Abstract
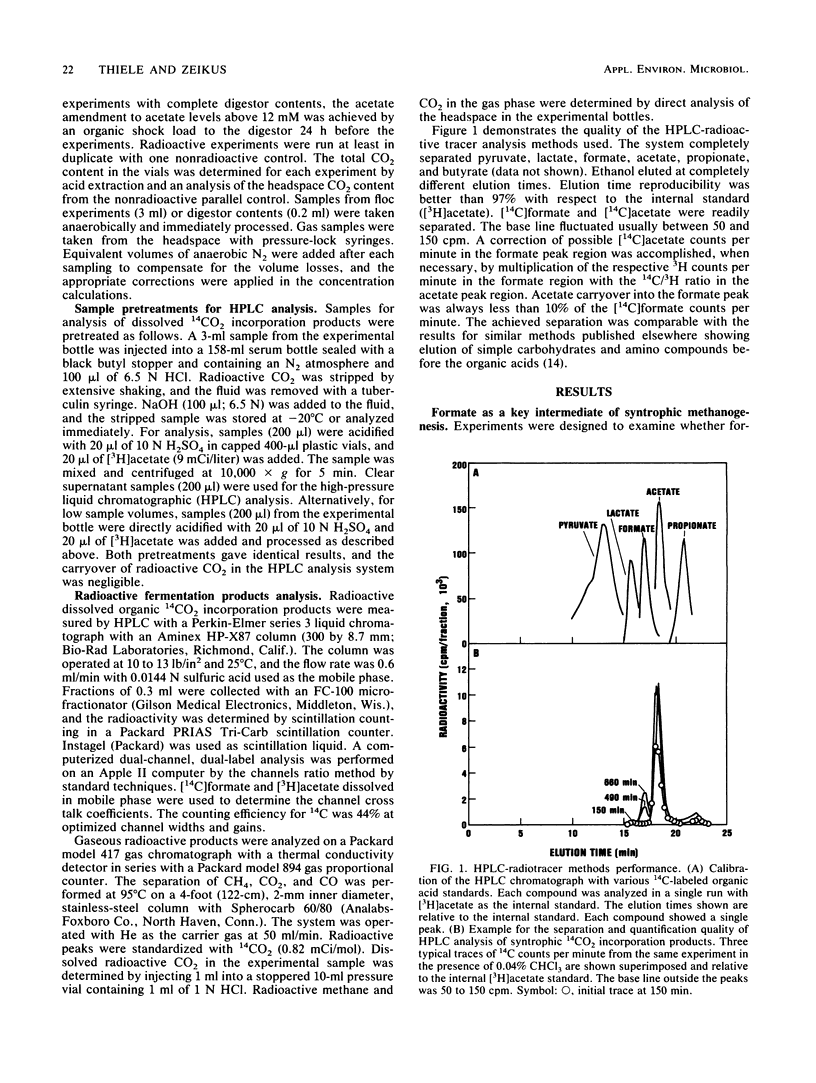
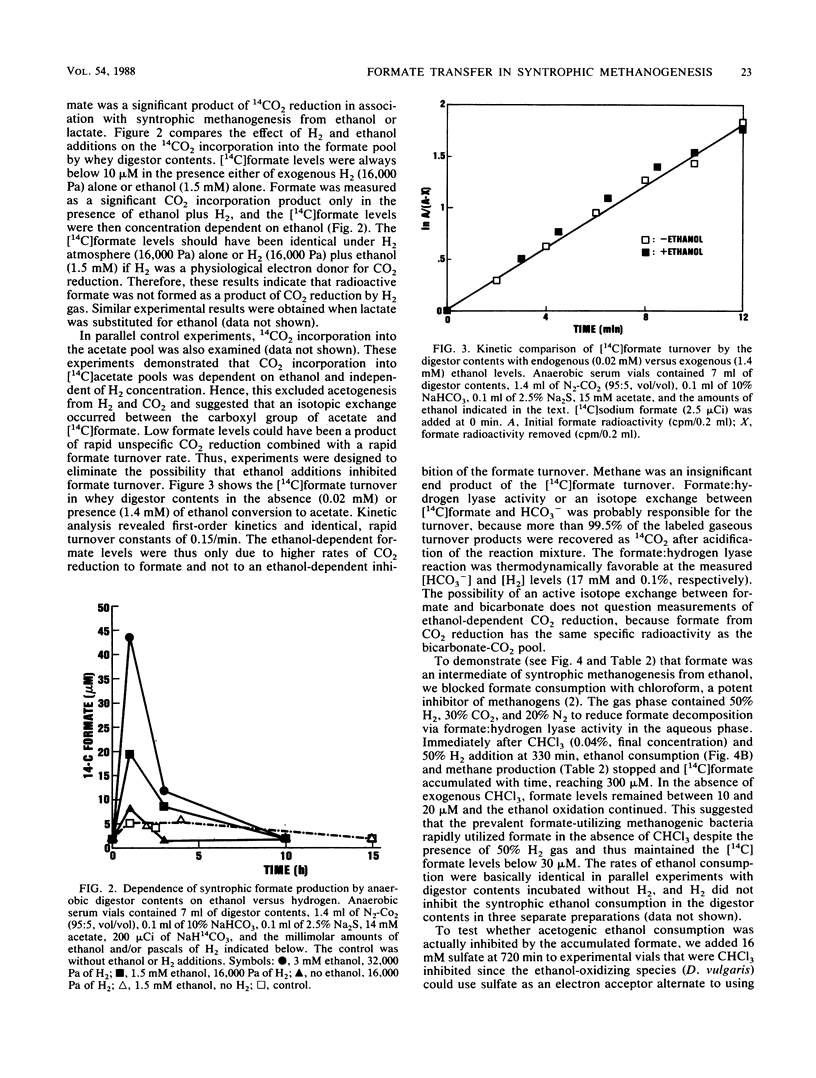
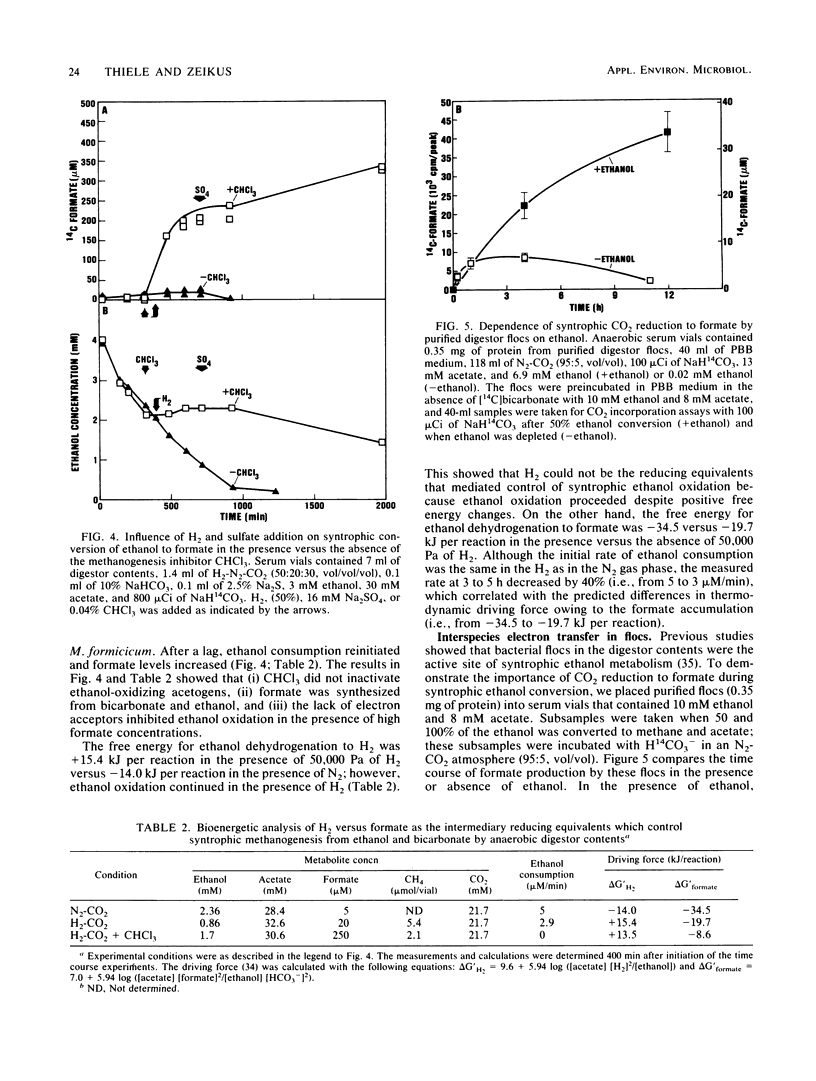
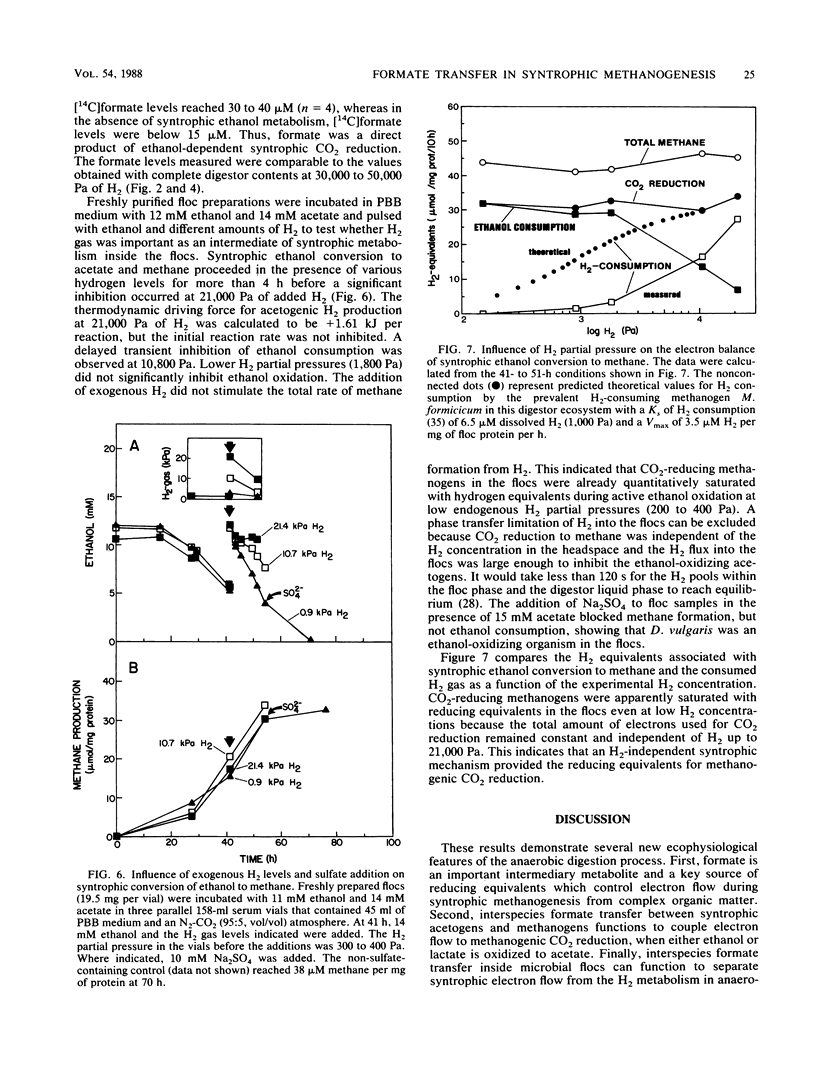
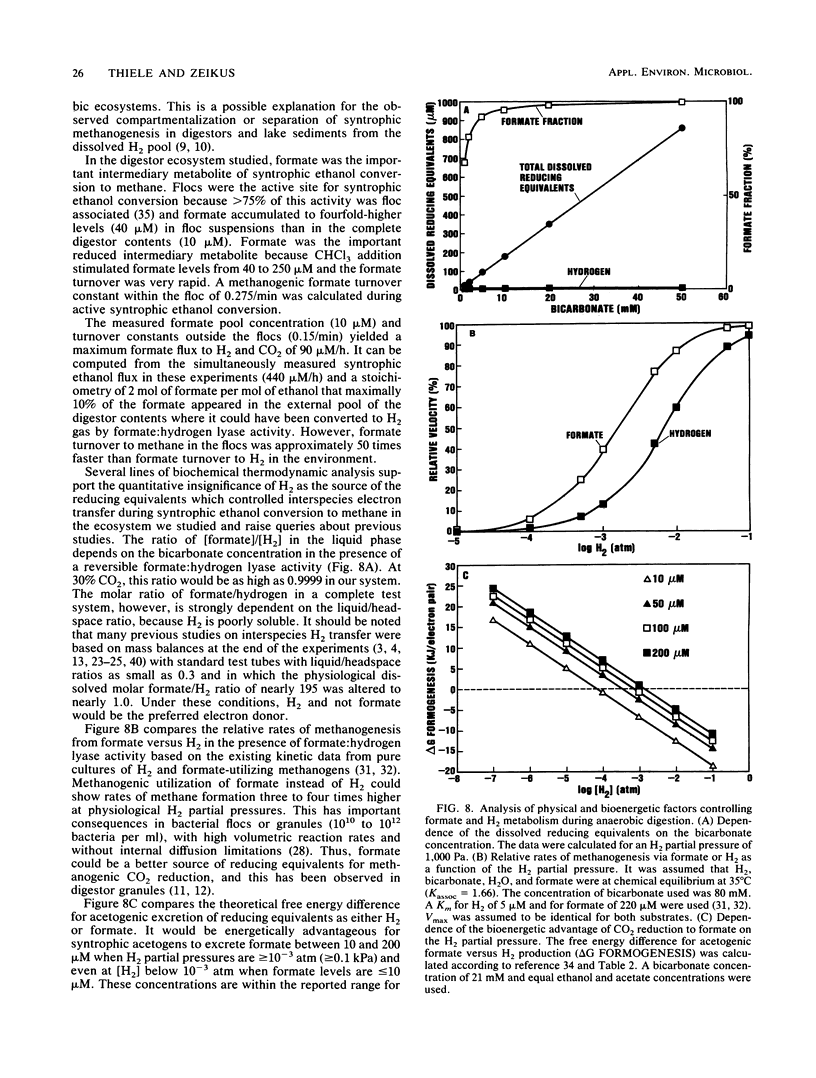
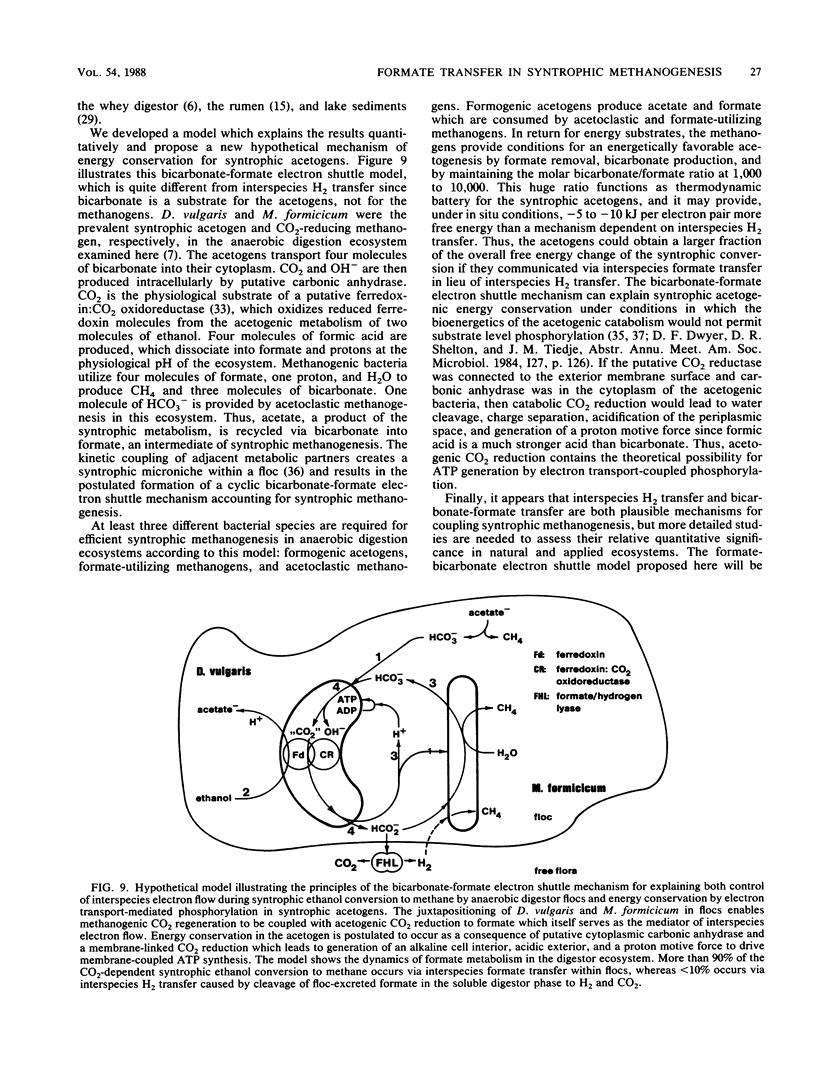
Microbial formate production and consumption during syntrophic conversion of ethanol or lactate to methane was examined in purified flocs and digestor contents obtained from a whey-processing digestor. Formate production by digestor contents or purified digestor flocs was dependent on CO2 and either ethanol or lactate but not H2 gas as an electron donor. During syntrophic methanogenesis, flocs were the primary site for formate production via ethanol-dependent CO2 reduction, with a formate production rate and methanogenic turnover constant of 660 μM/h and 0.044/min, respectively. Floc preparations accumulated fourfold-higher levels of formate (40 μM) than digestor contents, and the free flora was the primary site for formate cleavage to CO2 and H2 (90 μM formate per h). Inhibition of methanogenesis by CHCl3 resulted in formate accumulation and suppression of syntrophic ethanol oxidation. H2 gas was an insignificant intermediary metabolite of syntrophic ethanol conversion by flocs, and its exogenous addition neither stimulated methanogenesis nor inhibited the initial rate of ethanol oxidation. These results demonstrated that >90% of the syntrophic ethanol conversion to methane by mixed cultures containing primarily Desulfovibrio