Abstract
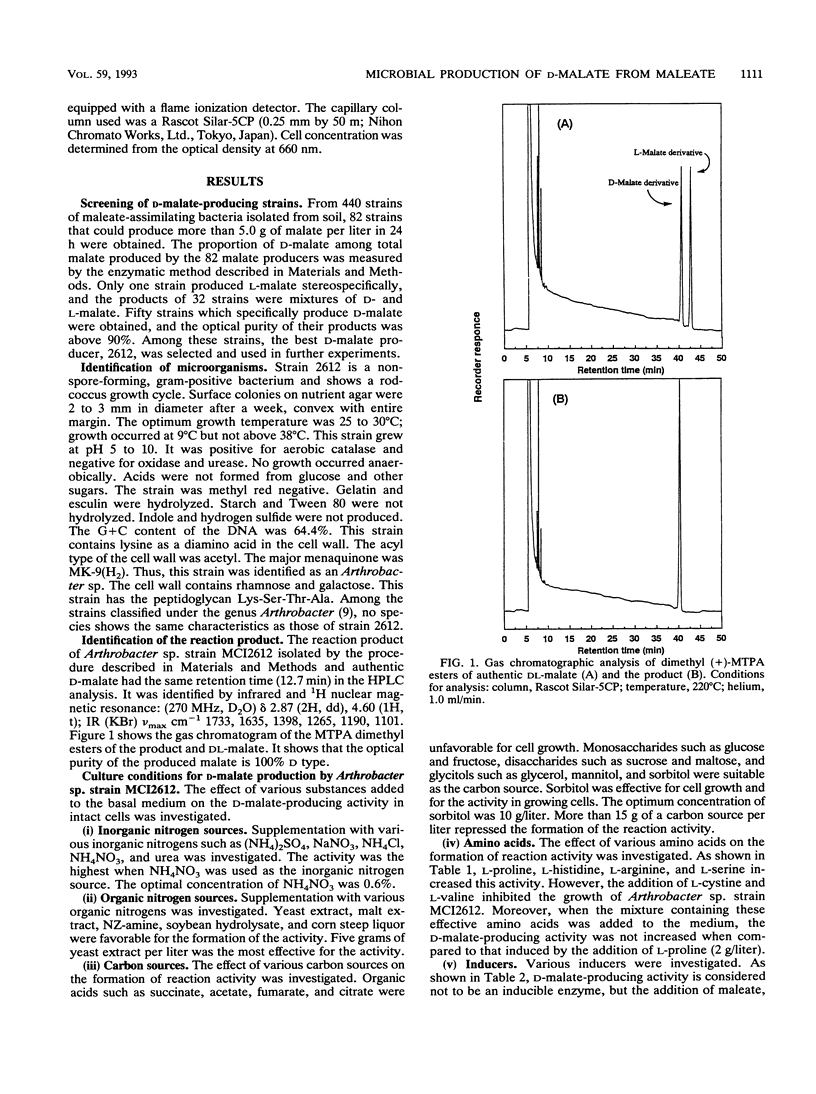
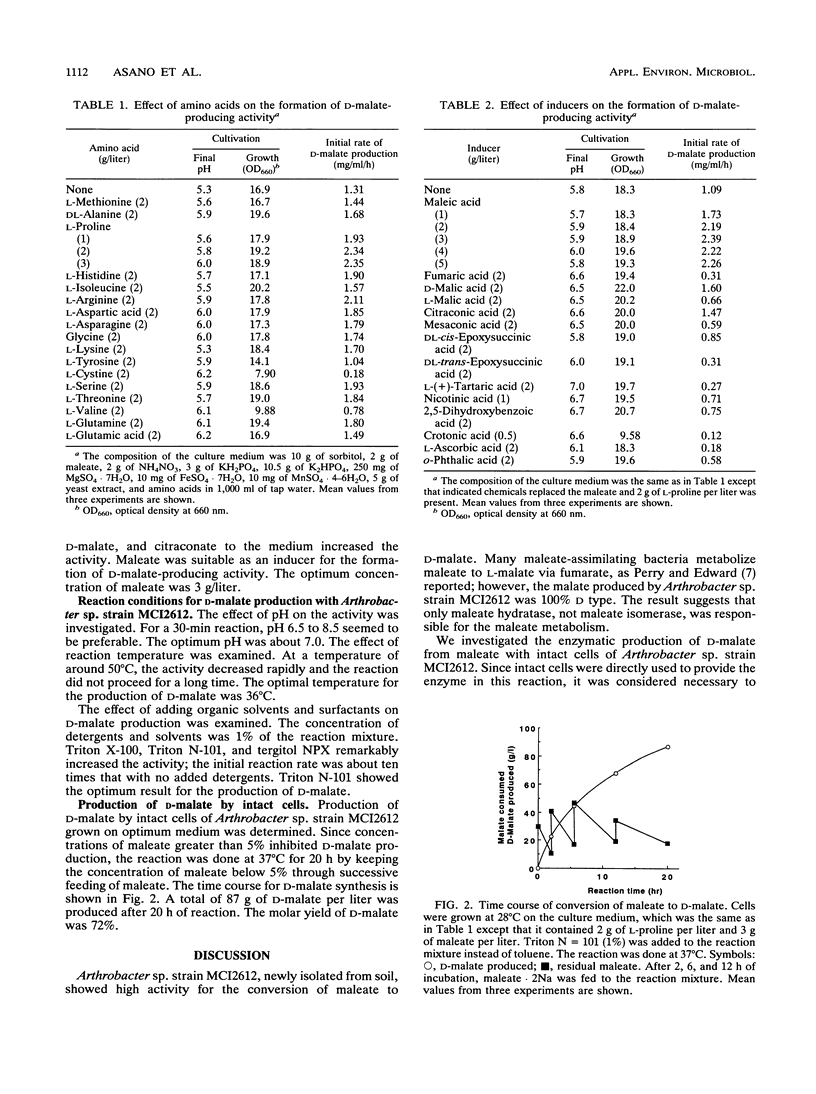
To produce D-malate from maleate by a microbial reaction, we screened a number of maleate-utilizing microorganisms for enzyme activity by an intact cell system. The strain which showed the best productivity among the 440 strains tested was identified taxonomically as Arthrobacter sp. strain MCI2612. The optical purity of the malate produced by this strain was 100% D type. The culture and reaction conditions for the production were studied for this strain. Addition of amino acids such as L-proline, L-histidine, and L-arginine to the culture medium promoted the formation of reaction activity as well as cell growth. Under optimum conditions, 87 g of D-malate per liter was produced in 20 h. The yield was 72 mol%.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Englard S., Britten J. S., Listowsky I. Stereochemical course of the maleate hydratase reaction. J Biol Chem. 1967 May 10;242(9):2255–2259. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopper D. J., Chapman P. J., Dagley S. Enzymic formation of D-malate. Biochem J. 1968 Dec;110(4):798–800. doi: 10.1042/bj1100798. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knichel W., Radler F. D-Malic enzyme of Pseudomonas fluorescens. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Apr;123(3):547–552. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb06567.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry J. T., Jr, Edwards V. H. Growth of Pseudomonas fluorescens with sodium maleate as a carbon source. Appl Microbiol. 1970 Nov;20(5):710–714. doi: 10.1128/am.20.5.710-714.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SACKS W., JENSEN C. O. Malease, a hydrase from corn kernels. J Biol Chem. 1951 Sep;192(1):231–236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



