Abstract
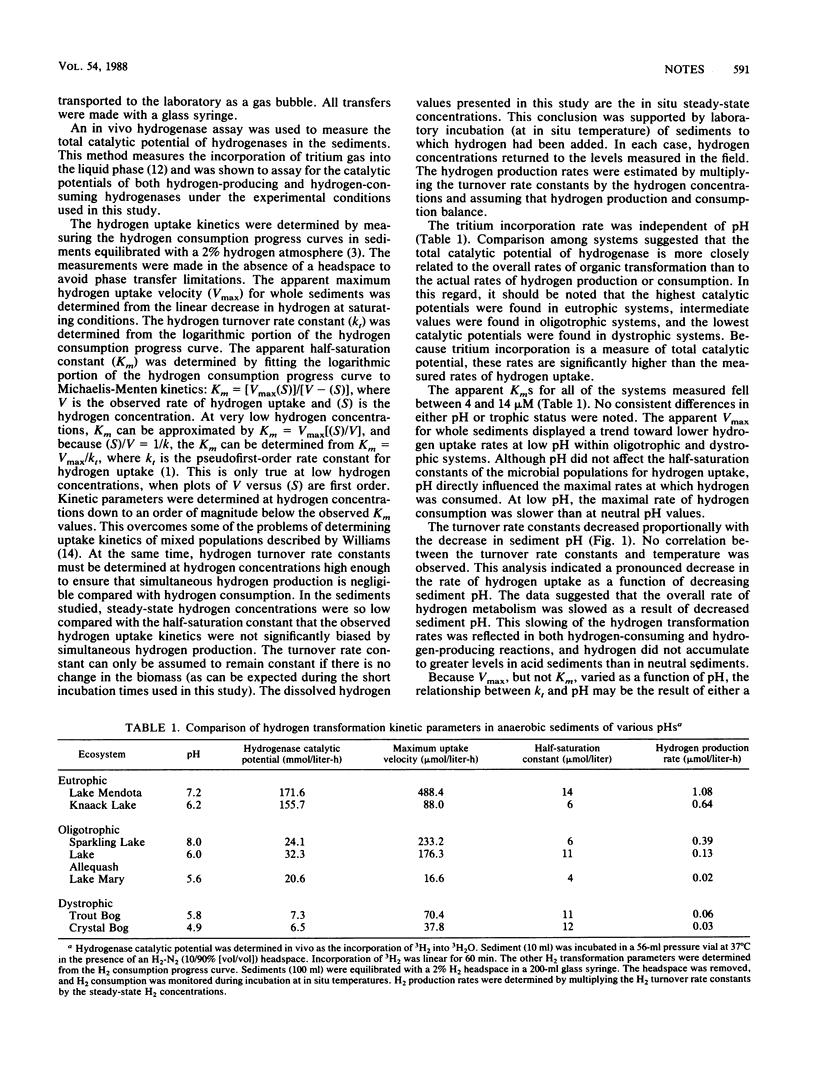
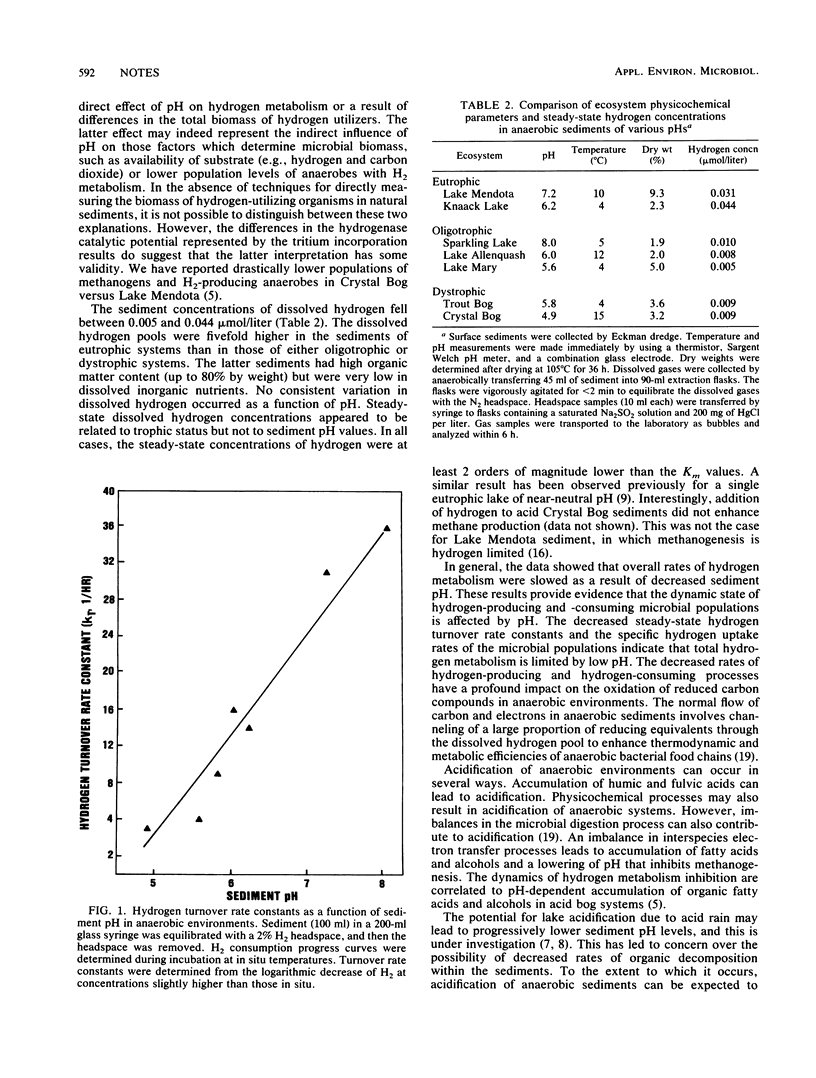
Hydrogen transformation kinetic parameters were measured in sediments from anaerobic systems covering a wide range of environmental pH values to assess the influence of pH on hydrogen metabolism. The concentrations of dissolved hydrogen were measured and hydrogen transformation kinetics of the sediments were monitored in the laboratory by monitoring hydrogen consumption progress curves. The hydrogen turnover rate constants (kt) decreased directly as a function of decreasing sediment pH, and the maximum hydrogen uptake velocities (Vmax) varied as a function of pH within each of the trophic states. Conversely, the half-saturation concentrations (Km) were independent of pH. The steady-state hydrogen concentrations were at least 2 orders of magnitude lower than the half-saturation constants for hydrogen uptake. Dissolved hydrogen concentrations were at least fivefold higher in sediments from eutrophic systems than from oligotrophic and dystrophic systems. The rates of hydrogen production determined from the assumption of steady state decreased with sediment pH. These data indicate that progressively lower pH values inhibit microbial hydrogen-producing and -consuming processes within sedimentary ecosystems.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Button D. K. Kinetics of nutrient-limited transport and microbial growth. Microbiol Rev. 1985 Sep;49(3):270–297. doi: 10.1128/mr.49.3.270-297.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conrad R., Aragno M., Seiler W. Production and consumption of hydrogen in a eutrophic lake. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Feb;45(2):502–510. doi: 10.1128/aem.45.2.502-510.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conrad R., Phelps T. J., Zeikus J. G. Gas metabolism evidence in support of the juxtaposition of hydrogen-producing and methanogenic bacteria in sewage sludge and lake sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Sep;50(3):595–601. doi: 10.1128/aem.50.3.595-601.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodwin S., Zeikus J. G. Ecophysiological adaptations of anaerobic bacteria to low pH: analysis of anaerobic digestion in acidic bog sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Jan;53(1):57–64. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.1.57-64.