Abstract
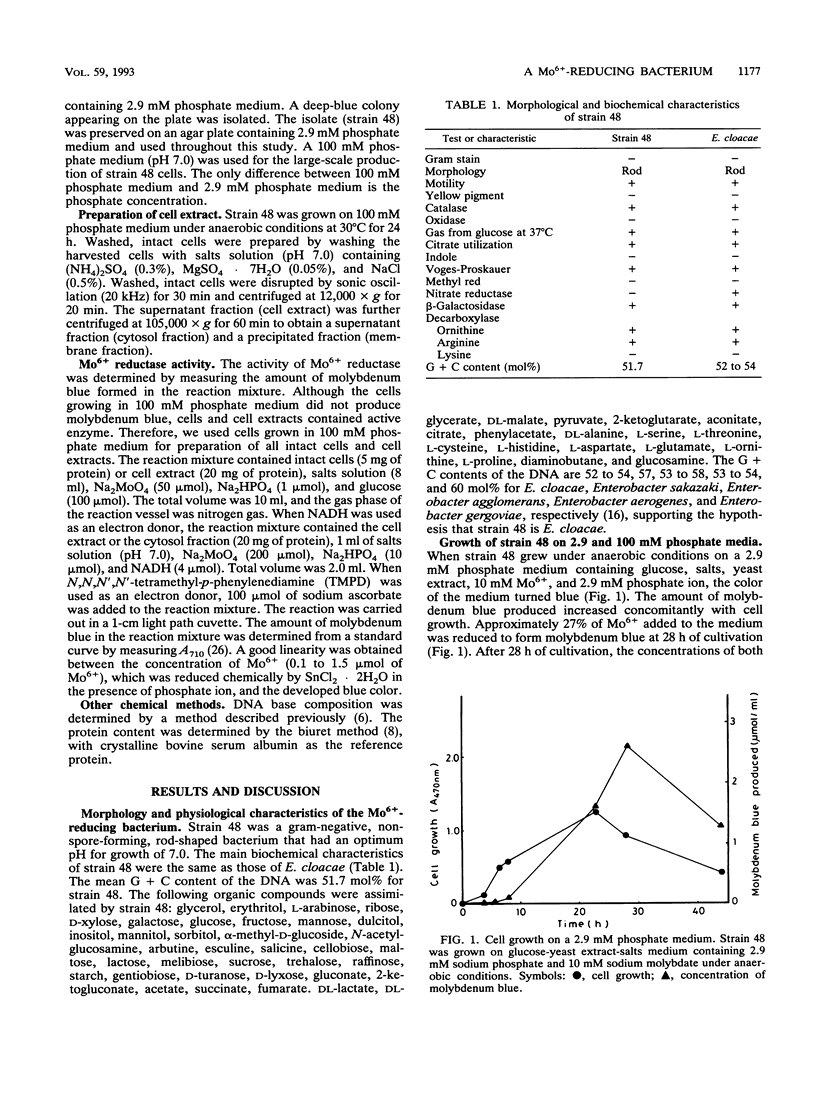
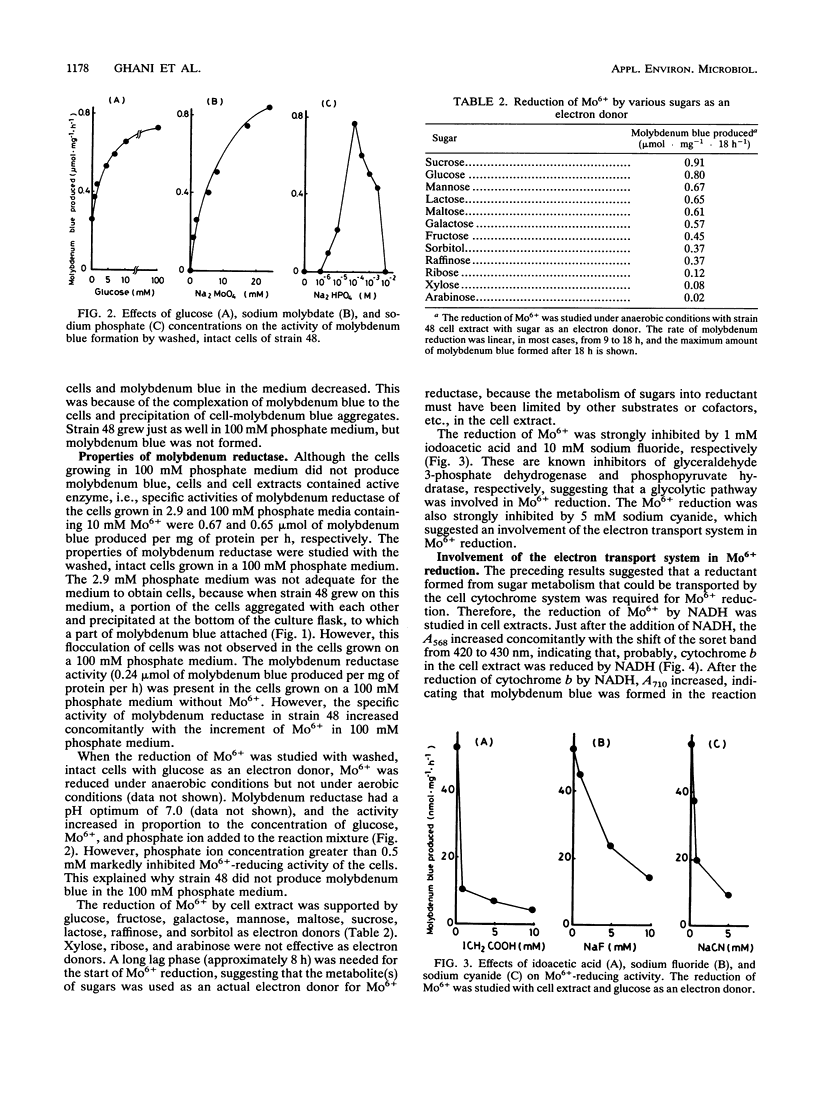
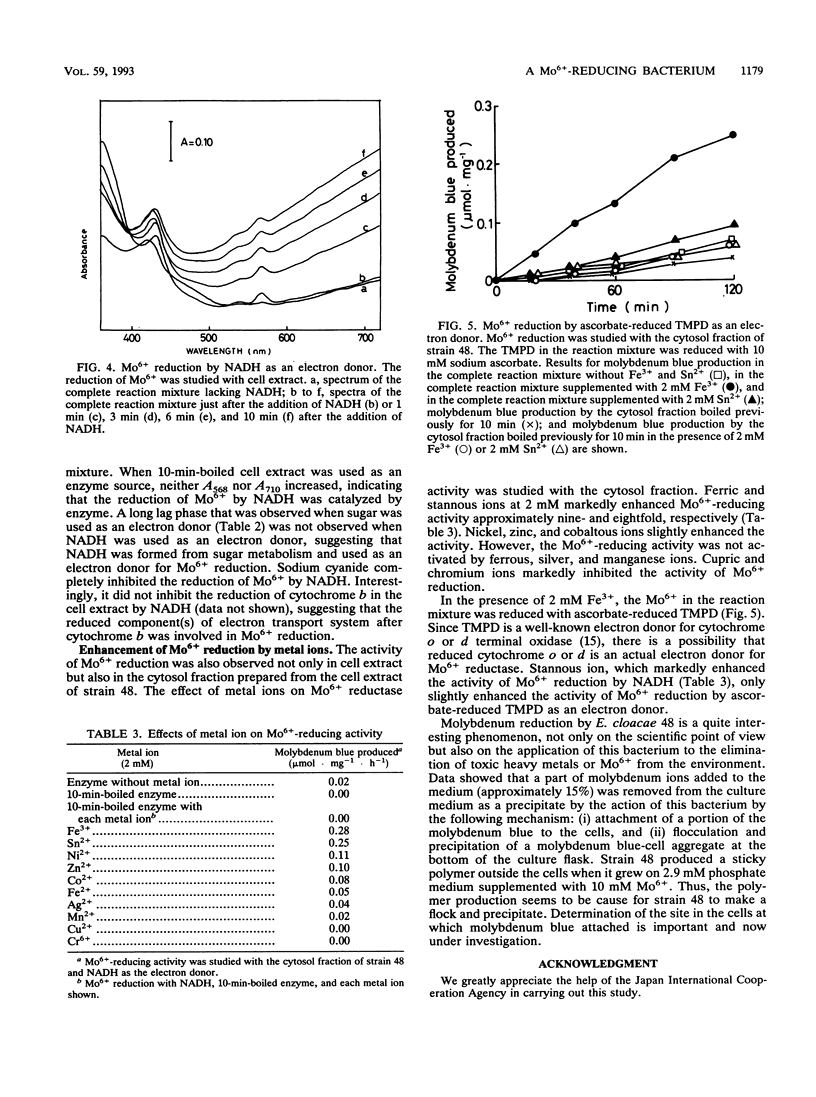
A Mo6+ -reducing bacterium (strain 48), which grew on medium supplemented with 200 mM Mo6+, was isolated from stream water obtained from Chengkau, Malaysia. The chemical properties of strain 48 conform to the characteristics of Enterobacter cloacae. Under anaerobic conditions in the glucose-yeast extract medium containing phosphate ion (2.9 mM) and Mo6+ (10 mM), the bacterium reduced Mo6+ to form molybdenum blue. Approximately 27% of Mo6+ added to the medium was reduced after 28 h of cultivation. The reduction of Mo6+ with glucose as an electron donor was strongly inhibited by iodoacetic acid, sodium fluoride, and sodium cyanide, suggesting an involvement of the glycolytic pathway and electron transport in Mo6+ reduction. NADH and N,N,N′,N′ -tetramethyl-p-phenylenediamine served as electron donors for Mo6+ reduction. When NADH was used as an electron donor, at first cytochrome b in the cell extract was reduced, and then molybdenum blue was formed. Sodium cyanide strongly inhibited Mo6+ reduction by NADH (5 mM) but not the reduction of cytochrome b in the cell extract, suggesting that the reduced component of the electron transport system after cytochrome b serves as an electron donor for Mo6+ reduction. Both ferric and stannous ions strongly enhanced the activity of Mo6+ reduction by NADH.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brock T. D., Gustafson J. Ferric iron reduction by sulfur- and iron-oxidizing bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Oct;32(4):567–571. doi: 10.1128/aem.32.4.567-571.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox C. D. Iron reductases from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1980 Jan;141(1):199–204. doi: 10.1128/jb.141.1.199-204.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dailey H. A., Jr, Lascelles J. Reduction of iron and synthesis of protoheme by Spirillum itersonii and other organisms. J Bacteriol. 1977 Feb;129(2):815–820. doi: 10.1128/jb.129.2.815-820.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huyer M., Page W. J. Ferric reductase activity in Azotobacter vinelandii and its inhibition by Zn2+. