Abstract
The cytocidal properties of metronidazole against hypoxic mammalian cells are described. This chemotherapeutic action has been shown to be dependent on drug concentration and duration of exposure. The x-ray TCD50 for a murine anaplastic carcinoma was reduced from 6081 rad to 4643 rad when animals were given metronidazole orally for 36 h before radiation treatment. The effect is attributed to the direct killing of hypoxic tumour cells by a mechanism analogous to that proposed for the action of the drug on anaerobic micro-organisms. It is concluded that further work with metronidazole as a cytotoxin specific for hypoxic cells is warranted, particularly in view of the reported lack of toxicity associated with the preliminary clinical use of the drug as a radiosensitizer in man.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Asquith J. C., Foster J. L., Willson R. L., Ings R., McFadzean J. A. Metronidazole ("Flagyl"). A radiosensitizer of hypoxic cells. Br J Radiol. 1974 Aug;47(560):474–481. doi: 10.1259/0007-1285-47-560-474. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
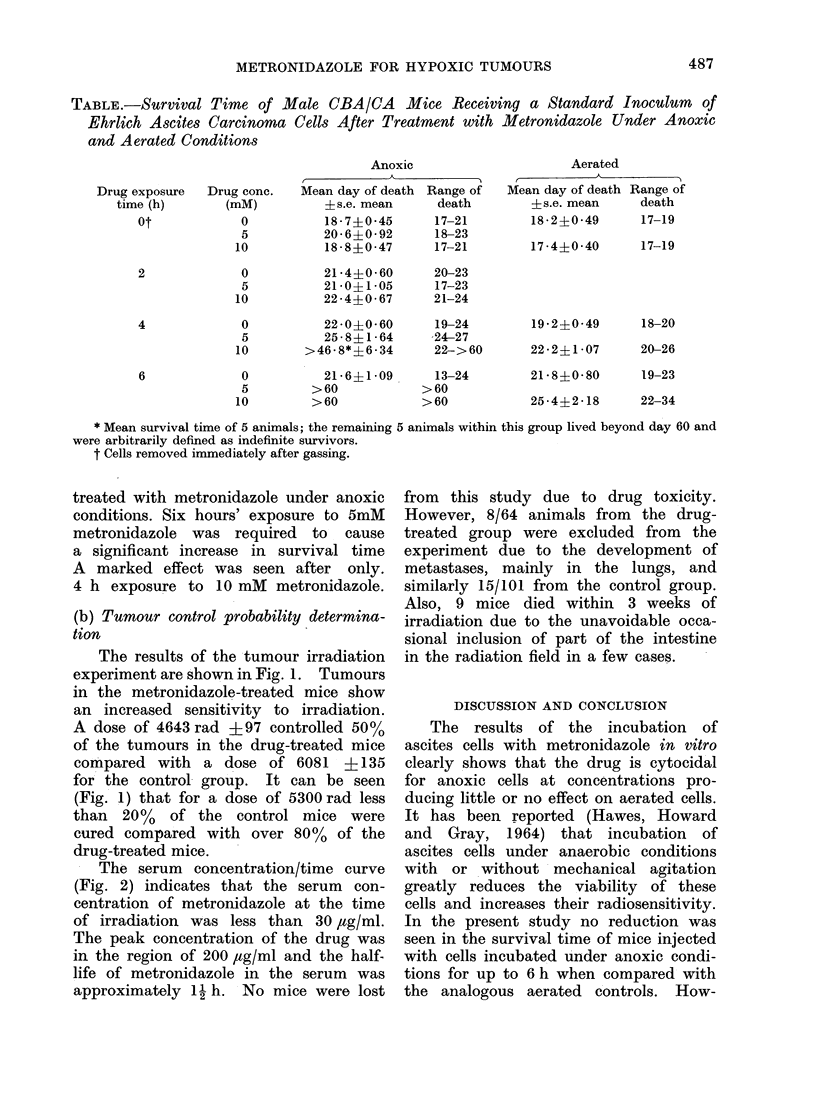
- Begg A. C., Sheldon P. W., Foster J. L. Demonstration of radiosensitization of hypoxic cells in solid tumours by metronidazole. Br J Radiol. 1974 Jul;47(559):399–404. doi: 10.1259/0007-1285-47-559-399. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
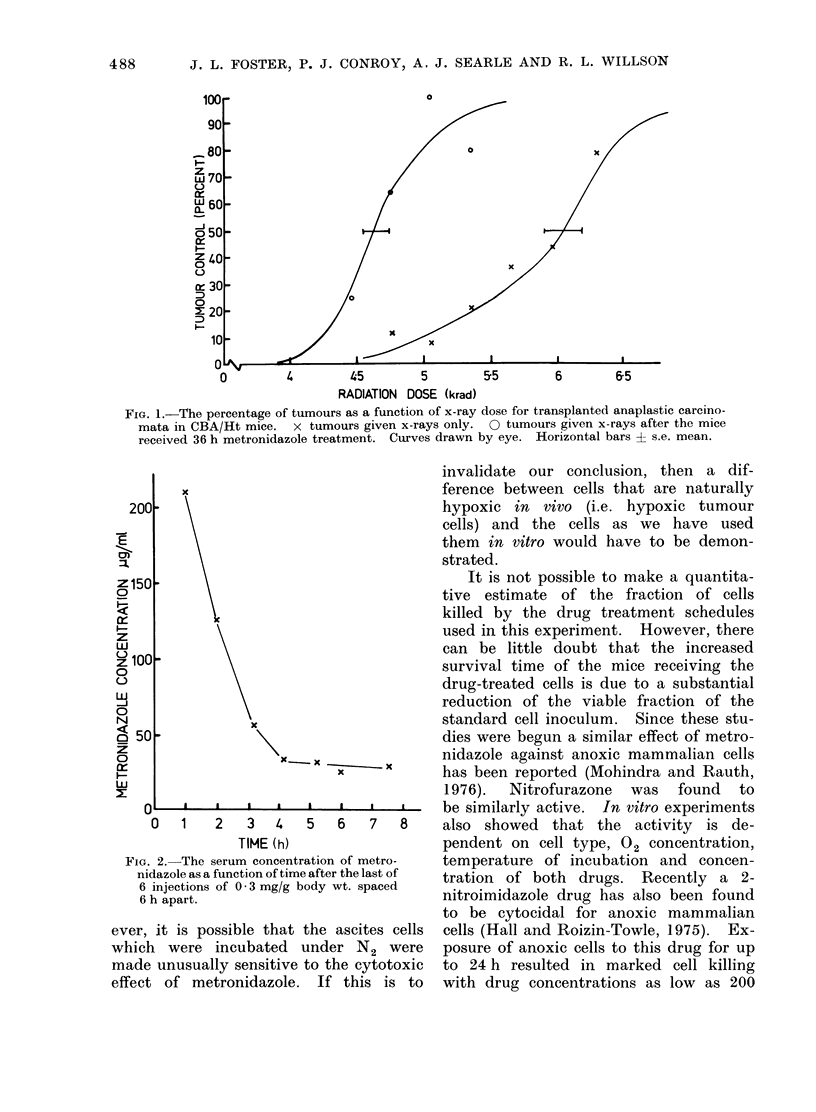
- Deutsch G., Foster J. L., McFadzean J. A., Parnell M. Human studies with "high dose" metronidazole: a non-toxic radiosensitizer of hypoxic cells. Br J Cancer. 1975 Jan;31(1):75–80. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1975.9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emmerson P. T., Howard-Flanders P. Preferential sensitization of anoxic bacteria to x-rays by organic nitroxide-free radicals. Radiat Res. 1965 Sep;26(1):54–62. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAWES C., HOWARD A., GRAY L. H. CHROMOSOME ABNORMALITY AND RADIATION SENSITIVITY IN STORED ASCITES-TUMOUR CELLS. Mutat Res. 1964 Jul;106:193–201. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(64)90022-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall E. J., Roizin-Towle L. Hypoxic sensitizers: radiobiological studies at the cellular level. Radiology. 