Abstract
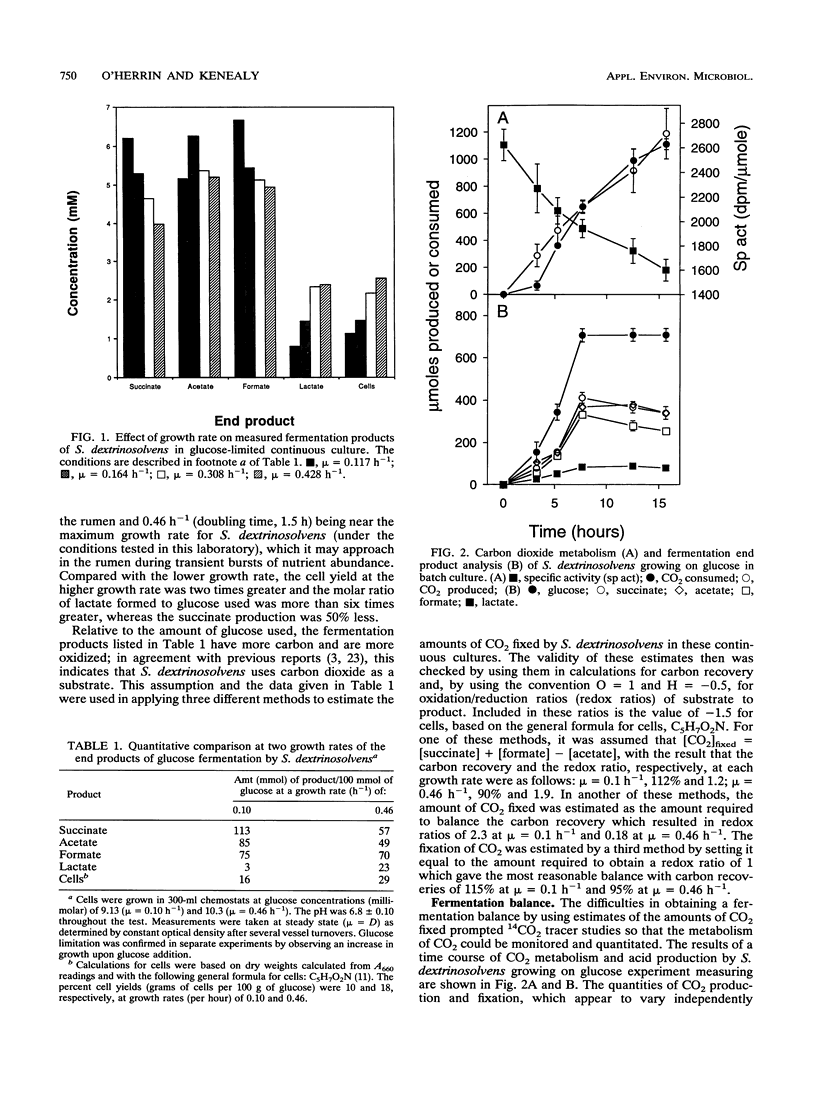
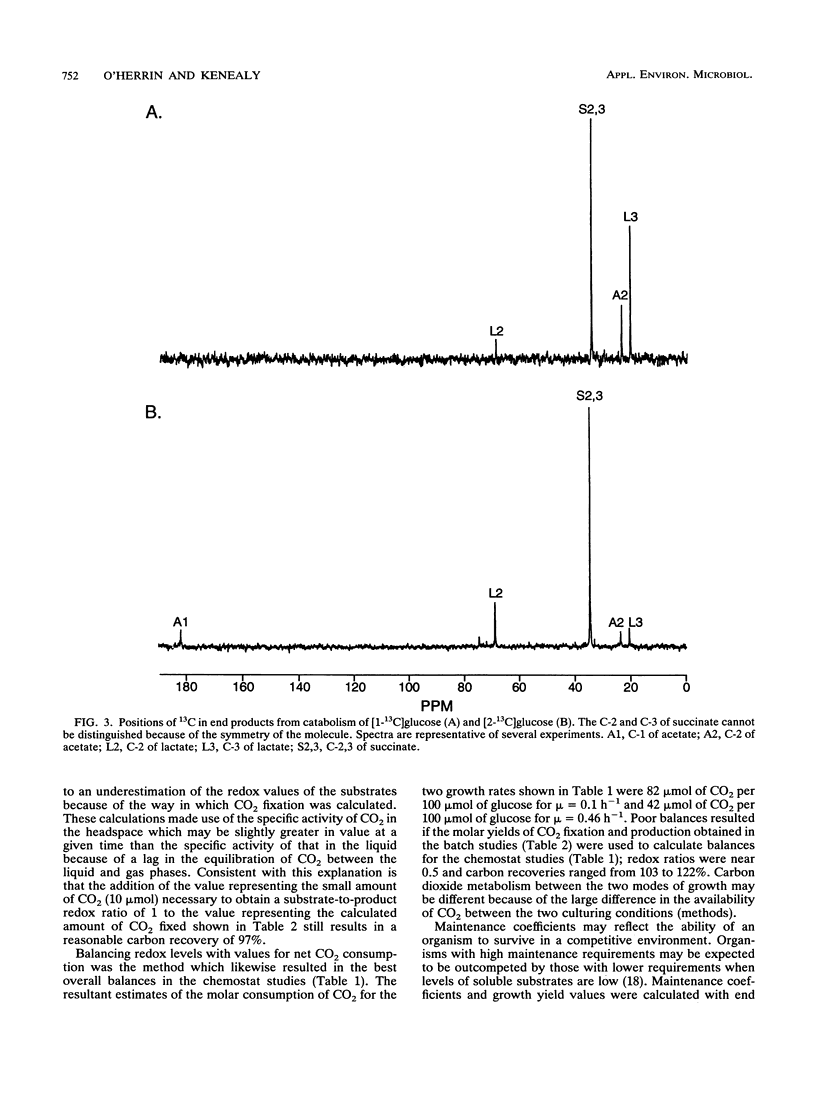
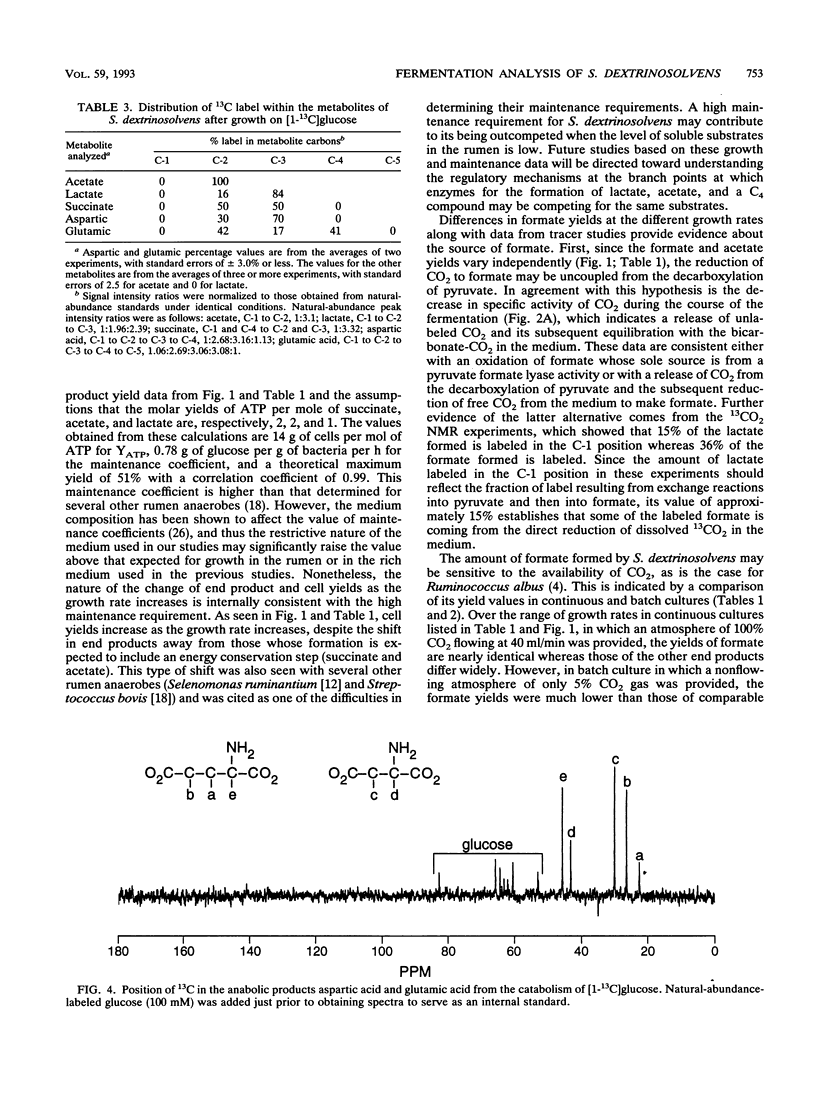
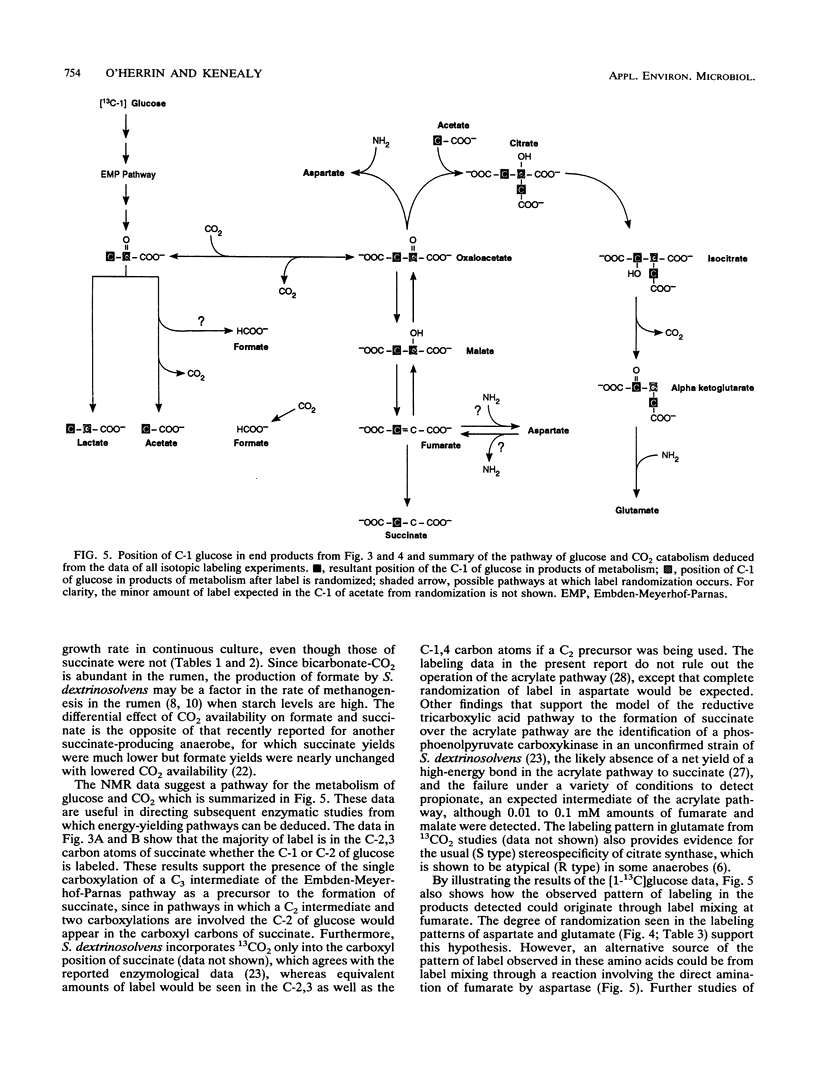
Growth rates and culture conditions affect the molar yields of catabolic end products and cells of Succinivibrio dextrinosolvens growing on glucose. When growth in chemostats occurred, a trend toward decreased succinate and acetate formation, increased lactate formation, and a higher yield of cells correlated with an increase in the growth rate. End product and cellular yields on defined medium indicate a high maintenance requirement for S. dextrinosolvens and are consistent with energy conservation steps during the formation of acetate and succinate. Simultaneous carbon dioxide consumption and production were determined from batch studies with NaH14CO3, and the amounts were used to calculate a fermentation balance. These data also indicated that CO2 consumption lags behind CO2 production early in the growth phase, becoming equivalent to it toward stationary phase. Significantly more CO2 was fixed by S. dextrinosolvens when the organism was cultured in chemostats sparged with CO2. Formate is in part derived from free CO2 in the medium, as shown by 13C nuclear magnetic resonance studies, and may be sensitive to CO2 availability. Nuclear magnetic resonance data are consistent with the carboxylation of a C3 intermediate of the Embden-Meyerhof-Parnas pathway of glycolysis to a C4 compound to eventually form succinate.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BRYANT M. P. Bacterial species of the rumen. Bacteriol Rev. 1959 Sep;23(3):125–153. doi: 10.1128/br.23.3.125-153.1959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRYANT M. P., SMALL N. Characteristics of two new genera of anaerobic curved rods isolated from the rumen of cattle. J Bacteriol. 1956 Jul;72(1):22–26. doi: 10.1128/jb.72.1.22-26.1956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryant M. P. Normal flora--rumen bacteria. Am J Clin Nutr. 1970 Nov;23(11):1440–1450. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/23.11.1440. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dehority B. A. Carbon dioxide requirement of various species of rumen bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1971 Jan;105(1):70–76. doi: 10.1128/jb.105.1.70-76.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomez-Alarcon R. A., O'Dowd C., Leedle J. A., Bryant M. P. 1,4-Naphthoquinone and other nutrient requirements of Succinivibrio dextrinosolvens. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Aug;44(2):346–350. doi: 10.1128/aem.44.2.346-350.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottschalk G., Barker H. A. Synthesis of glutamate and citrate by Clostridium kluyveri. A new type of citrate synthase. Biochemistry. 1966 Apr;5(4):1125–1133. doi: 10.1021/bi00868a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howlett M. R., Mountfort D. O., Turner K. W., Roberton A. M. Metabolism and growth yields in Bacteroides ruminicola strain b14. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Aug;32(2):274–283. doi: 10.1128/aem.32.2.274-283.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hungate R. E., Smith W., Bauchop T., Yu I., Rabinowitz J. C. Formate as an intermediate in the bovine rumen fermentation. J Bacteriol. 1970 May;102(2):389–397. doi: 10.1128/jb.102.2.389-397.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenealy W., Zeikus J. G. Influence of corrinoid antagonists on methanogen metabolism. J Bacteriol. 1981 Apr;146(1):133–140. doi: 10.1128/jb.146.1.133-140.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovley D. R., Greening R. C., Ferry J. G. Rapidly growing rumen methanogenic organism that synthesizes coenzyme M and has a high affinity for formate. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Jul;48(1):81–87. doi: 10.1128/aem.48.1.81-87.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melville S. B., Michel T. A., Macy J. M. Regulation of carbon flow in Selenomonas ruminantium grown in glucose-limited continuous culture. J Bacteriol. 1988 Nov;170(11):5305–5311. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.11.5305-5311.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel T. A., Macy J. M. Generation of a membrane potential by sodium-dependent succinate efflux in Selenomonas ruminantium. J Bacteriol. 1990 Mar;172(3):1430–1435. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.3.1430-1435.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson D. R., Zeikus J. G. Rapid method for the radioisotopic analysis of gaseous end products of anaerobic metabolism. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Aug;28(2):258–261. doi: 10.1128/am.28.2.258-261.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell J. B., Baldwin R. L. Comparison of maintenance energy expenditures and growth yields among several rumen bacteria grown on continuous culture. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Mar;37(3):537–543. doi: 10.1128/aem.37.3.537-543.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell J. B., Baldwin R. L. Comparison of substrate affinities among several rumen bacteria: a possible determinant of rumen bacterial competition. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Mar;37(3):531–536. doi: 10.1128/aem.37.3.531-536.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell J. B., Baldwin R. L. Substrate preferences in rumen bacteria: evidence of catabolite regulatory mechanisms. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Aug;36(2):319–329. doi: 10.1128/aem.36.2.319-329.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell J. B., Delfino F. J., Baldwin R. L. Effects of combinations of substrates on maximum growth rates of several rumen bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Mar;37(3):544–549. doi: 10.1128/aem.37.3.544-549.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell J. B., Hespell R. B. Microbial rumen fermentation. J Dairy Sci. 1981 Jun;64(6):1153–1169. doi: 10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(81)82694-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell J. B., Sharp W. M., Baldwin R. L. The effect of pH on maximum