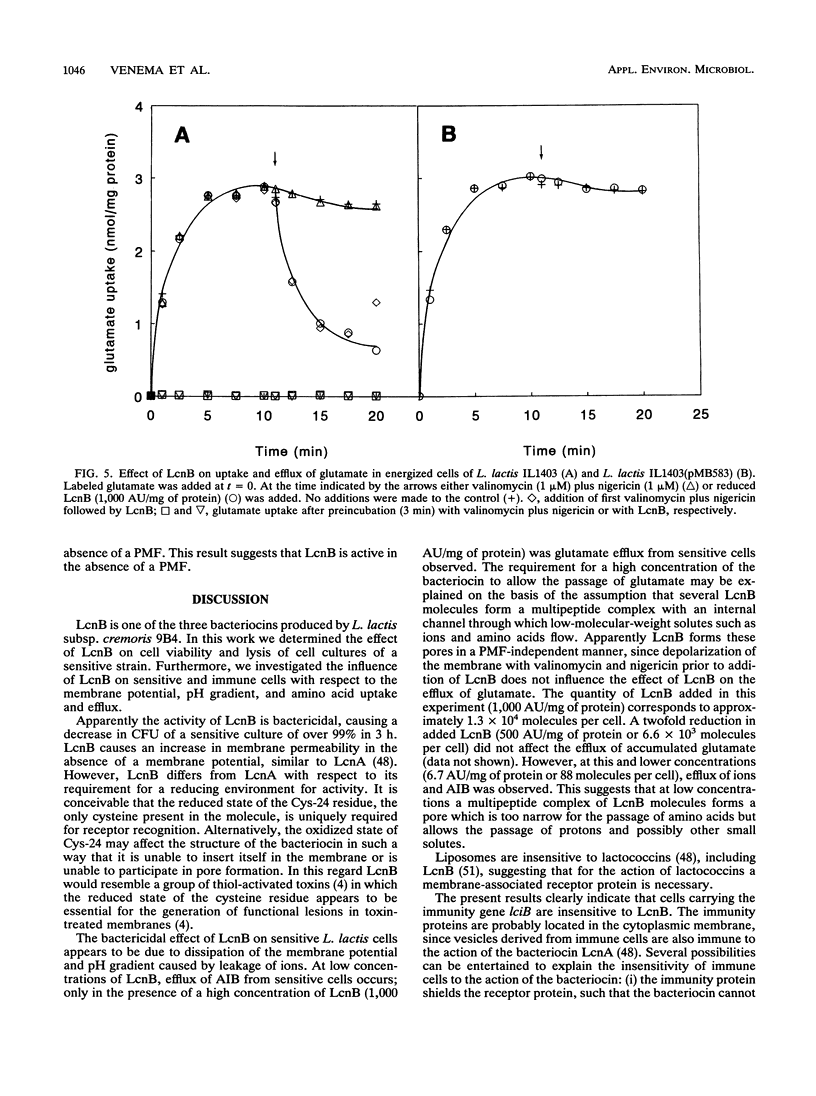
Abstract
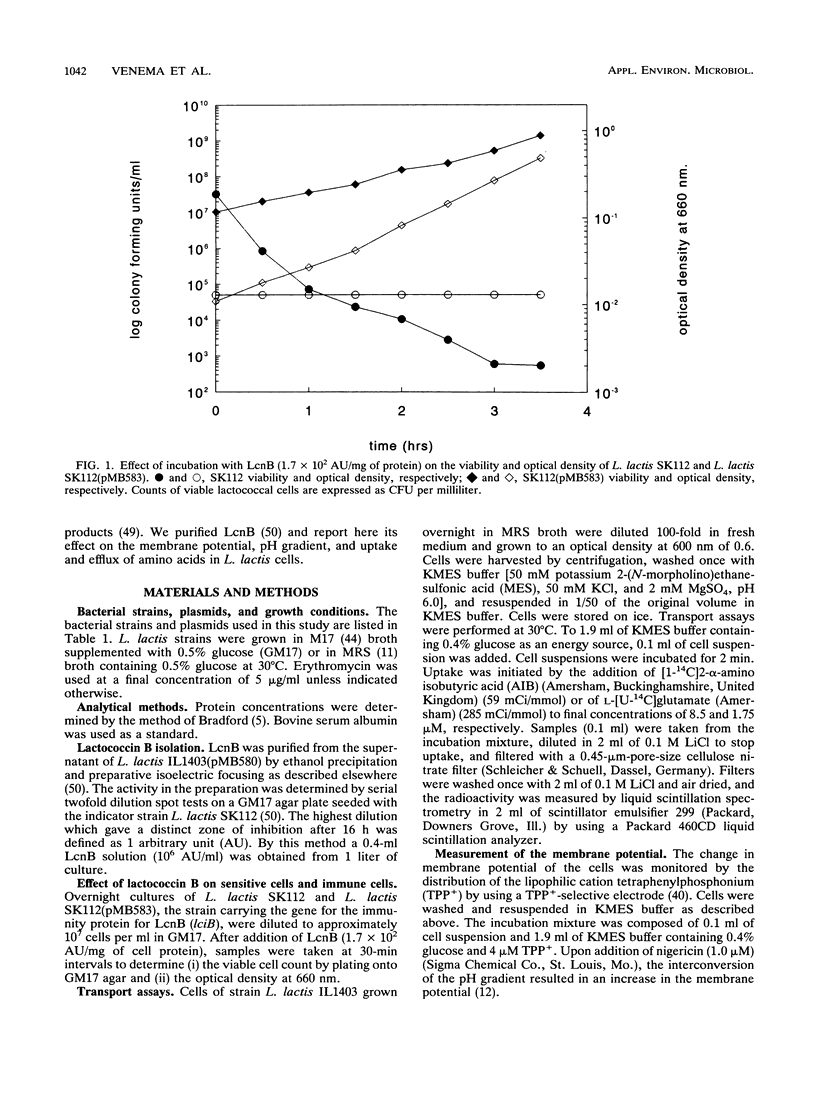
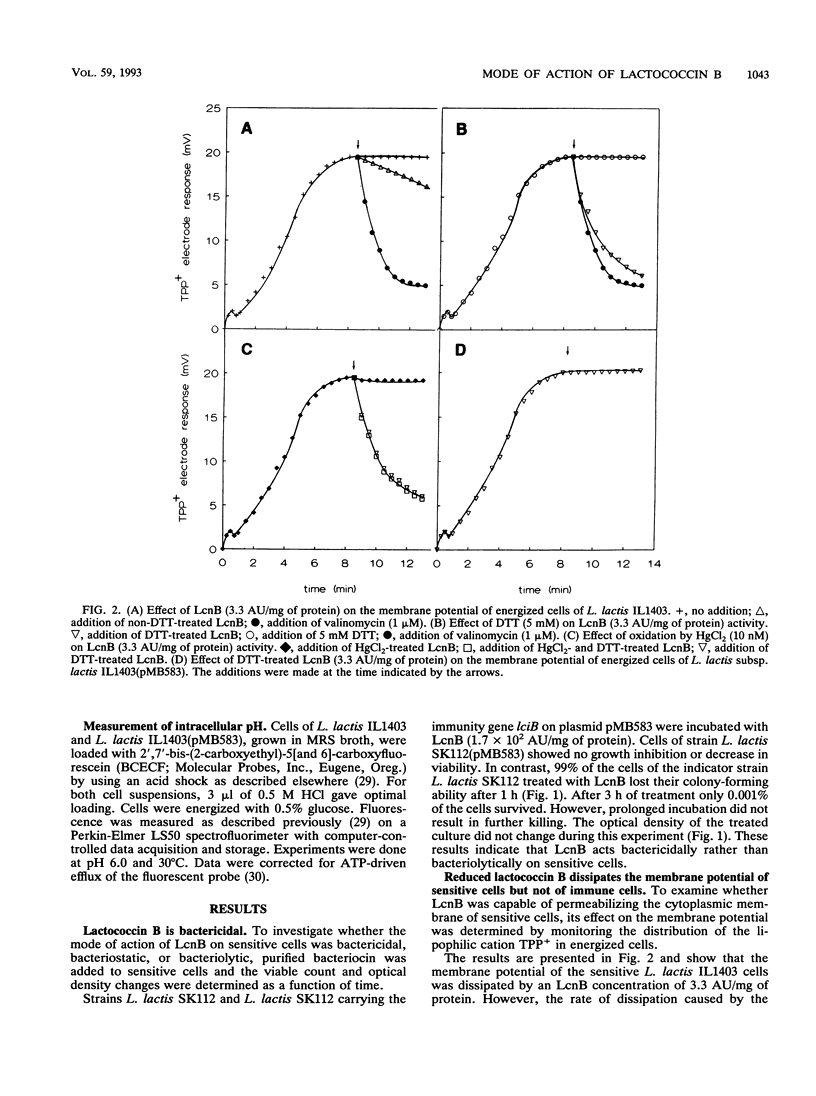
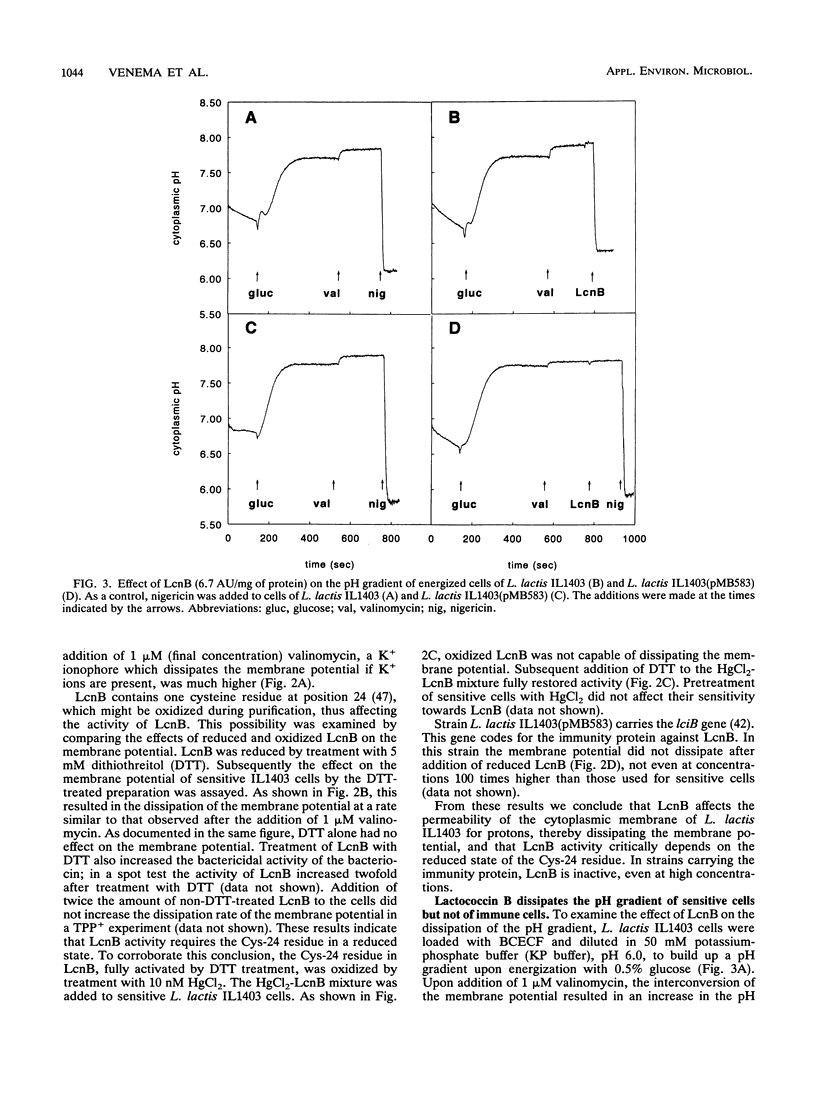
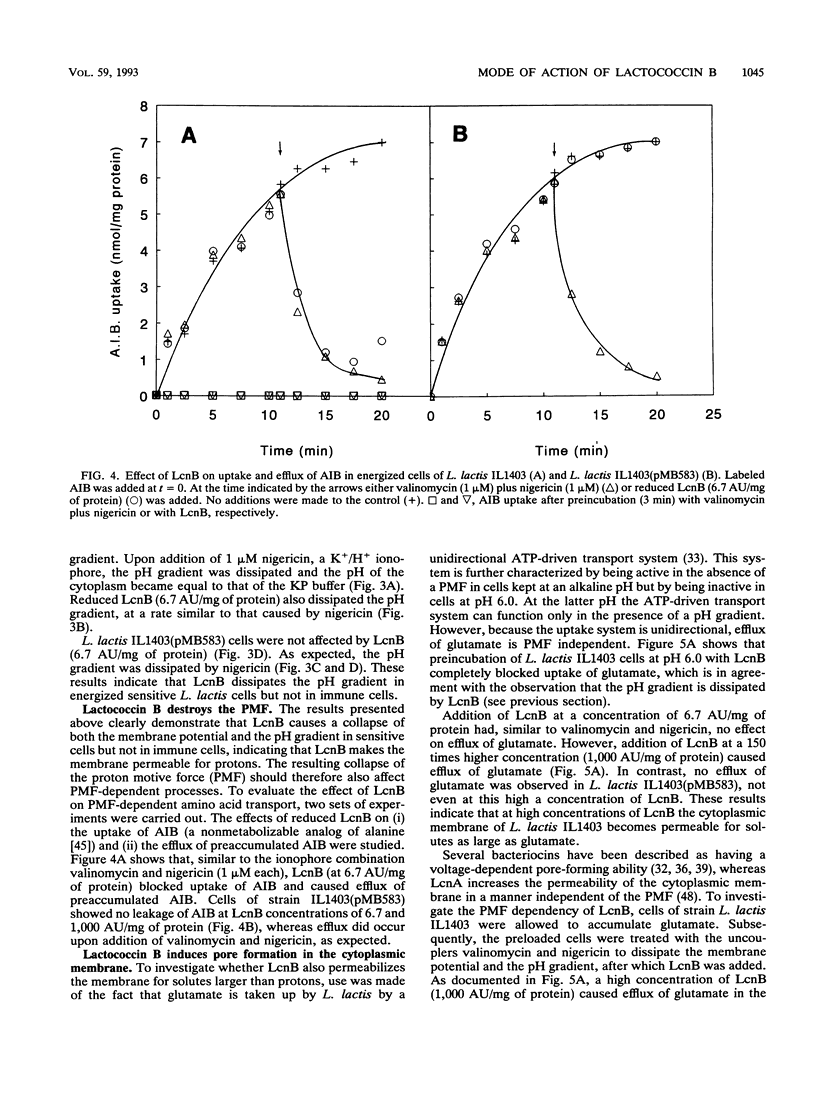
Lactococcin B (LcnB) is a small, hydrophobic, positively charged bacteriocin produced by Lactococcus lactis subsp. cremoris 9B4. Purified LcnB has a bactericidal effect on sensitive L. lactis cells by dissipating the proton motive force and causing leakage of intracellular substrates. The activity of LcnB depends on the reduced state of the Cys-24 residue. Uptake and efflux studies of different solutes suggest that LcnB forms pores in the cytoplasmic membrane of sensitive L. lactis cells in the absence of a proton motive force. At low concentrations of LcnB, efflux of those ions and amino acids which are taken up by proton motive force-driven systems was observed. However, a 150-fold higher LcnB concentration was required for efflux of glutamate, previously taken up via a unidirectional ATP-driven transport system. Strains carrying the genetic information for the immunity protein against LcnB were not affected by LcnB. The proton motive force of immune cells was not dissipated, and no leakage of intracellular substrates could be detected.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahn C., Stiles M. E. Plasmid-associated bacteriocin production by a strain of Carnobacterium piscicola from meat. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Aug;56(8):2503–2510. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.8.2503-2510.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhunia A. K., Johnson M. C., Ray B. Purification, characterization and antimicrobial spectrum of a bacteriocin produced by Pediococcus acidilactici. J Appl Bacteriol. 1988 Oct;65(4):261–268. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1988.tb01893.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulnois G. J., Paton J. C., Mitchell T. J., Andrew P. W. Structure and function of pneumolysin, the multifunctional, thiol-activated toxin of Streptococcus pneumoniae. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Nov;5(11):2611–2616. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb01969.