Abstract
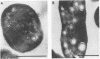
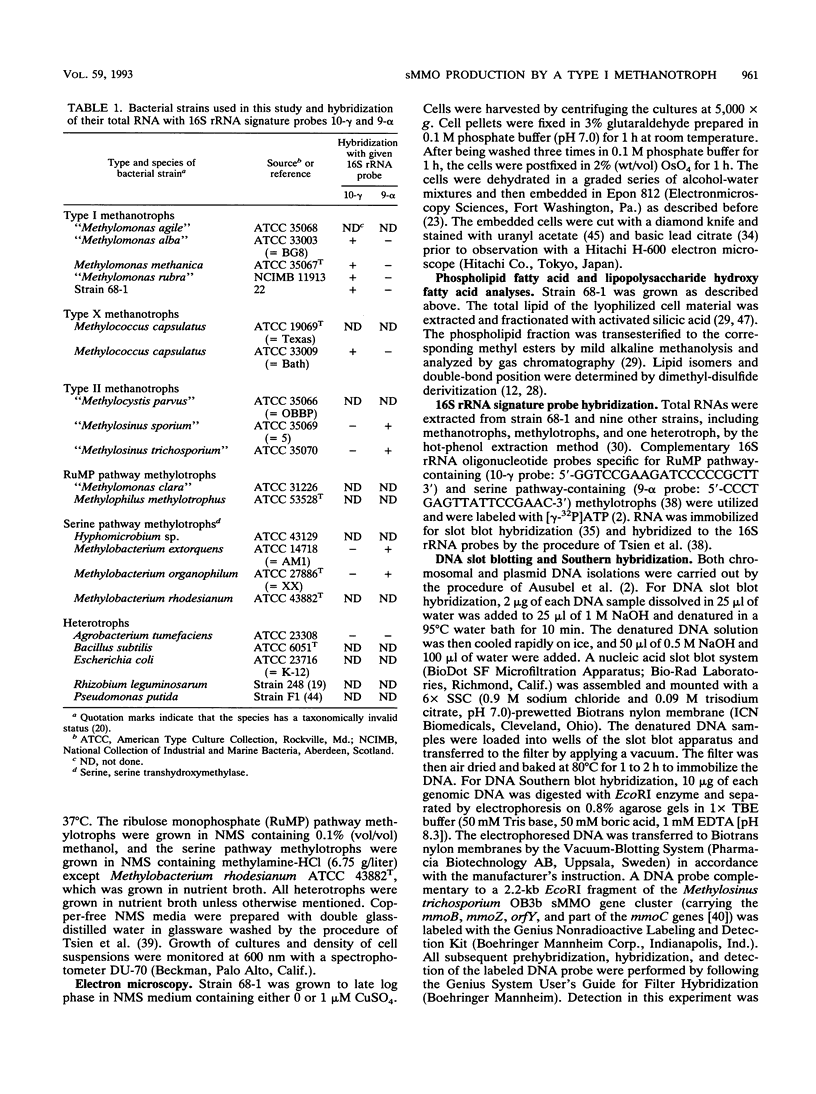
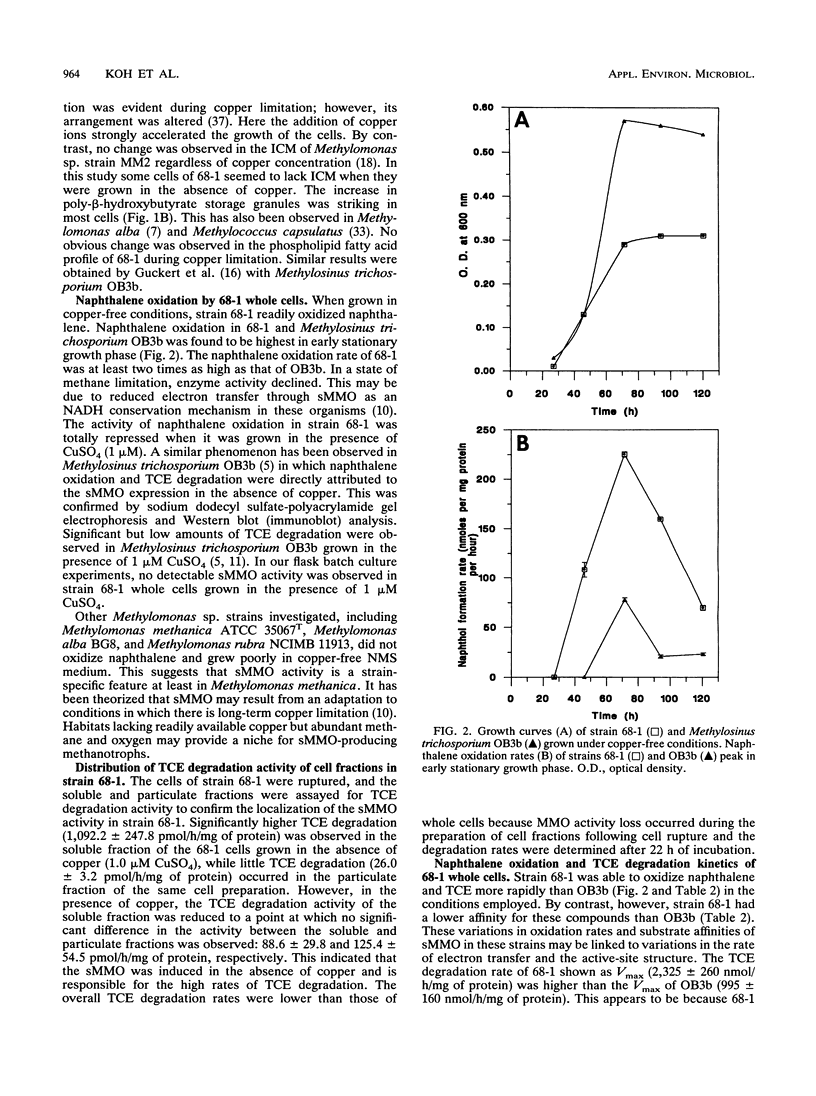
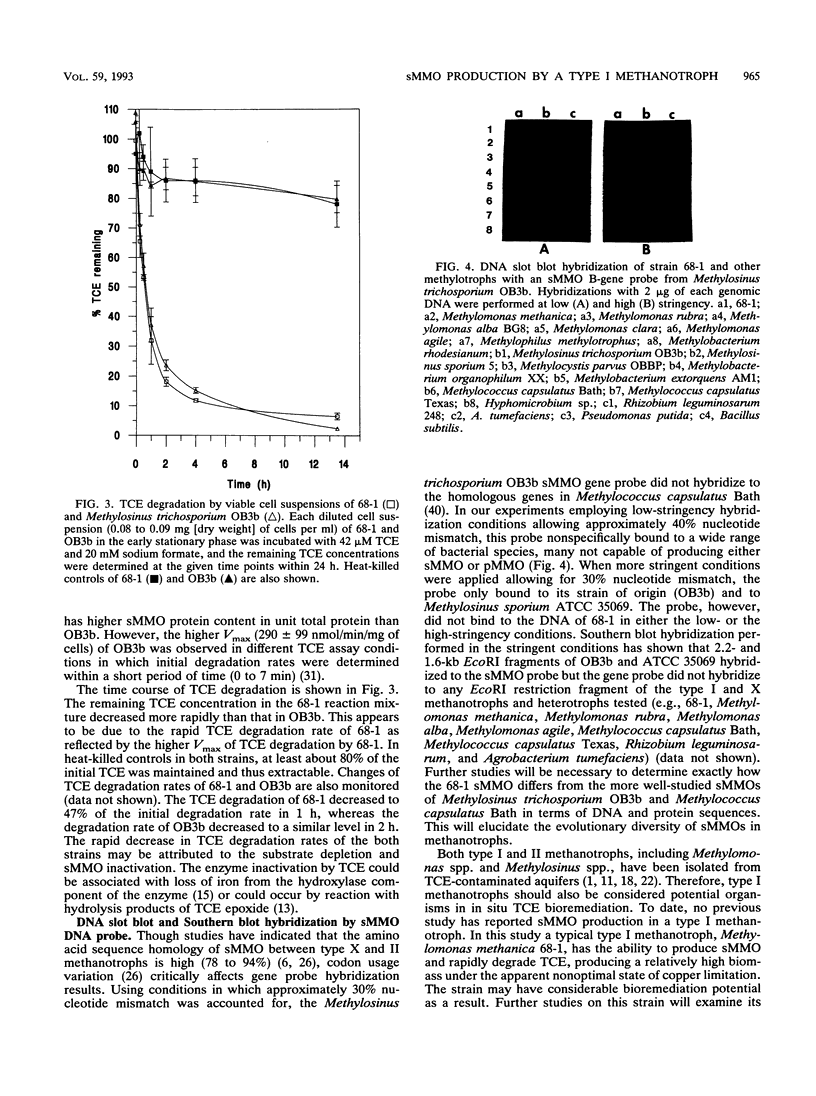
A methanotroph (strain 68-1), originally isolated from a trichloroethylene (TCE)-contaminated aquifer, was identified as the type I methanotroph Methylomonas methanica on the basis of intracytoplasmic membrane ultrastructure, phospholipid fatty acid profile, and 16S rRNA signature probe hybridization. Strain 68-1 was found to oxidize naphthalene and TCE via a soluble methane monooxygenase (sMMO) and thus becomes the first type I methanotroph known to be able to produce this enzyme. The specific whole-cell sMMO activity of 68-1, as measured by the naphthalene oxidation assay and by TCE biodegradation, was comparatively higher than sMMO activity levels in Methylosinus trichosporium OB3b grown in the same copper-free conditions. The maximal naphthalene oxidation rates of Methylomonas methanica 68-1 and Methylosinus trichosporium OB3b were 551 ± 27 and 321 ± 16 nmol h-1 mg of protein -1, respectively. The maximal TCE degradation rates of Methylomonas methanica 68-1 and Methylosinus trichosporium OB3b were 2,325 ± 260 and 995 ± 160 nmol h-1 mg of protein-1, respectively. The substrate affinity of 68-1 sMMO to naphthalene (Km, 70 ± 4 μM) and TCE (Km, 225 ± 13 μM), however, was comparatively lower than that of the sMMO of OB3b, which had affinities of 40 ± 3 and 126 ± 8 μM, respectively. Genomic DNA slot and Southern blot analyses with an sMMO gene probe from Methylosinus trichosporium OB3b showed that the sMMO genes of 68-1 have little genetic homology to those of OB3b. This result may indicate the evolutionary diversification of the sMMOs.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alvarez-Cohen L., McCarty P. L., Boulygina E., Hanson R. S., Brusseau G. A., Tsien H. C. Characterization of a methane-utilizing bacterium from a bacterial consortium that rapidly degrades trichloroethylene and chloroform. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992 Jun;58(6):1886–1893. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.6.1886-1893.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brusseau G. A., Tsien H. C., Hanson R. S., Wackett L. P. Optimization of trichloroethylene oxidation by methanotrophs and the use of a colorimetric assay to detect soluble methane monooxygenase activity. Biodegradation. 1990;1(1):19–29. doi: 10.1007/BF00117048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cardy D. L., Laidler V., Salmond G. P., Murrell J. C. Molecular analysis of the methane monooxygenase (MMO) gene cluster of Methylosinus trichosporium OB3b. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Feb;5(2):335–342. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb02114.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins M. L., Buchholz L. A., Remsen C. C. Effect of Copper on Methylomonas albus BG8. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Apr;57(4):1261–1264. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.4.1261-1264.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox B. G., Borneman J. G., Wackett L. P., Lipscomb J. D. Haloalkene oxidation by the soluble methane monooxygenase from Methylosinus trichosporium OB3b: mechanistic and environmental implications. Biochemistry. 1990 Jul 10;29(27):6419–6427. doi: 10.1021/bi00479a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green J., Dalton H. Substrate specificity of soluble methane monooxygenase. Mechanistic implications. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 25;264(30):17698–17703. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guckert J. B., Ringelberg D. B., White D. C., Hanson R. S., Bratina B. J. Membrane fatty acids as phenotypic markers in the polyphasic taxonomy of methylotrophs within the Proteobacteria. J Gen Microbiol. 1991 Nov;137(11):2631–2641. doi: 10.1099/00221287-137-11-2631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanson R. S., Wattenberg E. V. Ecology of methylotrophic bacteria. Biotechnology. 1991;18:325–348. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-7506-9188-8.50021-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUFT J. H. Improvements in epoxy resin embedding methods. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1961 Feb;9:409–414. doi: 10.1083/jcb.9.2.409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Little C. D., Palumbo A. V., Herbes S. E., Lidstrom M. E., Tyndall R. L., Gilmer P. J. Trichloroethylene biodegradation by a methane-oxidizing bacterium. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Apr;54(4):951–956. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.4.951-956.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MUNKRES K. D., RICHARDS F. M. THE PURIFICATION AND PROPERTIES OF NEUROSPORA MALATE DEHYDROGENASE. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1965 Mar;109:466–479. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(65)90391-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oldenhuis R., Oedzes J. Y., van der Waarde J. J., Janssen D. B. Kinetics of chlorinated hydrocarbon degradation by Methylosinus trichosporium OB3b and toxicity of trichloroethylene. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Jan;57(1):7–14. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.1.7-14.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oldenhuis R., Vink R. L., Janssen D. B., Witholt B. Degradation of chlorinated aliphatic hydrocarbons by Methylosinus trichosporium OB3b expressing soluble methane monooxygenase. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Nov;55(11):2819–2826. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.11.2819-2826.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REYNOLDS E. S. The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1963 Apr;17:208–212. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.1.208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeda K., Tanaka K. Ultrastructure of intracytoplasmic membranes of Methanomonas margaritae cells grown under different conditions. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1980;46(1):15–25. doi: 10.1007/BF00422225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsien H. C., Bratina B. J., Tsuji K., Hanson R. S. Use of oligodeoxynucleotide signature probes for identification of physiological groups of methylotrophic bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Sep;56(9):2858–2865. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.9.2858-2865.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsien H. C., Brusseau G. A., Hanson R. S., Waclett L. P. Biodegradation of trichloroethylene by Methylosinus trichosporium OB3b. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Dec;55(12):3155–3161. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.12.3155-3161.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsien H. C., Hanson R. S. Soluble methane monooxygenase component B gene probe for identification of methanotrophs that rapidly degrade trichloroethylene. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992 Mar;58(3):953–960. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.3.953-960.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuji K., Tsien H. C., Hanson R. S., DePalma S. R., Scholtz R., LaRoche S. 16S ribosomal RNA sequence analysis for determination of phylogenetic relationship among methylotrophs. J Gen Microbiol. 1990 Jan;136(1):1–10. doi: 10.1099/00221287-136-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WATSON M. L. Staining of tissue sections for electron microscopy with heavy metals. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1958 Jul 25;4(4):475–478. doi: 10.1083/jcb.4.4.475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wackett L. P., Gibson D. T. Degradation of trichloroethylene by toluene dioxygenase in whole-cell studies with Pseudomonas putida F1. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Jul;54(7):1703–1708. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.7.1703-1708.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wackett L. P., Gibson D. T. Rapid method for detection and quantitation of hydroxylated aromatic intermediates produced by microorganisms. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Mar;45(3):1144–1147. doi: 10.1128/aem.45.3.1144-1147.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]