Abstract
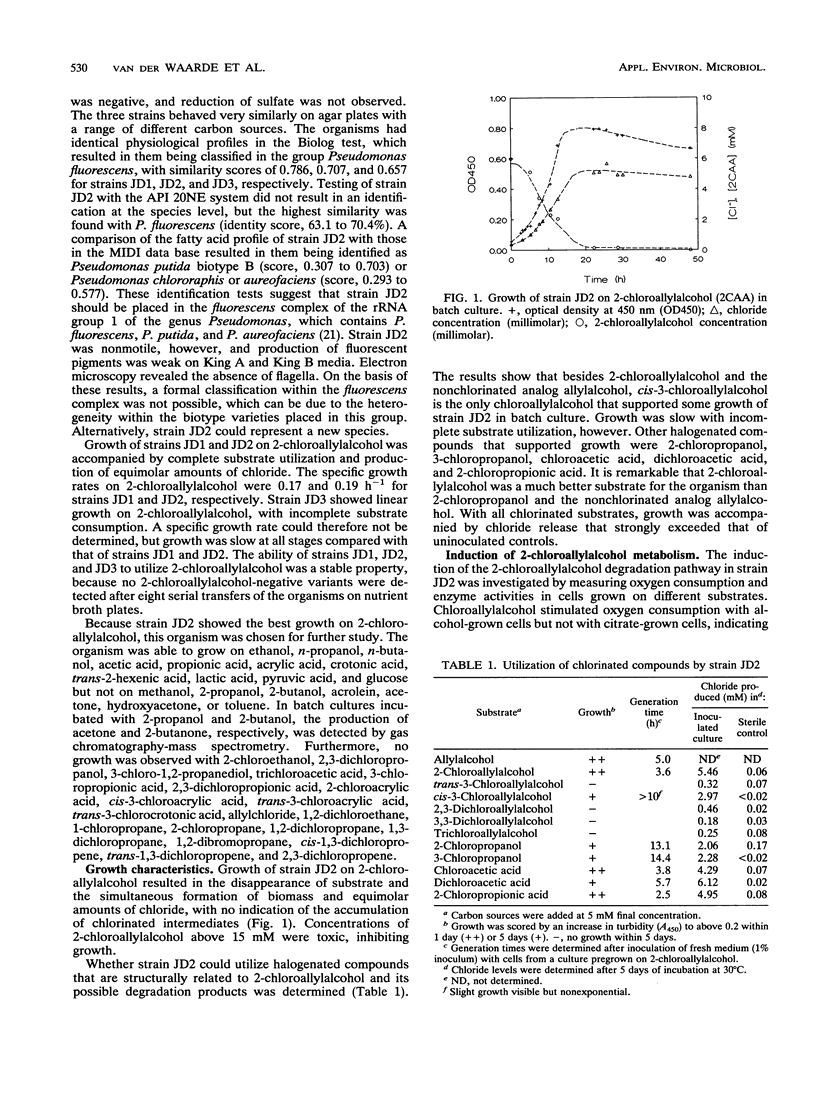
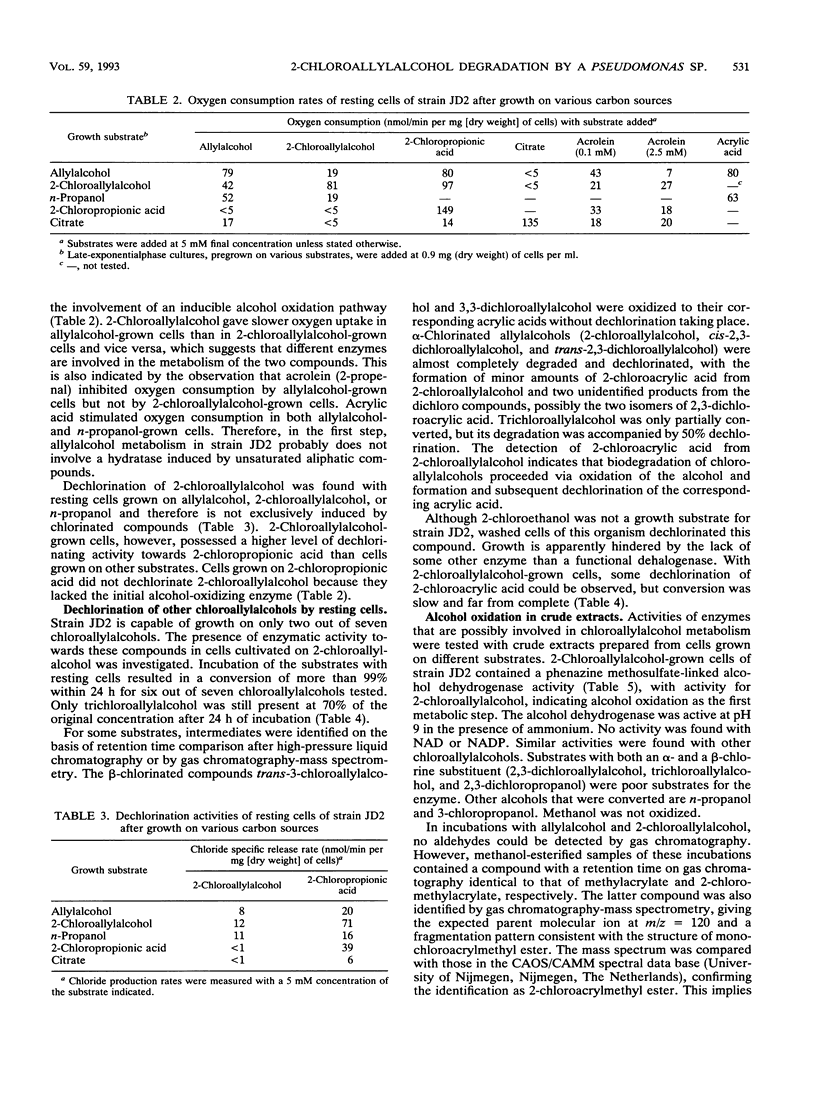
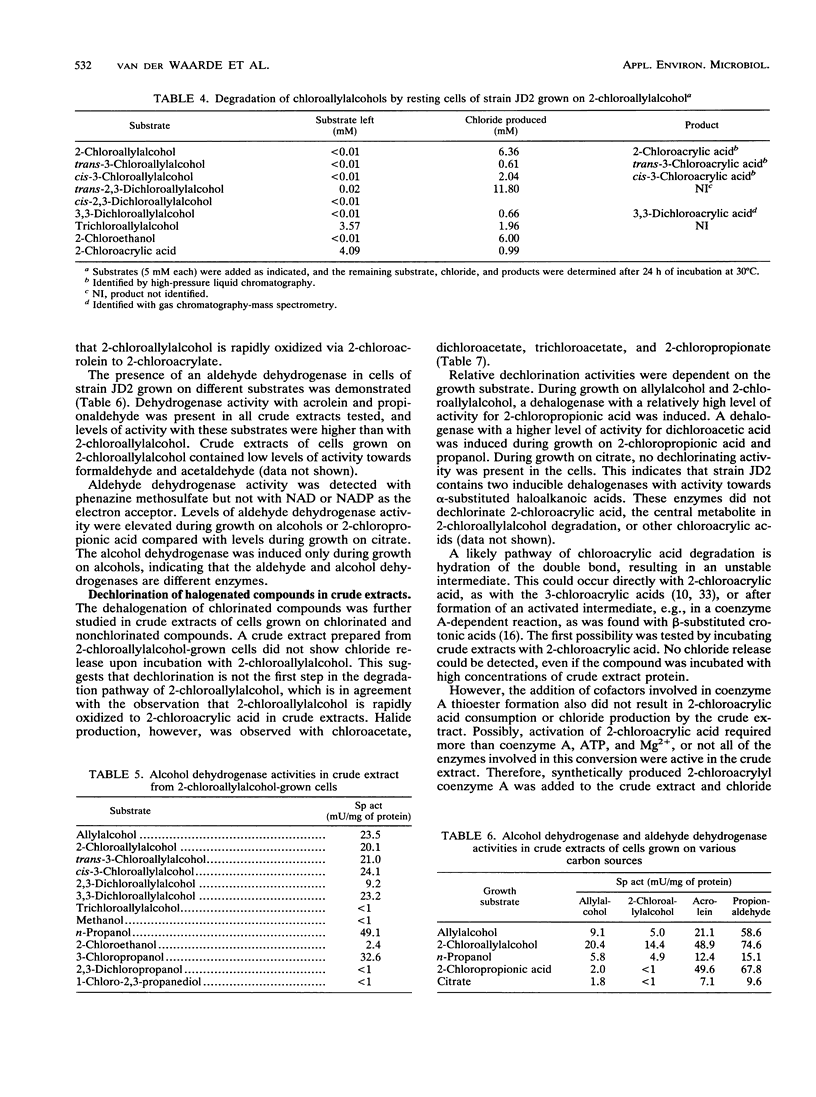
Three Pseudomonas strains capable of utilizing 2-chloroallylalcohol (2-chloropropenol) as the sole carbon source for growth were isolated from soil. The fastest growth was observed with strain JD2, with a generation time of 3.6 h. Degradation of 2-chloroallylalcohol was accompanied by complete dehalogenation. Chloroallylalcohols that did not support growth were dechlorinated by resting cells; the dechlorination level was highest if an alpha-chlorine substituent was present. Crude extracts of strain JD2 contained inducible alcohol dehydrogenase activity that oxidized mono- and dichloroallylalcohols but not trichloroallylalcohol. The enzyme used phenazine methosulfate as an artificial electron acceptor. Further oxidation yielded 2-chloroacrylic acid. The organism also produced hydrolytic dehalogenases converting 2-chloroacetic acid and 2-chloropropionic acid.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Belser N. O., Castro C. E. Biodehalogenation. The metabolism of the nematocides cis- and trans-3-chloroallyl alcohol by a bacterium ioolated from soil. J Agric Food Chem. 1971 Jan-Feb;19(1):23–26. doi: 10.1021/jf60173a047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duine J. A., Frank J., Jongejan J. A. Enzymology of quinoproteins. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1987;59:169–212. doi: 10.1002/9780470123058.ch4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernández-Briera A., Garrido-Pertierra A. A degradation pathway of propionate in Salmonella typhimurium LT-2. Biochimie. 1988 Jun;70(6):757–768. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(88)90105-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardman D. J. Biotransformation of halogenated compounds. Crit Rev Biotechnol. 1991;11(1):1–40. doi: 10.3109/07388559109069182. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartmans S., Jansen M. W., van der Werf M. J., de Bont J. A. Bacterial metabolism of 3-chloroacrylic acid. J Gen Microbiol. 1991 Aug;137(8):2025–2032. doi: 10.1099/00221287-137-8-2025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janssen D. B., Gerritse J., Brackman J., Kalk C., Jager D., Witholt B. Purification and characterization of a bacterial dehalogenase with activity toward halogenated alkanes, alcohols and ethers. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Jan 15;171(1-2):67–72. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb13759.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janssen D. B., Scheper A., Dijkhuizen L., Witholt B. Degradation of halogenated aliphatic compounds by Xanthobacter autotrophicus GJ10. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Mar;49(3):673–677. doi: 10.1128/aem.49.3.673-677.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohler-Staub D., Kohler H. P. Microbial degradation of beta-chlorinated four-carbon aliphatic acids. J Bacteriol. 1989 Mar;171(3):1428–1434. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.3.1428-1434.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsden P. J., Casida J. E. 2-Haloacrylic acids as indicators of mutagenic 2-haloacrolein intermediates in mammalian metabolism of selected promutagens and carcinogens. J Agric Food Chem. 1982 Jul-Aug;30(4):627–631. doi: 10.1021/jf00112a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meier J. R., Ringhand H. P., Coleman W. E., Munch J. W., Streicher R. P., Kaylor W. H., Schenck K. M. Identification of mutagenic compounds formed during chlorination of humic acid. Mutat Res. 1985 Aug-Sep;157(2-3):111–122. doi: 10.1016/0165-1218(85)90105-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Motosugi K., Soda K. Microbial degradation of synthetic organochlorine compounds. Experientia. 1983 Nov 15;39(11):1214–1220. doi: 10.1007/BF01990358. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel J. M., Wood J. C., Leibman K. C. The biotransformation of allyl alcohol and acrolein in rat liver and lung preparations. Drug Metab Dispos. 1980 Sep-Oct;8(5):305–308. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson M., Bull R. J., Olson G. R., Stober J. Carcinogenic activity associated with halogenated acetones and acroleins in the mouse skin assay. Cancer Lett. 1989 Dec;48(3):197–203. doi: 10.1016/0304-3835(89)90118-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen J. D., Segall Y., Casida J. E. Mutagenic potency of haloacroleins and related compounds. Mutat Res. 1980 Jun;78(2):113–119. doi: 10.1016/0165-1218(80)90090-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wegener W. S., Reeves H. C., Ajl S. J. Propionate oxidation in Escherichia coli. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1967 Aug;121(2):440–442. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(67)90098-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weightman A. J., Weightman A. L., Slater J. H. Stereospecificity of 2-monochloropropionate dehalogenation by the two dehalogenases of Pseudomonas putida PP3: evidence for two different dehalogenation mechanisms. J Gen Microbiol. 1982 Aug;128(8):1755–1762. doi: 10.1099/00221287-128-8-1755. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Hylckama Vlieg J. E., Janssen D. B. Bacterial degradation of 3-chloroacrylic acid and the characterization of cis- and trans-specific dehalogenases. Biodegradation. 1991;2(3):139–150. doi: 10.1007/BF00124488. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Wijngaard A. J., Reuvekamp P. T., Janssen D. B. Purification and characterization of haloalcohol dehalogenase from Arthrobacter sp. strain AD2. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jan;173(1):124–129. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.1.124-129.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