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchman G. W., Banerjee S., Hansen J. N. Structure, expression, and evolution of a gene encoding the precursor of nisin, a small protein antibiotic. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 5;263(31):16260–16266. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chopin A., Chopin M. C., Moillo-Batt A., Langella P. Two plasmid-determined restriction and modification systems in Streptococcus lactis. Plasmid. 1984 May;11(3):260–263. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(84)90033-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen B., Fink J., Merrifield R. B., Mauzerall D. Channel-forming properties of cecropins and related model compounds incorporated into planar lipid membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(14):5072–5076. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.14.5072. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davey G. P. Plasmid associated with diplococcin production in Streptococcus. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Oct;48(4):895–896. doi: 10.1128/aem.48.4.895-896.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Driessen A. J., Kodde J., de Jong S., Konings W. N. Neutral amino acid transport by membrane vesicles of Streptococcus cremoris is subject to regulation by internal pH. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jun;169(6):2748–2754. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.6.2748-2754.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dufour A., Thuault D., Boulliou A., Bourgeois C. M., Le Pennec J. P. Plasmid-encoded determinants for bacteriocin production and immunity in a Lactococcus lactis strain and purification of the inhibitory peptide. J Gen Microbiol. 1991 Oct;137(10):2423–2429. doi: 10.1099/00221287-137-10-2423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gao F. H., Abee T., Konings W. N. Mechanism of action of the peptide antibiotic nisin in liposomes and cytochrome c oxidase-containing proteoliposomes. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Aug;57(8):2164–2170. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.8.2164-2170.