Abstract
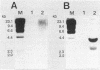
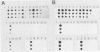
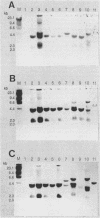
DNA of 10 lines of rice yellow dwarf (RYD) mycoplasmalike organisms (MLOs) from Japan, the Phillippines, and Thailand hybridized with four probes containing chromosomal and six probes containing extrachromosomal DNA of a Tochigi (Japan) line of RYD MLO. One chromosomal probe (RYD9) and all six extrachromosomal probes hybridized with various other MLOs (sugarcane white leaf, onion yellows, cineraria witches'-broom, Japanese hornwort witches'-broom, water dropwort wiches'-broom, gentian witches'-broom, udo dwarf, tsuwabuki witches'-broom, pelargonium witches's-broom, peach western-X, and pear decline). DNA from the culturable mollicutes Spiroplasma kunkelii, Spiroplasma citri, Mycoplasma hominis, and Mycoplasma orale did not hybridize with RYD MLO probes. The extrachromosomal DNAs hybridizing with the probes showed variations in electrophoretic behavior.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bonissol C., Sasaki T., Stoiljkovic B. Assay for detection of adenosine phosphorylase from mycoplasmas. Ann Inst Pasteur Microbiol. 1988 Nov-Dec;139(6):703–715. doi: 10.1016/0769-2609(88)90075-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirkpatrick B. C., Stenger D. C., Morris T. J., Purcell A. H. Cloning and Detection of DNA from a Nonculturable Plant Pathogenic Mycoplasma-like Organism. Science. 1987 Oct 9;238(4824):197–200. doi: 10.1126/science.238.4824.197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuske C. R., Kirkpatrick B. C. Identification and characterization of plasmids from the western aster yellows mycoplasmalike organism. J Bacteriol. 1990 Mar;172(3):1628–1633. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.3.1628-1633.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee I. M., Davis R. E., Dewitt N. D. Nonradioactive screening method for isolation of disease-specific probes to diagnose plant diseases caused by mycoplasmalike organisms. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 May;56(5):1471–1475. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.5.1471-1475.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee I. M., Davis R. E., Hiruki C. Genetic Interrelatedness among Clover Proliferation Mycoplasmalike Organisms (MLOs) and Other MLOs Investigated by Nucleic Acid Hybridization and Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism Analyses. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Dec;57(12):3565–3569. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.12.3565-3569.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee I. M., Gundersen D. E., Davis R. E., Chiykowski L. N. Identification and analysis of a genomic strain cluster of mycoplasmalike organisms associated with Canadian peach (eastern) X disease, western X disease, and clover yellow edge. J Bacteriol. 1992 Oct;174(20):6694–6698. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.20.6694-6698.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakashima K., Kakutani T., Minobe Y. Sequence analysis and product assignment of segment 7 of the rice dwarf virus genome. J Gen Virol. 1990 Mar;71(Pt 3):725–729. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-71-3-725. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakashima K., Kato S., Iwanami S., Murata N. Cloning and detection of chromosomal and extrachromosomal DNA from mycoplasmalike organisms that cause yellow dwarf disease of rice. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Dec;57(12):3570–3575. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.12.3570-3575.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]