vulgaris and Methanobacterium formicicum was mediated via interspecies formate transfer and that <10% was mediated via interspecies H2 transfer. The results are discussed in relation to biochemical thermodynamics. A model is presented which describes the dynamics of a bicarbonate-formate electron shuttle mechanism for control of carbon and electron flow during syntrophic methanogenesis and provides a novel mechanism for energy conservation by syntrophic acetogens.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bauchop T. Inhibition of rumen methanogenesis by methane analogues. J Bacteriol. 1967 Jul;94(1):171–175. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.1.171-175.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boone D. R., Bryant M. P. Propionate-Degrading Bacterium, Syntrophobacter wolinii sp. nov. gen. nov., from Methanogenic Ecosystems. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Sep;40(3):626–632. doi: 10.1128/aem.40.3.626-632.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryant M. P., Campbell L. L., Reddy C. A., Crabill M. R. Growth of desulfovibrio in lactate or ethanol media low in sulfate in association with H2-utilizing methanogenic bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 May;33(5):1162–1169. doi: 10.1128/aem.33.5.1162-1169.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryant M. P., Wolin E. A., Wolin M. J., Wolfe R. S. Methanobacillus omelianskii, a symbiotic association of two species of bacteria. Arch Mikrobiol. 1967;59(1):20–31. doi: 10.1007/BF00406313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chartrain M., Bhatnagar L., Zeikus J. G. Microbial ecophysiology of whey biomethanation: comparison of carbon transformation parameters, species composition, and starter culture performance in continuous culture. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 May;53(5):1147–1156. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.5.1147-1156.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chartrain M., Zeikus J. G. Microbial ecophysiology of whey biomethanation: characterization of bacterial trophic populations and prevalent species in continuous culture. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Jan;51(1):188–196. doi: 10.1128/aem.51.1.188-196.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chartrain M., Zeikus J. G. Microbial ecophysiology of whey biomethanation: intermediary metabolism of lactose degradation in continuous culture. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Jan;51(1):180–187. doi: 10.1128/aem.51.1.180-187.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conrad R., Phelps T. J., Zeikus J. G. Gas metabolism evidence in support of the juxtaposition of hydrogen-producing and methanogenic bacteria in sewage sludge and lake sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Sep;50(3):595–601. doi: 10.1128/aem.50.3.595-601.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolfing J., Mulder J. W. Comparison of methane production rate and coenzyme f(420) content of methanogenic consortia in anaerobic granular sludge. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 May;49(5):1142–1145. doi: 10.1128/aem.49.5.1142-1145.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferry J. G., Wolfe R. S. Anaerobic degradation of benzoate to methane by a microbial consortium. Arch Microbiol. 1976 Feb;107(1):33–40. doi: 10.1007/BF00427864. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerrant G. O., Lambert M. A., Moss C. W. Analysis of short-chain acids from anaerobic bacteria by high-performance liquid chromatography. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Aug;16(2):355–360. doi: 10.1128/jcm.16.2.355-360.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hungate R. E., Smith W., Bauchop T., Yu I., Rabinowitz J. C. Formate as an intermediate in the bovine rumen fermentation. J Bacteriol. 1970 May;102(2):389–397. doi: 10.1128/jb.102.2.389-397.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iannotti E. L., Kafkewitz D., Wolin M. J., Bryant M. P. Glucose fermentation products in Ruminococcus albus grown in continuous culture with Vibrio succinogenes: changes caused by interspecies transfer of H 2 . J Bacteriol. 1973 Jun;114(3):1231–1240. doi: 10.1128/jb.114.3.1231-1240.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones W. J., Guyot J. P., Wolfe R. S. Methanogenesis from sucrose by defined immobilized consortia. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Jan;47(1):1–6. doi: 10.1128/aem.47.1.1-6.