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jul;171(7):4031–4037. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.7.4031-4037.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lascelles J., Burke K. A. Reduction of ferric iron by L-lactate and DL-glycerol-3-phosphate in membrane preparations from Staphylococcus aureus and interactions with the nitrate reductase system. J Bacteriol. 1978 May;134(2):585–589. doi: 10.1128/jb.134.2.585-589.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovley D. R. Dissimilatory Fe(III) and Mn(IV) reduction. Microbiol Rev. 1991 Jun;55(2):259–287. doi: 10.1128/mr.55.2.259-287.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovley D. R., Phillips E. J., Lonergan D. J. Hydrogen and Formate Oxidation Coupled to Dissimilatory Reduction of Iron or Manganese by Alteromonas putrefaciens. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Mar;55(3):700–706. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.3.700-706.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovley D. R., Phillips E. J. Novel mode of microbial energy metabolism: organic carbon oxidation coupled to dissimilatory reduction of iron or manganese. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Jun;54(6):1472–1480. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.6.1472-1480.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovley D. R., Phillips E. J. Organic matter mineralization with reduction of ferric iron in anaerobic sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Apr;51(4):683–689. doi: 10.1128/aem.51.4.683-689.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oremland R. S., Hollibaugh J. T., Maest A. S., Presser T. S., Miller L. G., Culbertson C. W. Selenate reduction to elemental selenium by anaerobic bacteria in sediments and culture: biogeochemical significance of a novel, sulfate-independent respiration. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Sep;55(9):2333–2343. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.9.2333-2343.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver S., Walderhaug M. Gene regulation of plasmid- and chromosome-determined inorganic ion transport in bacteria. Microbiol Rev. 1992 Mar;56(1):195–228. doi: 10.1128/mr.56.1.195-228.