Abstract
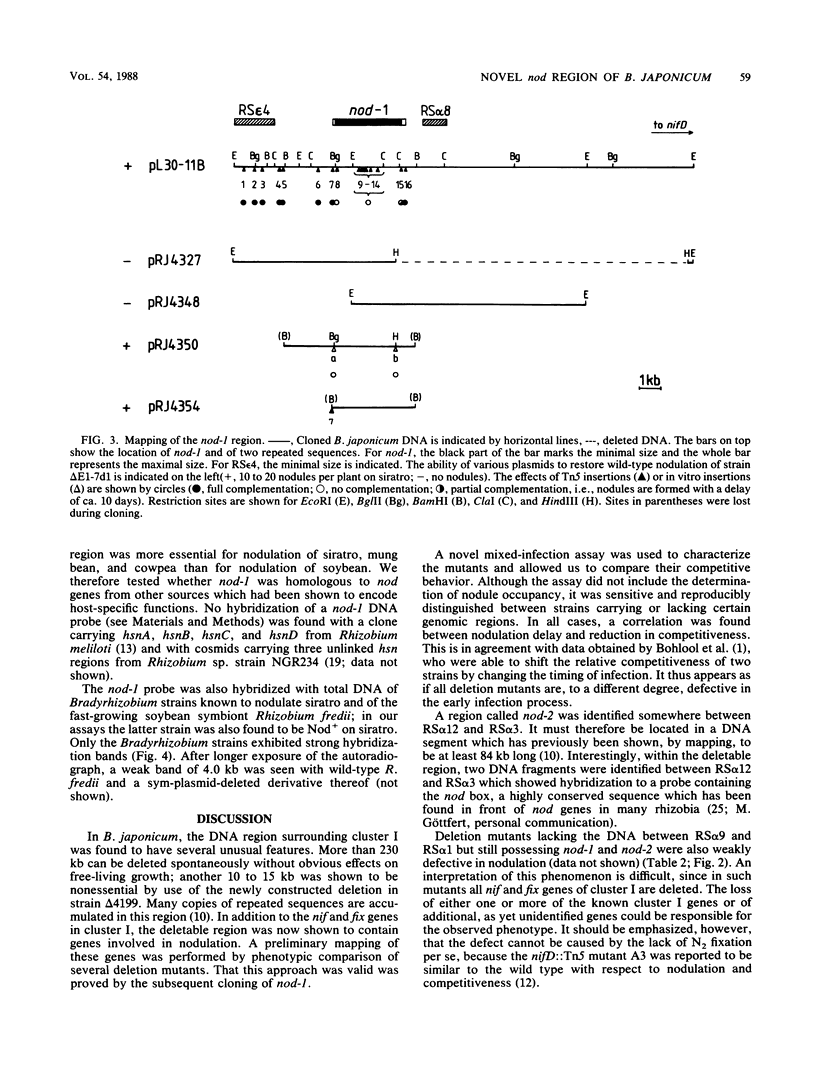
The phenotypes of a set of Bradyrhizobium japonicum 110 mutants with large deletions in the region of symbiotic gene cluster I were tested. The majority of the mutants showed a delayed nodulation on soybean and, by mixed-infection experiments, were found to be strongly reduced in their competitiveness. Phenotypic comparison of mutants with different deletion endpoints allowed a preliminary localization of two genomic regions, called nod-1 and nod-2, which were required for normal nodulation on soybean. Loss of nod-1 was found to result in a Nod− phenotype on cowpea, mung bean, and siratro. A recombinant cosmid was identified which fully restored nodulation ability of a mutant lacking nod-1. Using Tn5-containing derivatives and subclones of this cosmid for complementation, we delimited the nod-1 region to a DNA segment of 3.1 to 3.5 kilobase pairs.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Casadaban M. J., Martinez-Arias A., Shapira S. K., Chou J. Beta-galactosidase gene fusions for analyzing gene expression in escherichia coli and yeast. Methods Enzymol. 1983;100:293–308. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)00063-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole M. A., Elkan G. H. Transmissible resistance to penicillin G, neomycin, and chloramphenicol in Rhizobium japonicum. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1973 Sep;4(3):248–253. doi: 10.1128/aac.4.3.248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ditta G., Stanfield S., Corbin D., Helinski D. R. Broad host range DNA cloning system for gram-negative bacteria: construction of a gene bank of Rhizobium meliloti. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7347–7351. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman A. M., Long S. R., Brown S. E., Buikema W. J., Ausubel F. M. Construction of a broad host range cosmid cloning vector and its use in the genetic analysis of Rhizobium mutants. Gene. 1982 Jun;18(3):289–296. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90167-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn M., Hennecke H. Mapping of a Bradyrhizobium japonicum DNA Region Carrying Genes for Symbiosis and an Asymmetric Accumulation of Reiterated Sequences. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Sep;53(9):2247–2252. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.9.2247-2252.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horvath B., Kondorosi E., John M., Schmidt J., Török I., Györgypal Z., Barabas I., Wieneke U., Schell J., Kondorosi A. Organization, structure and symbiotic function of Rhizobium meliloti nodulation genes determining host specificity for alfalfa. Cell. 1986 Aug 1;46(3):335–343. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90654-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorgensen R. A., Rothstein S. J., Reznikoff W. S. A restriction enzyme cleavage map of Tn5 and location of a region encoding neomycin resistance. Mol Gen Genet. 1979;177(1):65–72. doi: 10.1007/BF00267254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaluza K., Hahn M., Hennecke H. Repeated sequences similar to insertion elements clustered around the nif region of the Rhizobium japonicum genome. J Bacteriol. 1985 May;162(2):535–542. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.2.535-542.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keyser H. H., van Berkum P., Weber D. F. A Comparative Study of the Physiology of Symbioses Formed by Rhizobium japonicum with Glycine max, Vigna unguiculata, and Macroptilium atropurpurem. Plant Physiol. 1982 Dec;70(6):1626–1630. doi: 10.1104/pp.70.6.1626. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nieuwkoop A. J., Banfalvi Z., Deshmane N., Gerhold D., Schell M. G., Sirotkin K. M., Stacey G. A locus encoding host range is linked to the common nodulation genes of Bradyrhizobium japonicum. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jun;169(6):2631–2638. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.6.2631-2638.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noti J. D., Folkerts O., Turken A. N., Szalay A. A. Organization and characterization of genes essential for symbiotic nitrogen fixation from Bradyrhizobium japonicum I110. J Bacteriol. 1986 Sep;167(3):774–783. doi: 10.1128/jb.167.3.774-783.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao R. N., Rogers S. G. Plasmid pKC7: a vector containing ten restriction endonuclease sites suitable for cloning DNA segments. Gene. 1979 Sep;7(1):79–82. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(79)90044-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regensburger B., Hennecke H. RNA polymerase from Rhizobium japonicum. Arch Microbiol. 1983 Aug;135(2):103–109. doi: 10.1007/BF00408017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rostas K., Kondorosi E., Horvath B., Simoncsits A., Kondorosi A. Conservation of extended promoter regions of nodulation genes in Rhizobium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(6):1757–1761. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.6.1757. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]