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones W. J., Nagle D. P., Jr, Whitman W. B. Methanogens and the diversity of archaebacteria. Microbiol Rev. 1987 Mar;51(1):135–177. doi: 10.1128/mr.51.1.135-177.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenealy W., Zeikus J. G. Influence of corrinoid antagonists on methanogen metabolism. J Bacteriol. 1981 Apr;146(1):133–140. doi: 10.1128/jb.146.1.133-140.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovley D. R., Dwyer D. F., Klug M. J. Kinetic analysis of competition between sulfate reducers and methanogens for hydrogen in sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Jun;43(6):1373–1379. doi: 10.1128/aem.43.6.1373-1379.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McInerney M. J., Bryant M. P., Hespell R. B., Costerton J. W. Syntrophomonas wolfei gen. nov. sp. nov., an Anaerobic, Syntrophic, Fatty Acid-Oxidizing Bacterium. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Apr;41(4):1029–1039. doi: 10.1128/aem.41.4.1029-1039.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odom J. M., Peck H. D., Jr Hydrogenase, electron-transfer proteins, and energy coupling in the sulfate-reducing bacteria Desulfovibrio. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1984;38:551–592. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.38.100184.003003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phelps T. J., Zeikus J. G. Effect of fall turnover on terminal carbon metabolism in lake mendota sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Nov;50(5):1285–1291. doi: 10.1128/aem.50.5.1285-1291.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schauer N. L., Brown D. P., Ferry J. G. Kinetics of Formate Metabolism in Methanobacterium formicicum and Methanospirillum hungatei. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Sep;44(3):549–554. doi: 10.1128/aem.44.3.549-554.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schauer N. L., Ferry J. G. Metabolism of formate in Methanobacterium formicicum. J Bacteriol. 1980 Jun;142(3):800–807. doi: 10.1128/jb.142.3.800-807.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thauer R. K., Jungermann K., Decker K. Energy conservation in chemotrophic anaerobic bacteria. Bacteriol Rev. 1977 Mar;41(1):100–180. doi: 10.1128/br.41.1.100-180.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiele Jurgen H., Chartrain M., Zeikus J. Gregory. Control of Interspecies Electron Flow during Anaerobic Digestion: Role of Floc Formation in Syntrophic Methanogenesis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Jan;54(1):10–19. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.1.10-19.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wofford N. Q., Beaty P. S., McInerney M. J. Preparation of cell-free extracts and the enzymes involved in fatty acid metabolism in Syntrophomonas wolfei. J Bacteriol. 1986 Jul;167(1):179–185. doi: 10.1128/jb.167.1.179-185.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