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugio T., Domatsu C., Munakata O., Tano T., Imai K. Role of a Ferric Ion-Reducing System in Sulfur Oxidation of Thiobacillus ferrooxidans. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Jun;49(6):1401–1406. doi: 10.1128/aem.49.6.1401-1406.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugio T., Hirayama K., Inagaki K., Tanaka H., Tano T. Molybdenum oxidation by Thiobacillus ferrooxidans. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992 May;58(5):1768–1771. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.5.1768-1771.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugio T., Mizunashi W., Inagaki K., Tano T. Purification and some properties of sulfur:ferric ion oxidoreductase from Thiobacillus ferrooxidans. J Bacteriol. 1987 Nov;169(11):4916–4922. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.11.4916-4922.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugio T., Tsujita Y., Inagaki K., Tano T. Reduction of Cupric Ions with Elemental Sulfur by Thiobacillus ferrooxidans. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Mar;56(3):693–696. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.3.693-696.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugio T., Tsujita Y., Katagiri T., Inagaki K., Tano T. Reduction of Mo6+ with elemental sulfur by Thiobacillus ferrooxidans. J Bacteriol. 1988 Dec;170(12):5956–5959. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.12.5956-5959.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang P. C., Mori T., Komori K., Sasatsu M., Toda K., Ohtake H. Isolation and Characterization of an Enterobacter cloacae Strain That Reduces Hexavalent Chromium under Anaerobic Conditions. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Jul;55(7):1665–1669. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.7.1665-1669.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang P. C., Mori T., Toda K., Ohtake H. Membrane-associated chromate reductase activity from Enterobacter cloacae. J Bacteriol. 1990 Mar;172(3):1670–1672. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.3.1670-1672.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


