Abstract
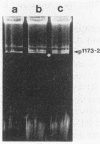
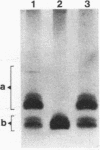
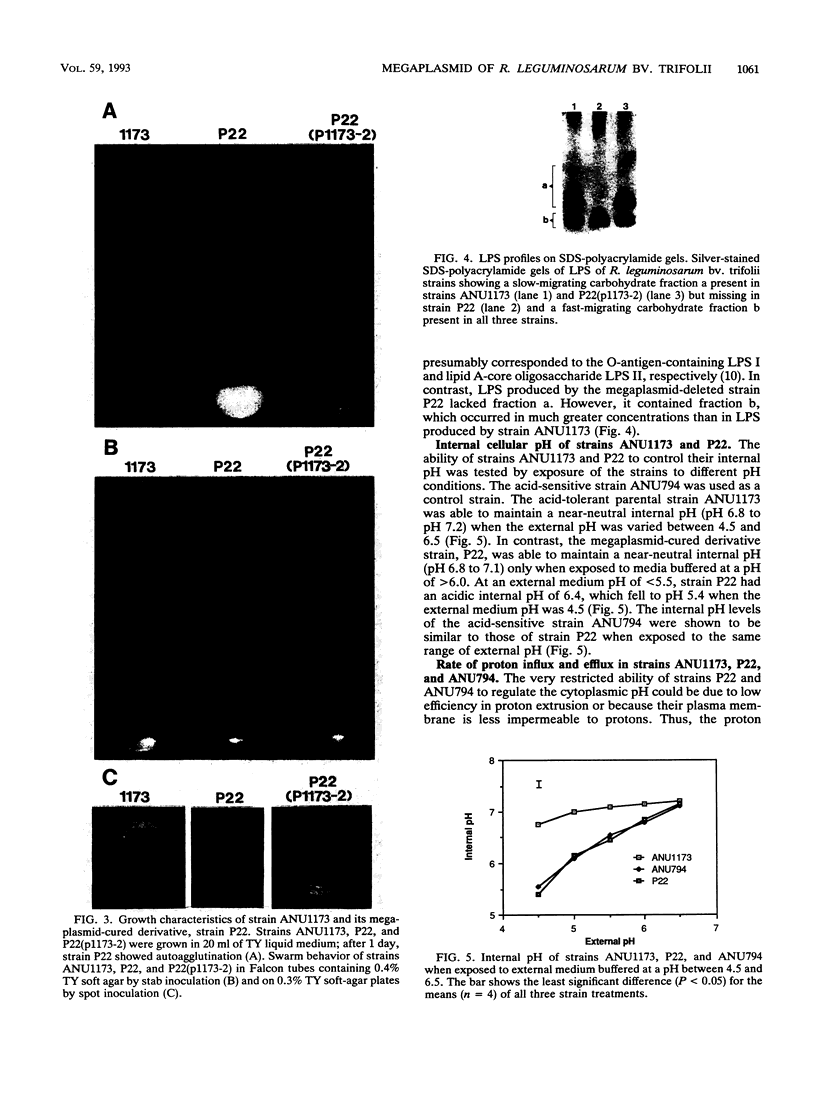
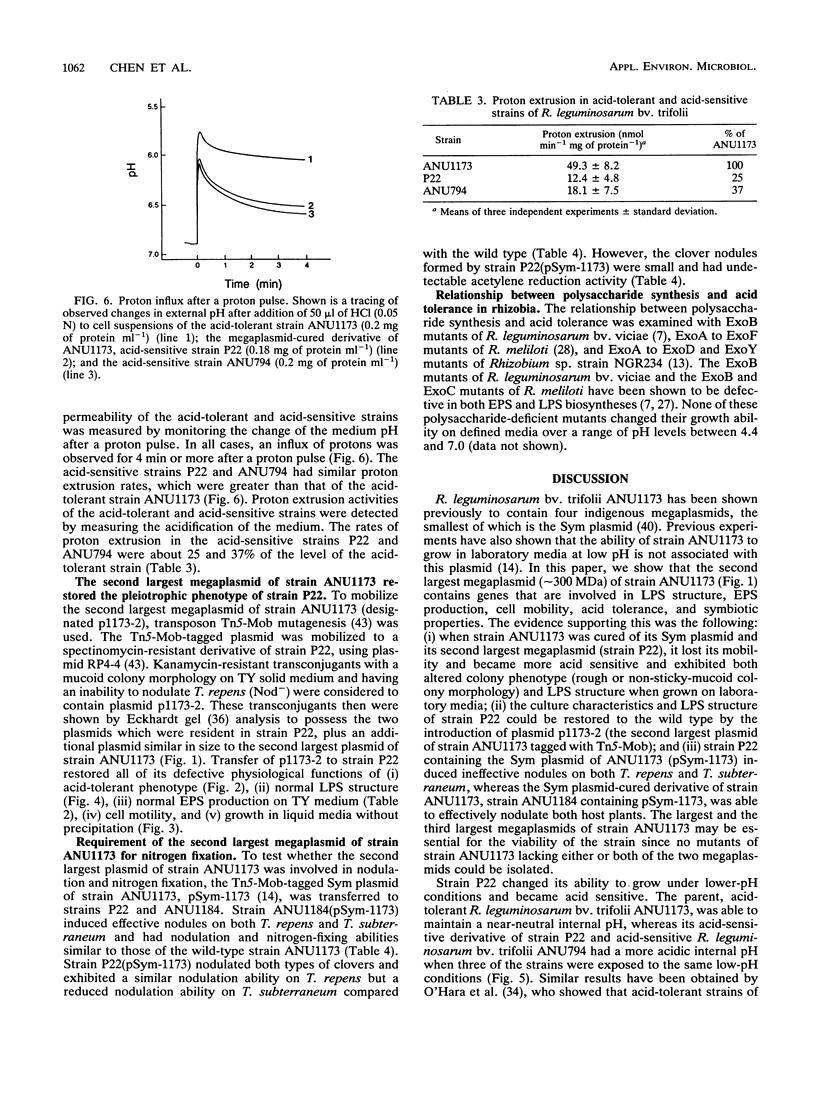
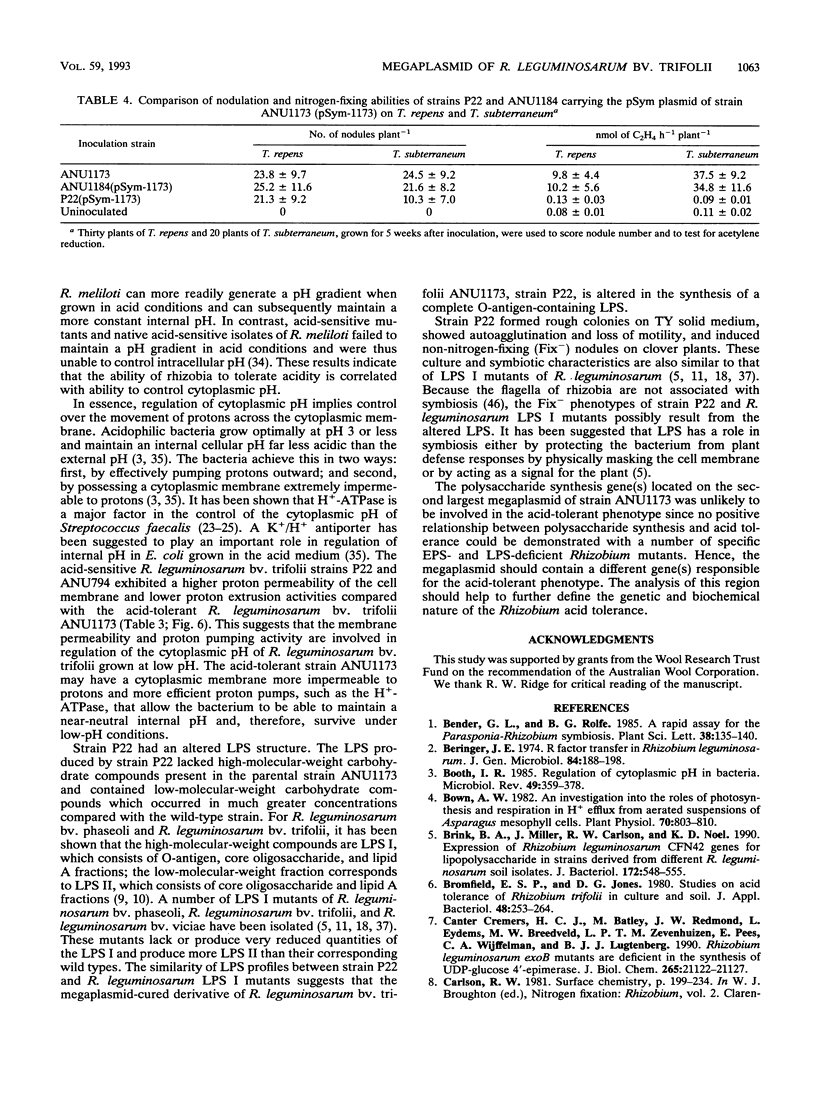
The acid-tolerant Rhizobium leguminosarum biovar trifolii strain ANU1173 exhibited several new phenotypes when cured of its symbiotic (Sym) plasmid and the second largest megaplasmid. Strain P22, which has lost these two plasmids, had reduced exopolysaccharide production and cell mobility on TY medium. The parent strain ANU1173 was able to grow easily in laboratory media at pH 4.5, whereas the derivative strain P22 was unable to grow in media at a pH of <4.7. The intracellular pH of strain ANU1173 was 6.8 when the external pH was 4.5. In contrast, strain P22 had an acidic intracellular pH of <6.4 when the external pH was <5.5. Strain P22 had a dramatically increased membrane permeability to protons and decreased proton extrusion activity. Analysis with sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gels showed that strain P22 lacked a slow-migrating lipopolysaccharide (LPS) banding group which was present in the parent strain. Mobilization of the second largest megaplasmid of strain ANU1173 back into strain P22 restored the altered LPS structure and physiological characteristics of strain P22. Mobilization of the Sym plasmid of strain ANU1173 into strain P22 showed that the second largest megaplasmid of strain ANU1173 was required for the establishment of nitrogen-fixing nodules on Trifolium repens and Trifolium subterraneum. Furthermore, an examination of a large number of specific exopolysaccharide- or LPS-deficient Rhizobium mutants did not show a positive correlation between exopolysaccharide or LPS synthesis and acid tolerance.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beringer J. E. R factor transfer in Rhizobium leguminosarum. J Gen Microbiol. 1974 Sep;84(1):188–198. doi: 10.1099/00221287-84-1-188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Booth I. R. Regulation of cytoplasmic pH in bacteria. Microbiol Rev. 1985 Dec;49(4):359–378. doi: 10.1128/mr.49.4.359-378.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bown A. W. An investigation into the roles of photosynthesis and respiration in h efflux from aerated suspensions of asparagus mesophyll cells. Plant Physiol. 