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gálvez A., Maqueda M., Martínez-Bueno M., Valdivia E. Permeation of bacterial cells, permeation of cytoplasmic and artificial membrane vesicles, and channel formation on lipid bilayers by peptide antibiotic AS-48. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jan;173(2):886–892. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.2.886-892.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall J. E., Vodyanoy I., Balasubramanian T. M., Marshall G. R. Alamethicin. A rich model for channel behavior. Biophys J. 1984 Jan;45(1):233–247. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(84)84151-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanke W., Methfessel C., Wilmsen H. U., Katz E., Jung G., Boheim G. Melittin and a chemically modified trichotoxin form alamethicin-type multi-state pores. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Jan 5;727(1):108–114. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(83)90374-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holo H., Nilssen O., Nes I. F. Lactococcin A, a new bacteriocin from Lactococcus lactis subsp. cremoris: isolation and characterization of the protein and its gene. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jun;173(12):3879–3887. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.12.3879-3887.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joerger M. C., Klaenhammer T. R. Characterization and purification of helveticin J and evidence for a chromosomally determined bacteriocin produced by Lactobacillus helveticus 481. J Bacteriol. 1986 Aug;167(2):439–446. doi: 10.1128/jb.167.2.439-446.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joerger M. C., Klaenhammer T. R. Cloning, expression, and nucleotide sequence of the Lactobacillus helveticus 481 gene encoding the bacteriocin helveticin J. J Bacteriol. 1990 Nov;172(11):6339–6347. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.11.6339-6347.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kellner R., Jung G., Hörner T., Zähner H., Schnell N., Entian K. D., Götz F. Gallidermin: a new lanthionine-containing polypeptide antibiotic. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Oct 15;177(1):53–59. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14344.