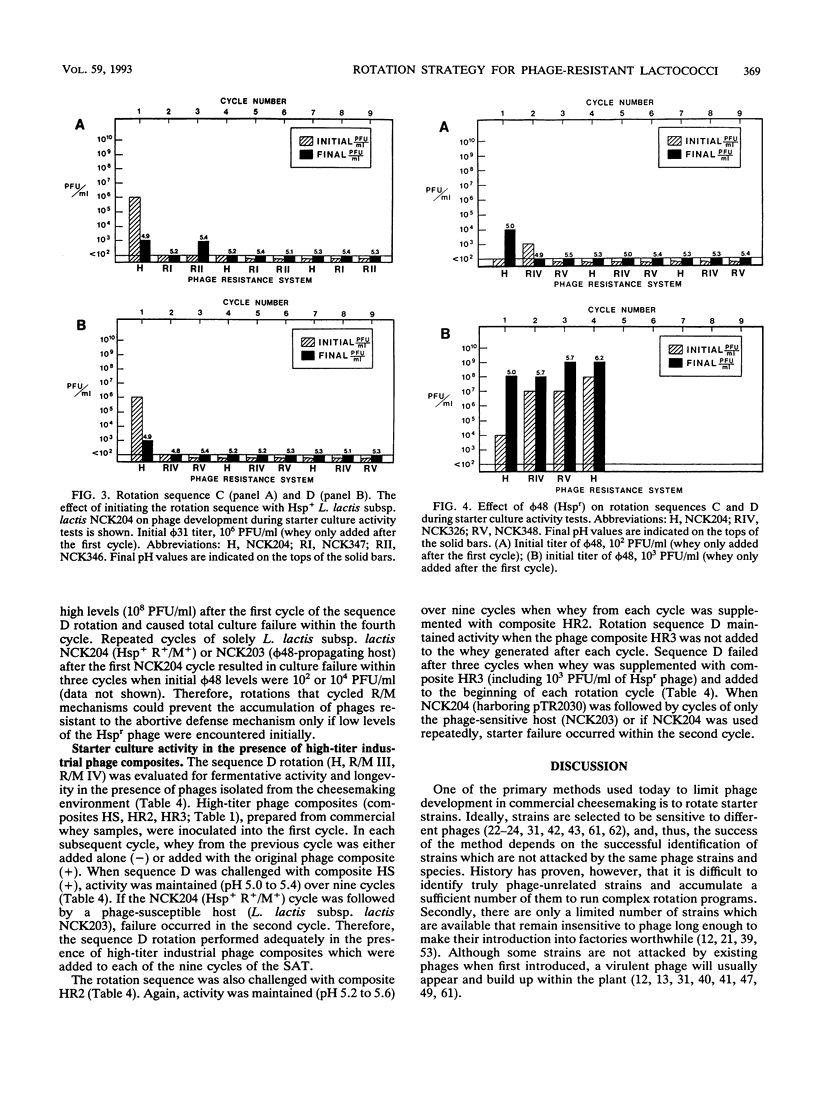
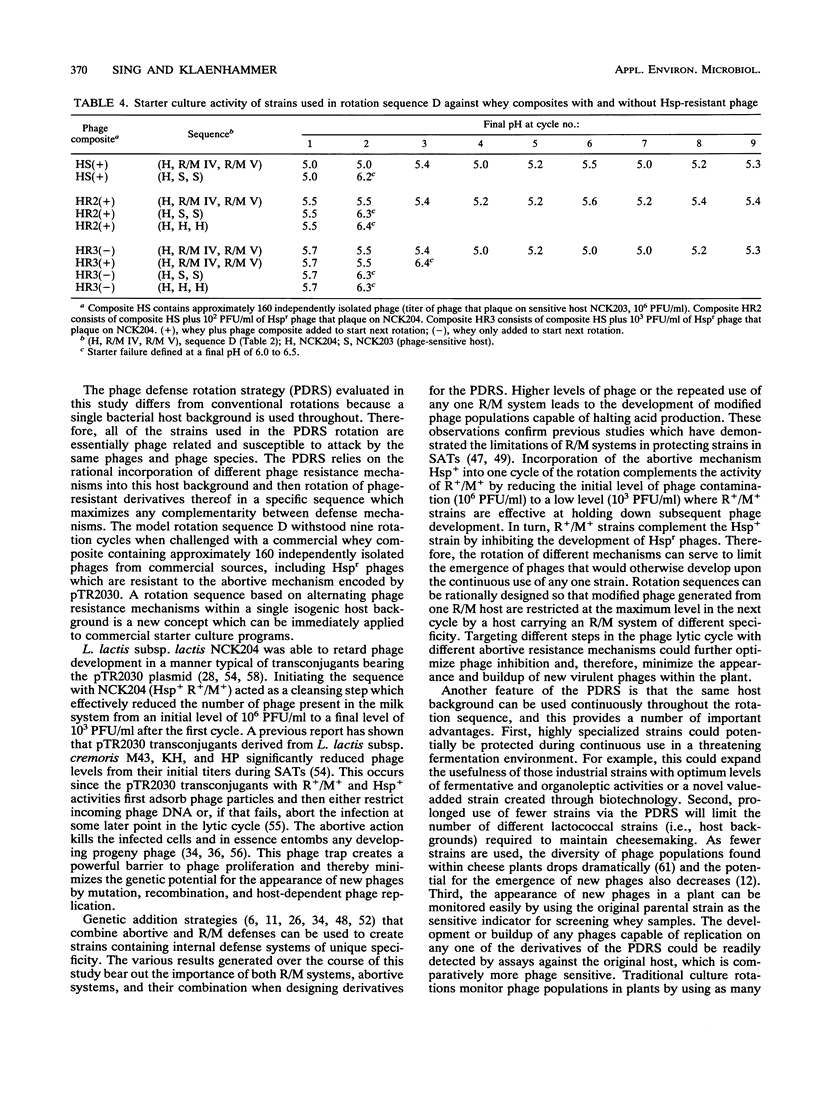
A new strategy for starter culture rotations was developed for a series of phage-resistant clones genetically derived from a single strain of Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis. Phage-resistant derivatives carrying different defense systems were constructed via conjugation with various plasmids encoding abortive infection (Abi/Hsp) and/or restriction and modification (R/M) systems of different specificity. The plasmids included pTR2030 (Hsp+ R+/M+), pTN20 (Abi+ R+/M+), pTRK11 (R+/M+), and pTRK68 (R+/M+). Selected phage-resistant transconjugants or transformants were evaluated in different rotation sequences through cycles of the Heap-Lawrence starter culture activity test in milk contaminated with phage and whey from the previous cycle. When used in consecutive sequence, derivative strains carrying the R/M systems encoded by pTN20, pTRK11, and pTRK68 retarded phage development when the initial levels of phage contamination were below 102 PFU/ml but not when levels were increased to 103 PFU/ml. Use of a derivative bearing pTR2030 (Hsp+ R+/M+) at the beginning of the rotation prevented phage development, even when the initial levels of phage contamination were high (106 PFU/ml). Alternating the type and specificity of R/M and Abi defenses through the rotation prevented phage proliferation and in some cases eliminated contaminating phages. A model rotation sequence for the phage defense rotation strategy was developed and performed successfully over nine cycles of the Heap-Lawrence starter culture activity test in the presence of high-titer commercial phage composites. This phage defense rotation strategy is designed to protect a highly specialized Lactococcus strain from phage attack during continuous and extended use in the dairy industry.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alatossava T., Klaenhammer T. R. Molecular Characterization of Three Small Isometric-Headed Bacteriophages Which Vary in Their Sensitivity to the Lactococcal Phage Resistance Plasmid pTR2030. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 May;57(5):1346–1353. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.5.1346-1353.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boussemaer J. P., Schrauwen P. P., Sourrouille J. L., Guy P. Multiple modification/restriction systems in lactic streptococci and their significance in defining a phage-typing system. J Dairy Res. 1980 Oct;47(3):401–409. doi: 10.1017/s0022029900021294. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chopin A., Chopin M. C., Moillo-Batt A., Langella P. Two plasmid-determined restriction and modification systems in Streptococcus lactis. Plasmid. 1984 May;11(3):260–263. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(84)90033-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung D. K., Chung S. K., Batt C. A. Antisense RNA directed against the major capsid protein of Lactococcus lactis subsp. cremoris bacteriophage 4-1 confers partial resistance to the host. