Abstract
Kraft pulps, prepared from softwoods, and small chips of birch wood were treated with heme and tert-butyl hydroperoxide in aqueous solutions at reflux temperature. Analyses of treated pulps showed decreases in kappa number (a measure of lignin content) from about 36 to less than 2, with concomitant increases in brightness (80% increase in the better samples). Analyses of treated wood chips revealed selective delignification and removal of hemicelluloses. After 48 h of treatment, lignin losses from the wood chips approached 40%, and xylose/mannose (hemicellulose) losses approached 70%, while glucose (cellulose) losses were less than 10%. Examination of delignified chips by transmission electron microscopy showed that the removal of lignin occurred in a manner virtually indistinguishable from that seen after decay by white rot fungi. Various metalloporphyrins, which act as biomimetic catalysts, were compared to horseradish peroxidase and fungal manganese peroxidase in their abilities to oxidize syringaldazine in an organic solvent, dioxane. The metalloporphyrins and peroxidases behaved similarly, and it appeared that the activities of the peroxidases resulted from the extraction of heme into the organic phase, rather than from the activities of the enzymes themselves. We concluded that heme-tert-butyl hydroperoxide systems in the absence of a protein carrier mimic the decay of lignified tissues by white rot fungi.
Full text
PDF

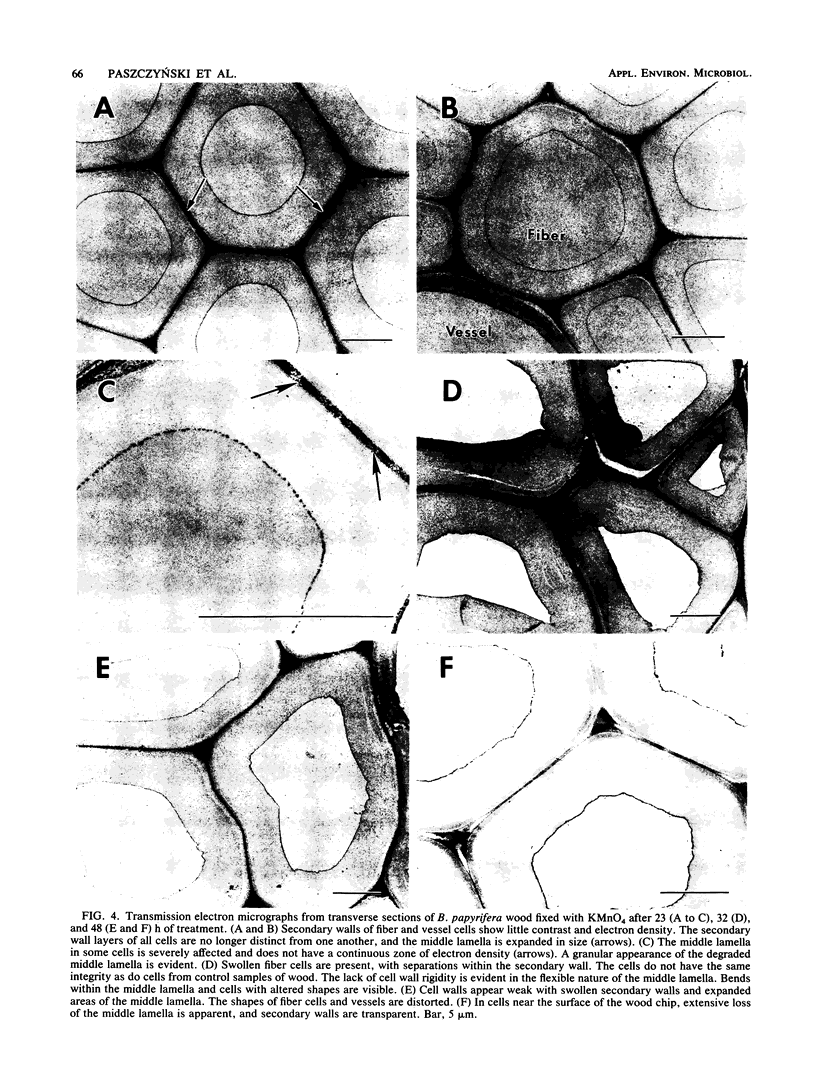


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersson L. A., Renganathan V., Chiu A. A., Loehr T. M., Gold M. H. Spectral characterization of diarylpropane oxygenase, a novel peroxide-dependent, lignin-degrading heme enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1985 May 25;260(10):6080–6087. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
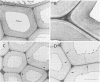
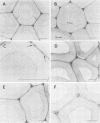
- Blanchette R. A., Reid I. D. Ultrastructural Aspects of Wood Delignification by Phlebia (Merulius) tremellosus. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Aug;52(2):239–245. doi: 10.1128/aem.52.2.239-245.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanchette R. A. Screening wood decayed by white rot fungi for preferential lignin degradation. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Sep;48(3):647–653. doi: 10.1128/aem.48.3.647-653.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dordick J. S., Marletta M. A., Klibanov A. M. Peroxidases depolymerize lignin in organic media but not in water. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(17):6255–6257. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.17.6255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faison B. D., Kirk T. K. Relationship Between Lignin Degradation and Production of Reduced Oxygen Species by Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Nov;46(5):1140–1145. doi: 10.1128/aem.46.5.1140-1145.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenn J. K., Akileswaran L., Gold M. H. Mn(II) oxidation is the principal function of the extracellular Mn-peroxidase from Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1986 Dec;251(2):688–696. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(86)90378-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenn J. K., Gold M. H. Purification and characterization of an extracellular Mn(II)-dependent peroxidase from the lignin-degrading basidiomycete, Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1985 Nov 1;242(2):329–341. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(85)90217-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold M. H., Kuwahara M., Chiu A. A., Glenn J. K. Purification and characterization of an extracellular H2O2-requiring diarylpropane oxygenase from the white rot basidiomycete, Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1984 Nov 1;234(2):353–362. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(84)90280-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huynh V. B. Biomimetic oxidation of lignin model compounds by simple inorganic complexes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Sep 30;139(3):1104–1110. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(86)80291-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paszczyński A., Huynh V. B., Crawford R. Comparison of ligninase-I and peroxidase-M2 from the white-rot fungus Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1986 Feb 1;244(2):750–765. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(86)90644-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimada M., Habe T., Umezawa T., Higuchi T., Okamoto T. The C-C bond cleavage of a lignin model compound, 1,2-diarylpropane-1,3-diol, with a heme-enzyme model catalyst tetraphenylporphyrinatoiron(III)chloride in the presence of tert-butylhydroperoxide. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Aug 16;122(3):1247–1252. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)91226-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tien M., Kirk T. K., Bull C., Fee J. A. Steady-state and transient-state kinetic studies on the oxidation of 3,4-dimethoxybenzyl alcohol catalyzed by the ligninase of Phanerocheate chrysosporium Burds. J Biol Chem. 1986 Feb 5;261(4):1687–1693. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tien M., Kirk T. K. Lignin-degrading enzyme from Phanerochaete chrysosporium: Purification, characterization, and catalytic properties of a unique H(2)O(2)-requiring oxygenase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(8):2280–2284. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.8.2280. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]