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klaenhammer T. R. Bacteriocins of lactic acid bacteria. Biochimie. 1988 Mar;70(3):337–349. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(88)90206-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kordel M., Schüller F., Sahl H. G. Interaction of the pore forming-peptide antibiotics Pep 5, nisin and subtilin with non-energized liposomes. FEBS Lett. 1989 Feb 13;244(1):99–102. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81171-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molenaar D., Abee T., Konings W. N. Continuous measurement of the cytoplasmic pH in Lactococcus lactis with a fluorescent pH indicator. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Nov 14;1115(1):75–83. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(91)90014-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muriana P. M., Klaenhammer T. R. Purification and partial characterization of lactacin F, a bacteriocin produced by Lactobacillus acidophilus 11088. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Jan;57(1):114–121. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.1.114-121.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poolman B., Hellingwerf K. J., Konings W. N. Regulation of the glutamate-glutamine transport system by intracellular pH in Streptococcus lactis. J Bacteriol. 1987 May;169(5):2272–2276. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.5.2272-2276.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruhr E., Sahl H. G. Mode of action of the peptide antibiotic nisin and influence on the membrane potential of whole cells and on cytoplasmic and artificial membrane vesicles. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 May;27(5):841–845. doi: 10.1128/aac.27.5.841. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sahl H. G. Bactericidal cationic peptides involved in bacterial antagonism and host defence. Microbiol Sci. 1985 Jul;2(7):212–217. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sahl H. G., Kordel M., Benz R. Voltage-dependent depolarization of bacterial membranes and artificial lipid bilayers by the peptide antibiotic nisin. Arch Microbiol. 1987;149(2):120–124. doi: 10.1007/BF00425076. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sansom M. S., Kerr I. D., Mellor I. R. Ion channels formed by amphipathic helical peptides. A molecular modelling study. Eur Biophys J. 1991;20(4):229–240. doi: 10.1007/BF00183460. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherwitz K. M., Baldwin K. A., McKay L. L. Plasmid linkage of a bacteriocin-like substance in Streptococcus lactis subsp. diacetylactis strain WM4: transferability to Streptococcus lactis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 May;45(5):1506–1512. doi: 10.1128/aem.45.5.1506-1512.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schüller F., Benz R., Sahl H. G. The peptide antibiotic subtilin acts by formation of voltage-dependent multi-state pores in bacterial and artificial membranes. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Jun 1;182(1):181–186. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb14815.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinbo T., Kamo N., Kurihara K., Kobatake Y. A PVC-based electrode sensitive to DDA+ as a device for monitoring the membrane potential in biological systems. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1978 Apr 30;187(2):414–422. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(78)90052-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sijtsma L., Wouters J. T., Hellingwerf K. J. Isolation and characterization of lipoteichoic acid, a cell envelope component involved in preventing phage adsorption, from Lactococcus lactis subsp. cremoris SK110. J Bacteriol. 1990 Dec;172(12):7126–7130. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.12.7126-7130.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoddard G. W., Petzel J. P., van Belkum M. J., Kok J., McKay L. L. Molecular analyses of the lactococcin A gene cluster from Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis biovar diacetylactis WM4. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992 Jun;58(6):1952–1961. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.6.1952-1961.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tagg J. R., Dajani A. S., Wannamaker L. W. Bacteriocins of gram-positive bacteria. Bacteriol Rev. 1976 Sep;40(3):722–756. doi: 10.1128/br.40.3.722-756.