1982 Sep;70(3):803–810. doi: 10.1104/pp.70.3.803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brink B. A., Miller J., Carlson R. W., Noel K. D. Expression of Rhizobium leguminosarum CFN42 genes for lipopolysaccharide in strains derived from different R. leguminosarum soil isolates. J Bacteriol. 1990 Feb;172(2):548–555. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.2.548-555.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canter Cremers H. C., Batley M., Redmond J. W., Eydems L., Breedveld M. W., Zevehuizen L. P., Pees E., Wijffelman C. A., Lugtenberg B. J. Rhizobium leguminosarum exoB mutants are deficient in the synthesis of UDP-glucose 4'-epimerase. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 5;265(34):21122–21127. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson R. W., Hollingsworth R. L., Dazzo F. B. A core oligosaccharide component from the lipopolysaccharide of Rhizobium trifolii ANU843. Carbohydr Res. 1988 May 1;176(1):127–135. doi: 10.1016/0008-6215(88)84064-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson R. W., Shatters R., Duh J. L., Turnbull E., Hanley B., Rolfe B. G., Djordjevic M. A. The Isolation and Partial Characterization of the Lipopolysaccharides from Several Rhizobium trifolii Mutants Affected in Root Hair Infection. Plant Physiol. 1987 Jun;84(2):421–427. doi: 10.1104/pp.84.2.421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cava J. R., Elias P. M., Turowski D. A., Noel K. D. Rhizobium leguminosarum CFN42 genetic regions encoding lipopolysaccharide structures essential for complete nodule development on bean plants. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jan;171(1):8–15. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.1.8-15.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakravorty A. K., Zurkowski W., Shine J., Rolfe B. G. Symbiotic nitrogen fixation: molecular cloning of Rhizobium genes involved in exopolysaccharide synthesis and effective nodulation. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(6):585–596. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen H., Richardson A. E., Gartner E., Djordjevic M. A., Roughley R. J., Rolfe B. G. Construction of an Acid-Tolerant Rhizobium leguminosarum Biovar Trifolii Strain with Enhanced Capacity for Nitrogen Fixation. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Jul;57(7):2005–2011. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.7.2005-2011.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kido N., Ohta M., Kato N. Detection of lipopolysaccharides by ethidium bromide staining after sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Bacteriol. 