Abstract
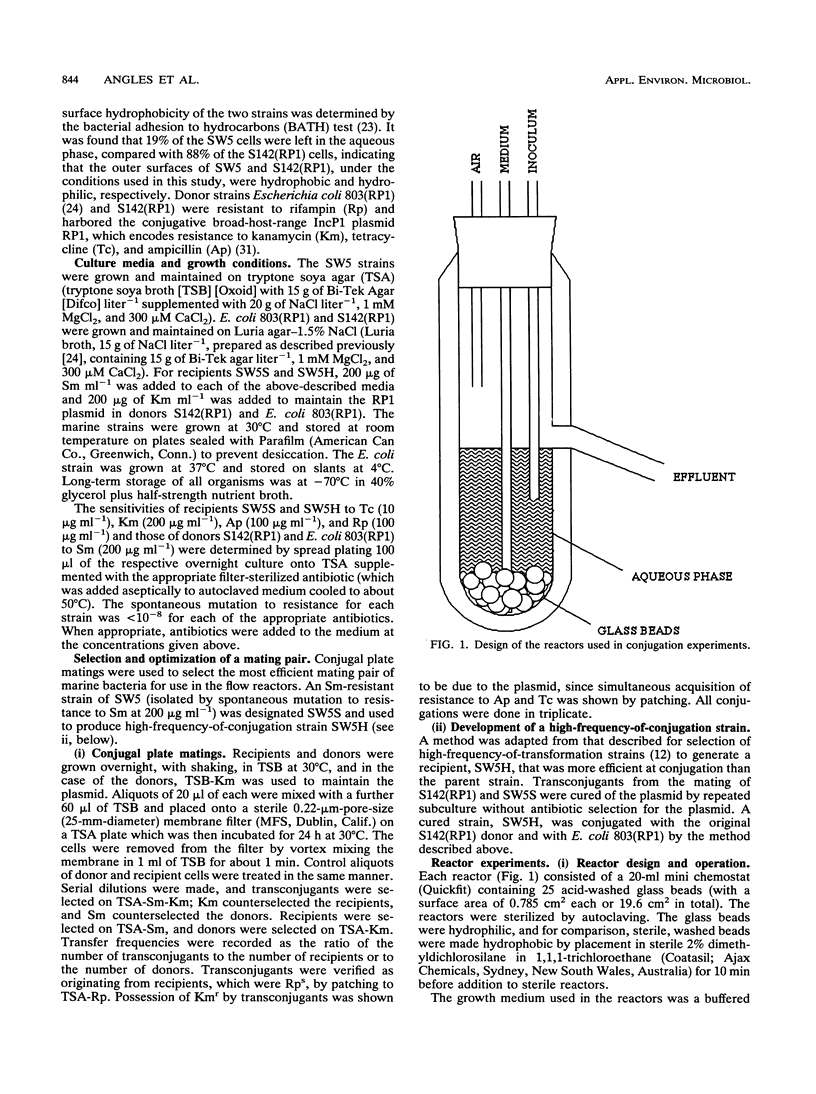
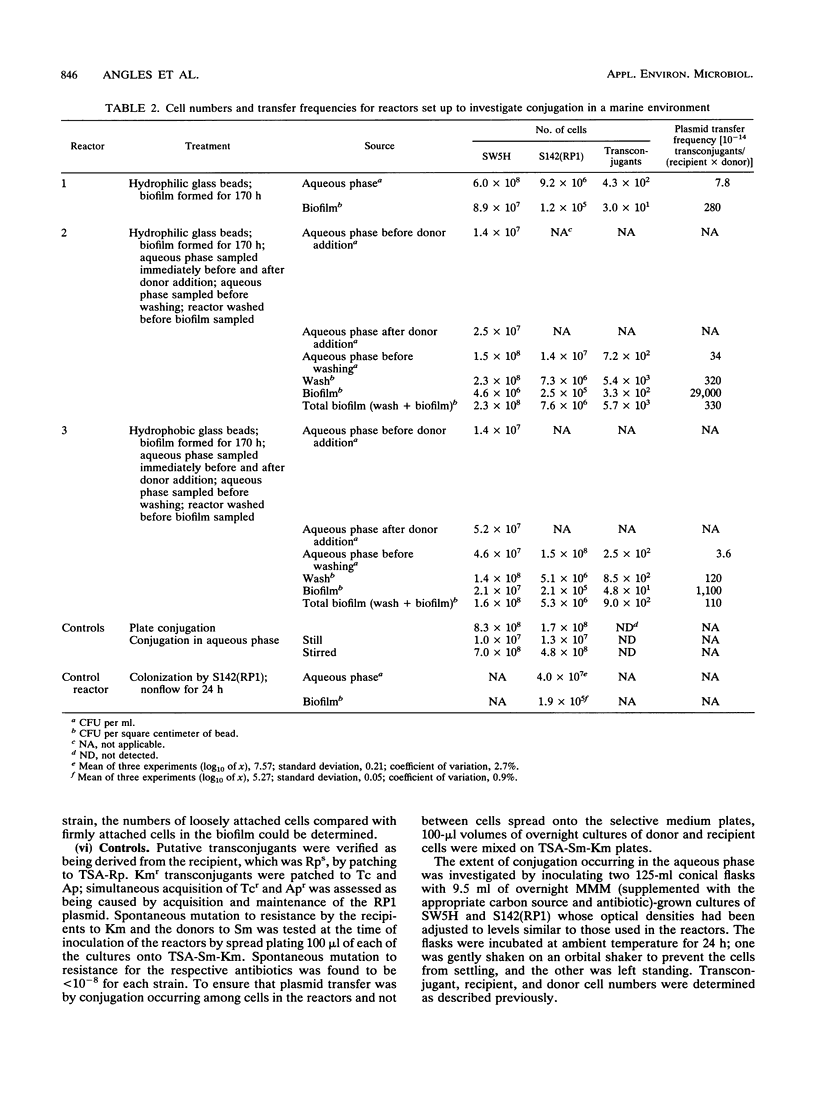
Plasmid transfer of broad-host-range plasmid RP1 from marine Vibrio sp. strain S14 to marine strain SW5 under optimum conditions on the surface of nutrient plates was improved 2 orders of magnitude by using the plasmid transfer process to select an SW5 recipient more efficient than the wild type in receiving and/or maintaining the plasmid. This recipient strain, SW5H, was used to form biofilms under flow conditions on the surfaces of glass beads in reactors. The S142(RP1) donor strain was introduced to the reactors after either 48 or 170 h of biofilm formation, and production of transconjugants in the aqueous phases and biofilms without selection pressure was assessed. Plasmid transfer to the recipient cells in the biofilm was detected for biofilms formed for 170 h but not in those formed for 48 h. The plasmid transfer frequency was significantly higher (P < 0.05) among cells attached to the bead surfaces in the biofilm than among cells in the aqueous phase.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Absolom D. R., Lamberti F. V., Policova Z., Zingg W., van Oss C. J., Neumann A. W. Surface thermodynamics of bacterial adhesion. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Jul;46(1):90–97. doi: 10.1128/aem.46.1.90-97.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altherr M. R., Kasweck K. L. In situ studies with membrane diffusion chambers of antibiotic resistance transfer in Escherichia coli. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Oct;44(4):838–843. doi: 10.1128/aem.44.4.838-843.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bale M. J., Day M. J., Fry J. C. Novel method for studying plasmid transfer in undisturbed river epilithon. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Nov;54(11):2756–2758. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.11.2756-2758.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bale M. J., Fry J. C., Day M. J. Plasmid transfer between strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa on membrane filters attached to river stones. J Gen Microbiol. 1987 Nov;133(11):3099–3107. doi: 10.1099/00221287-133-11-3099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bale M. J., Fry J. C., Day M. J. Transfer and occurrence of large mercury resistance plasmids in river epilithon. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Apr;54(4):972–978. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.4.972-978.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bentjen S. A., Fredrickson J. K., Van Voris P., Li S. W. Intact soil-core microcosms for evaluating the fate and ecological impact of the release of genetically engineered microorganisms. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Jan;55(1):198–202. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.1.198-202.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley D. E., Taylor D. E., Cohen D. R. Specification of surface mating systems among conjugative drug resistance plasmids in Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1980 Sep;143(3):1466–1470. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.3.1466-1470.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fattom A., Shilo M. Hydrophobicity as an adhesion mechanism of benthic cyanobacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Jan;47(1):135–143. doi: 10.1128/aem.47.1.135-143.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez-Astorga A., Muela A., Cisterna R., Iriberri J., Barcina I. Biotic and abiotic factors affecting plasmid transfer in Escherichia coli strains. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992 Jan;58(1):392–398. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.1.392-398.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frischer M. E., Thurmond J. M., Paul J. H. Natural plasmid transformation in a high-frequency-of-transformation marine Vibrio strain. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Nov;56(11):3439–3444. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.11.3439-3444.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fulthorpe R. R., Wyndham R. C. Survival and activity of a 3-chlorobenzoate-catabolic genotype in a natural system. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Jun;55(6):1584–1590. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.6.1584-1590.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fulthorpe R. R., Wyndham R. C. Transfer and Expression of the Catabolic Plasmid pBRC60 in Wild Bacterial Recipients in a Freshwater Ecosystem. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 May;57(5):1546–1553. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.5.1546-1553.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gauthier M. J., Cauvin F., Breittmayer J. P. Influence of salts and temperature on the transfer of mercury resistance from a marine pseudomonad to Escherichia coli. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Jul;50(1):38–40. doi: 10.1128/aem.50.1.38-40.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall K. C. Adsorption and adhesion processes in microbial growth at interfaces. Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 1986 Jun;25(1):59–86. doi: 10.1016/0001-8686(86)80002-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sizemore R. K., Colwell R. R. Plasmids carried by antibiotic-resistant marine bacteria. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Sep;12(3):373–382. doi: 10.1128/aac.12.3.373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas C. M., Smith C. A. Incompatibility group P plasmids: genetics, evolution, and use in genetic manipulation. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1987;41:77–101. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.41.100187.000453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Loosdrecht M. C., Lyklema J., Norde W., Schraa G., Zehnder A. J. The role of bacterial cell wall hydrophobicity in adhesion. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Aug;53(8):1893–1897. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.8.1893-1897.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