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terzaghi B. E., Sandine W. E. Improved medium for lactic streptococci and their bacteriophages. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Jun;29(6):807–813. doi: 10.1128/am.29.6.807-813.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson J. Characteristics and energy requirements of an alpha-aminoisobutyric acid transport system in Streptococcus lactis. J Bacteriol. 1976 Aug;127(2):719–730. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.2.719-730.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel H. Comparison of the conformation and orientation of alamethicin and melittin in lipid membranes. Biochemistry. 1987 Jul 14;26(14):4562–4572. doi: 10.1021/bi00388a060. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zasloff M. Magainins, a class of antimicrobial peptides from Xenopus skin: isolation, characterization of two active forms, and partial cDNA sequence of a precursor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(15):5449–5453. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.15.5449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Belkum M. J., Hayema B. J., Geis A., Kok J., Venema G. Cloning of two bacteriocin genes from a lactococcal bacteriocin plasmid. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 May;55(5):1187–1191. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.5.1187-1191.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Belkum M. J., Kok J., Venema G. Cloning, sequencing, and expression in Escherichia coli of lcnB, a third bacteriocin determinant from the lactococcal bacteriocin plasmid p9B4-6. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992 Feb;58(2):572–577. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.2.572-577.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Belkum M. J., Kok J., Venema G., Holo H., Nes I. F., Konings W. N., Abee T. The bacteriocin lactococcin A specifically increases permeability of lactococcal cytoplasmic membranes in a voltage-independent, protein-mediated manner. J Bacteriol. 1991 Dec;173(24):7934–7941. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.24.7934-7941.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