1975 Nov;117(2):453–457. doi: 10.1148/117.2.453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ings R. M., McFadzean J. A., Ormerod W. E. The mode of action of metronidazole in Trichomonas vaginalis and other micro-organisms. Biochem Pharmacol. 1974 May 1;23(9):1421–1429. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(74)90362-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rauth A. M., Kaufman K. In vivo testing of hypoxic radiosensitizers using the KHT murine tumour assayed by the lung-colony technique. Br J Radiol. 1975 Mar;48(567):209–220. doi: 10.1259/0007-1285-48-567-209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone H. B., Withers H. R. Tumor and normal tissue response to metronidazole and irradiation in mice. Radiology. 1974 Nov;113(2):441–444. doi: 10.1148/113.2.441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland R. M. Selective chemotherapy of noncycling cells in an in vitro tumor model. Cancer Res. 1974 Dec;34(12):3501–3503. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urtasun R. C., Chapman J. D., Band P., Rabin H. R., Fryer C. G., Sturmwind J. Phase 1 study of high-dose metronidazole: a specific in vivo and in vitro radiosensitizer of hypoxic cells. Radiology. 1975 Oct;117(1):129–133. doi: 10.1148/117.1.129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urtasun R. C., Sturmwind J., Rabin H., Band P. R., Chapman J. D. Letter: "High-dose" metronidazole: a preliminary pharmacological study prior to its investigational use in clinical radiotherapy trials. Br J Radiol. 1974 May;47(557):297–299. doi: 10.1259/0007-1285-47-557-297-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willson R. L., Cramp W. A., Ings R. M. Metronidazole ('Flagyl'): mechanisms of radiosensitization. Int J Radiat Biol Relat Stud Phys Chem Med. 1974 Dec;26(6):557–569. doi: 10.1080/09553007414551591. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willson R. L., Searle A. J. Metronidazole (Flagyl): iron catalysed reaction with sulphydryl groups and tumour radiosensitisation. Nature. 1975 Jun 5;255(5508):498–500. doi: 10.1038/255498a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