1990 Feb;172(2):1145–1147. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.2.1145-1147.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi H. A proton-translocating ATPase regulates pH of the bacterial cytoplasm. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jan 10;260(1):72–76. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi H., Murakami N., Unemoto T. Regulation of the cytoplasmic pH in Streptococcus faecalis. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 25;257(22):13246–13252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi H., Unemoto T. Streptococcus faecalis mutants defective in regulation of cytoplasmic pH. J Bacteriol. 1980 Sep;143(3):1187–1193. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.3.1187-1193.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leigh J. A., Lee C. C. Characterization of polysaccharides of Rhizobium meliloti exo mutants that form ineffective nodules. J Bacteriol. 1988 Aug;170(8):3327–3332. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.8.3327-3332.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leigh J. A., Signer E. R., Walker G. C. Exopolysaccharide-deficient mutants of Rhizobium meliloti that form ineffective nodules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(18):6231–6235. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.18.6231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Long S. R. Rhizobium-legume nodulation: life together in the underground. Cell. 1989 Jan 27;56(2):203–214. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90893-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowendorf H. S., Alexander M. Identification of Rhizobium phaseoli Strains That Are Tolerant or Sensitive to Soil Acidity. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Mar;45(3):737–742. doi: 10.1128/aem.45.3.737-742.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'hara Graham W., Goss Thomas J., Dilworth Michael J., Glenn Andrew R. Maintenance of Intracellular pH and Acid Tolerance in Rhizobium meliloti. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Aug;55(8):1870–1876. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.8.1870-1876.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padan E., Zilberstein D., Schuldiner S. pH homeostasis in bacteria. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Dec;650(2-3):151–166. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(81)90004-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plazinski J., Cen Y. H., Rolfe B. G. General method for the identification of plasmid species in fast-growing soil microorganisms. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Apr;49(4):1001–1003. doi: 10.1128/aem.49.4.1001-1003.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Priefer U. B. Genes involved in lipopolysaccharide production and symbiosis are clustered on the chromosome of Rhizobium leguminosarum biovar viciae VF39. J Bacteriol. 1989 Nov;171(11):6161–6168. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.11.6161-6168.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson A. E., Simpson R. J., Djordjevic M. A., Rolfe B. G. Expression of Nodulation Genes in Rhizobium leguminosarum biovar trifolii Is Affected by Low pH and by Ca and Al Ions. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Oct;54(10):2541–2548. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.10.2541-2548.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon R. High frequency mobilization of gram-negative bacterial replicons by the in vitro constructed Tn5-Mob transposon. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;196(3):413–420. doi: 10.1007/BF00436188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slavík J. Intracellular pH of yeast cells measured with fluorescent probes. FEBS Lett. 1982 Apr 5;140(1):22–26. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80512-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smit G., Kijne J. W., Lugtenberg B. J. Roles of flagella, lipopolysaccharide, and a Ca2+-dependent cell surface protein in attachment of Rhizobium leguminosarum biovar viciae to pea root hair tips. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jan;171(1):569–572. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.1.569-572.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Maagd R. A., Rao A. S., Mulders I. H., Goosen-de Roo L., van Loosdrecht M. C., Wijffelman C. A., Lugtenberg B. J. Isolation and characterization of mutants of Rhizobium leguminosarum bv. viciae 248 with altered lipopolysaccharides: possible role of surface charge or hydrophobicity in bacterial release from the infection thread. J Bacteriol. 1989 Feb;171(2):1143–1150. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.2.1143-1150.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]