bacterial growth rate and its possible role as a determinant of bacterial competition in the rumen. J Anim Sci. 1979 Feb;48(2):251–255. doi: 10.2527/jas1979.482251x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuelov N. S., Lamed R., Lowe S., Zeikus J. G. Influence of CO(2)-HCO(3) Levels and pH on Growth, Succinate Production, and Enzyme Activities of Anaerobiospirillum succiniciproducens. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Oct;57(10):3013–3019. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.10.3013-3019.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheifinger C. C., Wolin M. J. Propionate formation from cellulose and soluble sugars by combined cultures of Bacteroides succinogenes and Selenomonas ruminantium. Appl Microbiol. 1973 Nov;26(5):789–795. doi: 10.1128/am.26.5.789-795.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stouthamer A. H., Bettenhaussen C. Utilization of energy for growth and maintenance in continuous and batch cultures of microorganisms. A reevaluation of the method for the determination of ATP production by measuring molar growth yields. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Feb 12;301(1):53–70. doi: 10.1016/0304-4173(73)90012-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tholozan J. L., Touzel J. P., Samain E., Grivet J. P., Prensier G., Albagnac G. Clostridium neopropionicum sp. nov., a strict anaerobic bacterium fermenting ethanol to propionate through acrylate pathway. Arch Microbiol. 1992;157(3):249–257. doi: 10.1007/BF00245158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallnöfer P., Baldwin R. L. Pathway of propionate formation in Bacteroides ruminicola. J Bacteriol. 1967 Jan;93(1):504–505. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.1.504-505.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weimer P. J., Zeikus J. G. Acetate assimilation pathway of Methanosarcina barkeri. J Bacteriol. 1979 Jan;137(1):332–339. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.1.332-339.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