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingvorsen K., Zeikus J. G., Brock T. D. Dynamics of bacterial sulfate reduction in a eutrophic lake. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Dec;42(6):1029–1036. doi: 10.1128/aem.42.6.1029-1036.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovley D. R., Dwyer D. F., Klug M. J. Kinetic analysis of competition between sulfate reducers and methanogens for hydrogen in sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Jun;43(6):1373–1379. doi: 10.1128/aem.43.6.1373-1379.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mah R. A., Ward D. M., Baresi L., Glass T. L. Biogenesis of methane. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1977;31:309–341. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.31.100177.001521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schink B., Lupton F. S., Zeikus J. G. Radioassay for hydrogenase activity in viable cells and documentation of aerobic hydrogen-consuming bacteria living in extreme environments. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 May;45(5):1491–1500. doi: 10.1128/aem.45.5.1491-1500.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuttle J. H., Randles C. I., Dugan P. R. Activity of microorganisms in acid mine water. I. Influence of acid water on aerobic heterotrophs of a normal stream. J Bacteriol. 1968 May;95(5):1495–1503. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.5.1495-1503.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams R. T., Crawford R. L. Methanogenic bacteria, including an Acid-tolerant strain, from peatlands. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Dec;50(6):1542–1544. doi: 10.1128/aem.50.6.1542-1544.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winfrey M. R., Nelson D. R., Klevickis S. C., Zeikus J. G. Association of hydrogen metabolism with methanogenesis in Lake Mendota sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Feb;33(2):312–318. doi: 10.1128/aem.33.2.312-318.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinder S. H., Mah R. A. Isolation and Characterization of a Thermophilic Strain of Methanosarcina Unable to Use H(2)-CO(2) for Methanogenesis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Nov;38(5):996–1008. doi: 10.1128/aem.38.5.996-1008.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


