Abstract
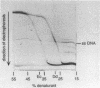
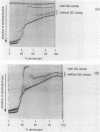
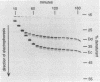
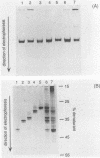
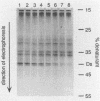
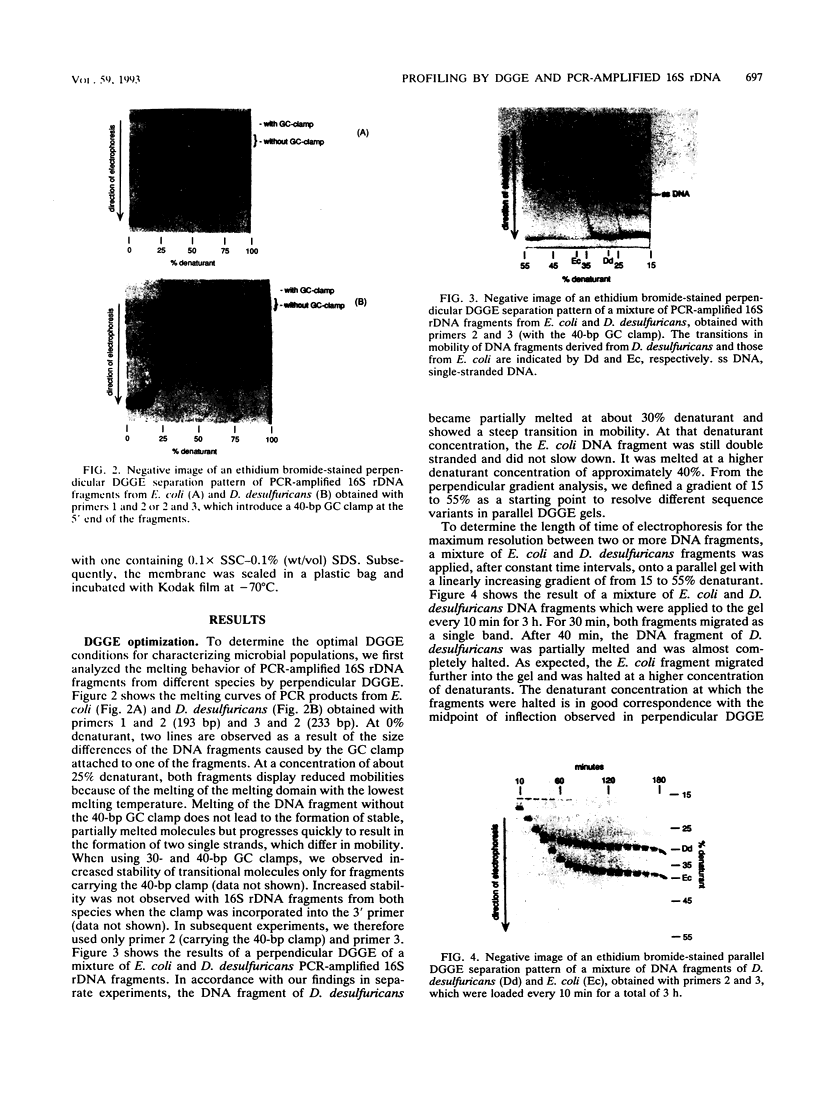
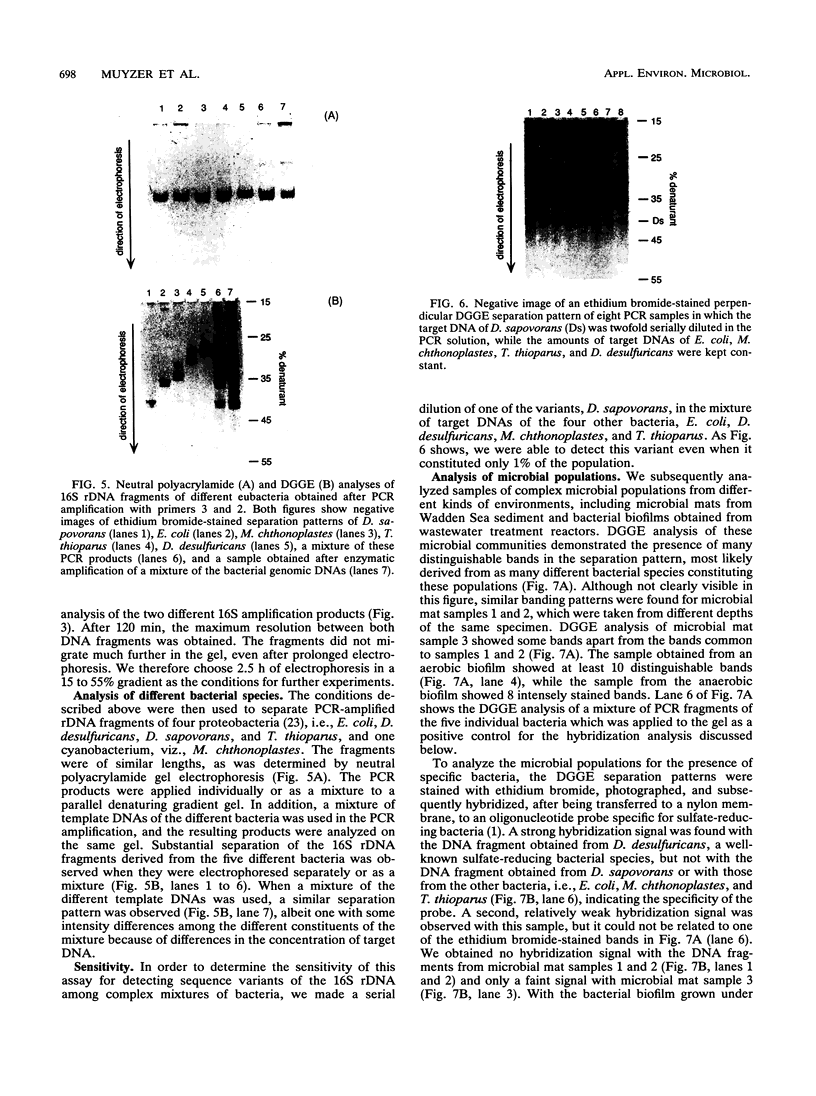
We describe a new molecular approach to analyzing the genetic diversity of complex microbial populations. This technique is based on the separation of polymerase chain reaction-amplified fragments of genes coding for 16S rRNA, all the same length, by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis (DGGE). DGGE analysis of different microbial communities demonstrated the presence of up to 10 distinguishable bands in the separation pattern, which were most likely derived from as many different species constituting these populations, and thereby generated a DGGE profile of the populations. We showed that it is possible to identify constituents which represent only 1% of the total population. With an oligonucleotide probe specific for the V3 region of 16S rRNA of sulfate-reducing bacteria, particular DNA fragments from some of the microbial populations could be identified by hybridization analysis. Analysis of the genomic DNA from a bacterial biofilm grown under aerobic conditions suggests that sulfate-reducing bacteria, despite their anaerobicity, were present in this environment. The results we obtained demonstrate that this technique will contribute to our understanding of the genetic diversity of uncharacterized microbial populations.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amann R. I., Binder B. J., Olson R. J., Chisholm S. W., Devereux R., Stahl D. A. Combination of 16S rRNA-targeted oligonucleotide probes with flow cytometry for analyzing mixed microbial populations. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Jun;56(6):1919–1925. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.6.1919-1925.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amann R. I., Stromley J., Devereux R., Key R., Stahl D. A. Molecular and microscopic identification of sulfate-reducing bacteria in multispecies biofilms. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992 Feb;58(2):614–623. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.2.614-623.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Børresen A. L., Hovig E., Brøgger A. Detection of base mutations in genomic DNA using denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis (DGGE) followed by transfer and hybridization with gene-specific probes. Mutat Res. 1988 Nov;202(1):77–83. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(88)90166-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cariello N. F., Scott J. K., Kat A. G., Thilly W. G., Keohavong P. Resolution of a missense mutant in human genomic DNA by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis and direct sequencing using in vitro DNA amplification: HPRT Munich. Am J Hum Genet. 1988 May;42(5):726–734. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Don R. H., Cox P. T., Wainwright B. J., Baker K., Mattick J. S. 'Touchdown' PCR to circumvent spurious priming during gene amplification. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jul 25;19(14):4008–4008. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.14.4008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer S. G., Lerman L. S. DNA fragments differing by single base-pair substitutions are separated in denaturing gradient gels: correspondence with melting theory. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(6):1579–1583. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.6.1579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer S. G., Lerman L. S. Length-independent separation of DNA restriction fragments in two-dimensional gel electrophoresis. Cell. 1979 Jan;16(1):191–200. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90200-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giovannoni S. J., Britschgi T. B., Moyer C. L., Field K. G. Genetic diversity in Sargasso Sea bacterioplankton. Nature. 1990 May 3;345(6270):60–63. doi: 10.1038/345060a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giovannoni S. J., Turner S., Olsen G. J., Barns S., Lane D. J., Pace N. R. Evolutionary relationships among cyanobacteria and green chloroplasts. J Bacteriol. 1988 Aug;170(8):3584–3592. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.8.3584-3592.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray M., Charpentier A., Walsh K., Wu P., Bender W. Mapping point mutations in the Drosophila rosy locus using denaturing gradient gel blots. Genetics. 1991 Jan;127(1):139–149. doi: 10.1093/genetics/127.1.139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerman L. S., Fischer S. G., Hurley I., Silverstein K., Lumelsky N. Sequence-determined DNA separations. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1984;13:399–423. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.13.060184.002151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medlin L., Elwood H. J., Stickel S., Sogin M. L. The characterization of enzymatically amplified eukaryotic 16S-like rRNA-coding regions. Gene. 1988 Nov 30;71(2):491–499. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90066-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers R. M., Fischer S. G., Lerman L. S., Maniatis T. Nearly all single base substitutions in DNA fragments joined to a GC-clamp can be detected by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 May 10;13(9):3131–3145. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.9.3131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers R. M., Maniatis T., Lerman L. S. Detection and localization of single base changes by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis. Methods Enzymol. 1987;155:501–527. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)55033-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neefs J. M., Van de Peer Y., Hendriks L., De Wachter R. Compilation of small ribosomal subunit RNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Apr 25;18 (Suppl):2237–2317. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.suppl.2237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Scharf S., Faloona F., Mullis K. B., Horn G. T., Erlich H. A., Arnheim N. Enzymatic amplification of beta-globin genomic sequences and restriction site analysis for diagnosis of sickle cell anemia. Science. 1985 Dec 20;230(4732):1350–1354. doi: 10.1126/science.2999980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheffield V. C., Cox D. R., Lerman L. S., Myers R. M. Attachment of a 40-base-pair G + C-rich sequence (GC-clamp) to genomic DNA fragments by the polymerase chain reaction results in improved detection of single-base changes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jan;86(1):232–236. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.1.232. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uitterlinden A. G., Slagboom P. E., Knook D. L., Vijg J. Two-dimensional DNA fingerprinting of human individuals. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(8):2742–2746. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.8.2742. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward D. M., Weller R., Bateson M. M. 16S rRNA sequences reveal numerous uncultured microorganisms in a natural community. Nature. 1990 May 3;345(6270):63–65. doi: 10.1038/345063a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woese C. R. Bacterial evolution. Microbiol Rev. 1987 Jun;51(2):221–271. doi: 10.1128/mr.51.2.221-271.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]