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 1992 Apr;37(1):79–83. doi: 10.1007/BF00174207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coffey A. G., Fitzgerald G. F., Daly C. Cloning and characterization of the determinant for abortive infection of bacteriophage from lactococcal plasmid pCI829. J Gen Microbiol. 1991 Jun;137(6):1355–1362. doi: 10.1099/00221287-137-6-1355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durmaz E., Higgins D. L., Klaenhammer T. R. Molecular characterization of a second abortive phage resistance gene present in Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis ME2. J Bacteriol. 1992 Nov;174(22):7463–7469. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.22.7463-7469.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Froseth B. R., Harlander S. K., McKay L. L. Plasmid-mediated reduced phage sensitivity in Streptococcus lactis KR5. J Dairy Sci. 1988 Feb;71(2):275–284. doi: 10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(88)79555-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gautier M., Chopin M. C. Plasmid-Determined Systems for Restriction and Modification Activity and Abortive Infection in Streptococcus cremoris. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 May;53(5):923–927. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.5.923-927.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrington A., Hill C. Construction of a Bacteriophage-Resistant Derivative of Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis 425A by Using the Conjugal Plasmid pNP40. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Dec;57(12):3405–3409. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.12.3405-3409.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins D. L., Sanozky-Dawes R. B., Klaenhammer T. R. Restriction and modification activities from Streptococcus lactis ME2 are encoded by a self-transmissible plasmid, pTN20, that forms cointegrates during mobilization of lactose-fermenting ability. J Bacteriol. 1988 Aug;170(8):3435–3442. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.8.3435-3442.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill C., Miller L. A., Klaenhammer T. R. Cloning, expression, and sequence determination of a bacteriophage fragment encoding bacteriophage resistance in Lactococcus lactis. J Bacteriol. 1990 Nov;172(11):6419–6426. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.11.6419-6426.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill C., Miller L. A., Klaenhammer T. R. In vivo genetic exchange of a functional domain from a type II A methylase between lactococcal plasmid pTR2030 and a virulent bacteriophage. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jul;173(14):4363–4370. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.14.4363-4370.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill C., Miller L. A., Klaenhammer T. R. Nucleotide sequence and distribution of the pTR2030 resistance determinant (hsp) which aborts bacteriophage infection in lactococci. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Jul;56(7):2255–2258. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.7.2255-2258.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill C., Pierce K., Klaenhammer T. R. The conjugative plasmid pTR2030 encodes two bacteriophage defense mechanisms in lactococci, restriction modification (R+/M+) and abortive infection (Hsp+). Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Sep;55(9):2416–2419. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.9.2416-2419.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarvis A. W., Heap H. A., Limsowtin G. K. Resistance against Industrial Bacteriophages Conferred on Lactococci by Plasmid pAJ1106 and Related Plasmids. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Jun;55(6):1537–1543. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.6.1537-1543.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarvis A. W., Klaenhammer T. R. Bacteriophage Resistance Conferred on Lactic Streptococci by the Conjugative Plasmid pTR2030: Effects on Small Isometric-, Large Isometric-, and Prolate-Headed Phages. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Jun;51(6):1272–1277. doi: 10.1128/aem.51.6.1272-1277.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarvis Audrey W. Conjugal Transfer in Lactic Streptococci of Plasmid-Encoded Insensitivity to Prolate- and Small Isometric-Headed Bacteriophages. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Mar;54(3):777–783. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.3.777-783.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Josephsen J., Klaenhammer T. Stacking of three different restriction and modification systems in Lactococcus lactis by cotransformation. Plasmid. 1990 Jan;23(1):71–75. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(90)90046-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim S. G., Bor Y. C., Batt C. A. Bacteriophage resistance in Lactococcus lactis ssp. lactis using antisense ribonucleic acid. J Dairy Sci. 1992 Jul;75(7):1761–1767. doi: 10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(92)77935-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klaenhammer T. R. Development of bacteriophage-resistant strains of lactic acid bacteria. Biochem Soc Trans. 1991 Aug;19(3):675–681. doi: 10.1042/bst0190675. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klaenhammer T. R., Sanozky R. B. Conjugal transfer from Streptococcus lactis ME2 of plasmids encoding phage resistance, nisin resistance and lactose-fermenting ability: evidence for a high-frequency conjugative plasmid responsible for abortive infection of virulent bacteriophage. J Gen Microbiol. 1985 Jun;131(6):1531–1541. doi: 10.1099/00221287-131-6-1531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kondo J. K., McKay L. L. Plasmid transformation of Streptococcus lactis protoplasts: optimization and use in molecular cloning. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Aug;48(2):252–259. doi: 10.1128/aem.48.2.252-259.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKay L. L., Baldwin K. A. Conjugative 40-megadalton plasmid in Streptococcus lactis subsp. diacetylactis DRC3 is associated with resistance to nisin and bacteriophage. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Jan;47(1):68–74. doi: 10.1128/aem.47.1.68-74.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKay L. L., Baldwin K. A., Walsh P. M. Conjugal transfer of genetic information in group N streptococci. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Jul;40(1):84–89. doi: 10.1128/aem.40.1.84-91.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy M. C., Steele J. L., Daly C., McKay L. L. Concomitant conjugal transfer of reduced-bacteriophage-sensitivity mechanisms with lactose- and sucrose-fermenting ability in lactic streptococci. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Aug;54(8):1951–1956. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.8.1951-1956.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders M. E., Klaenhammer T. R. Characterization of Phage-Sensitive Mutants from a Phage-Insensitive Strain of Streptococcus lactis: Evidence for a Plasmid Determinant that Prevents Phage Adsorption. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Nov;46(5):1125–1133. doi: 10.1128/aem.46.5.1125-1133.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders M. E., Klaenhammer T. R. Evidence for Plasmid Linkage of Restriction and Modification in Streptococcus cremoris KH. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Dec;42(6):944–950. doi: 10.1128/aem.42.6.944-950.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders M. E., Klaenhammer T. R. Restriction and modification in group N streptococci: effect of heat on development of modified lytic bacteriophage. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Sep;40(3):500–506. doi: 10.1128/aem.40.3.500-506.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders M. E., Leonhard P. J., Sing W. D., Klaenhammer T. R. Conjugal strategy for construction of fast Acid-producing, bacteriophage-resistant lactic streptococci for use in dairy fermentations. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Nov;52(5):1001–1007. doi: 10.1128/aem.52.5.1001-1007.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders M. E. Phage resistance in lactic acid bacteria. Biochimie. 1988 Mar;70(3):411–422. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(88)90215-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sing W. D., Klaenhammer T. R. Conjugal Transfer of Bacteriophage Resistance Determinants on pTR2030 into Streptococcus cremoris Strains. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Jun;51(6):1264–1271. doi: 10.1128/aem.51.6.1264-1271.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steenson L. R., Klaenhammer T. R. Plasmid heterogeneity in Streptococcus cremoris M12R: effects on proteolytic activity and host-dependent phage replication. J Dairy Sci. 1986 Sep;69(9):2227–2236. doi: 10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(86)80661-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steenson L. R., Klaenhammer T. R. Streptococcus cremoris M12R transconjugants carrying the conjugal plasmid pTR2030 are insensitive to attack by lytic bacteriophages. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Oct;50(4):851–858. doi: 10.1128/aem.50.4.851-858.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terzaghi B. E., Sandine W. E. Improved medium for lactic streptococci and their bacteriophages. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Jun;29(6):807–813. doi: 10.1128/am.29.6.807-813.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



