Abstract
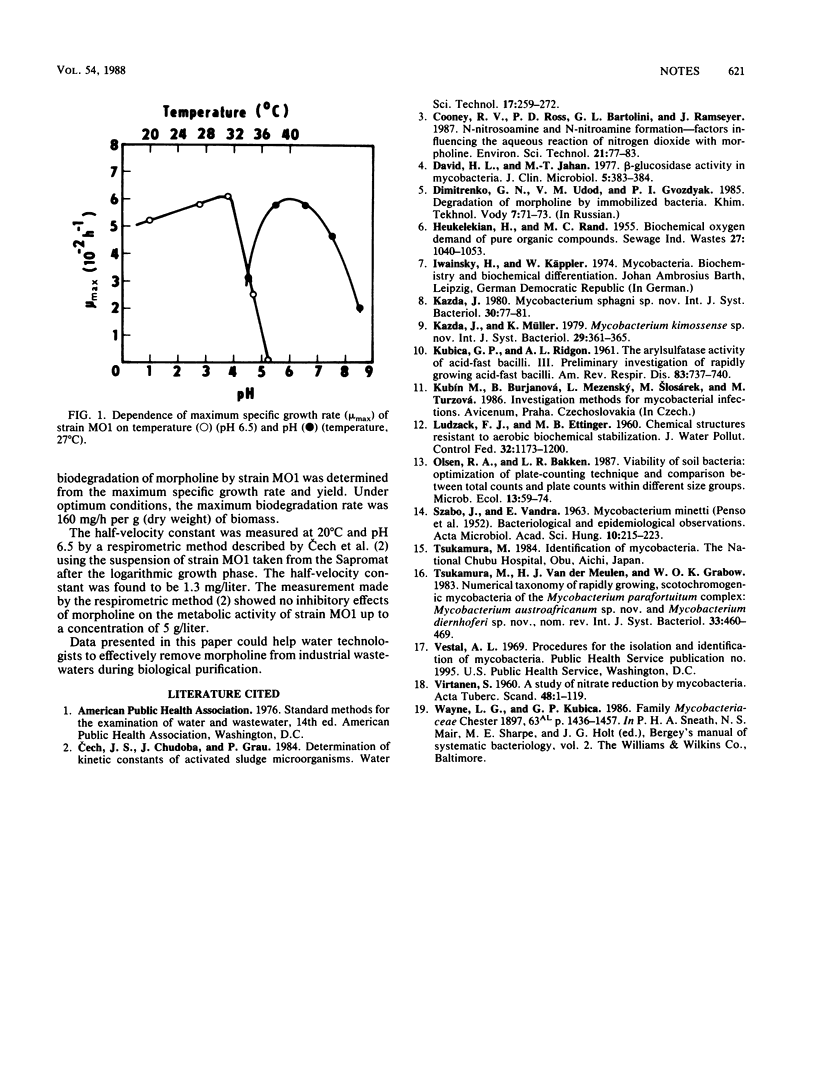
A gram-positive, slowly growing rod effectively utilizing morpholine as the sole source of organic carbon, nitrogen, and energy was isolated from a mixed culture in a laboratory reactor. The strain was tentatively identified as Mycobacterium aurum. Its growth characteristics at 20 degrees C and pH 6.5 were as follows: maximum specific growth rate, 0.052 h-1; half-velocity constant, 1.3 mg/liter; and yield, 0.37 g/g. The optimum temperature and pH were 31 degrees C and 6.0, respectively.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- David H. L., Jahan M. T. beta-Glucosidase activity in mycobacteria. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Mar;5(3):383–384. doi: 10.1128/jcm.5.3.383-384.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUBICA G. P., RIGDON A. L. The arylsulfatase activity of acid-fast bacilli. III. Preliminary investigation of rapidly growing acid-fast bacilli. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1961 May;83:737–740. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1961.83.5.737. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SZABO I., VANDRA E. MYCOBACTERIUM MINETTI (PENSO ET AL. 1952). BACTERIOLOGICAL AND EPIDEMIOLOGICAL OBSERVATIONS. Acta Microbiol Acad Sci Hung. 1963;10:215–223. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VIRTANEN S. A study of nitrate reduction by mycobacteria. The use of the nitrate reduction test in the identification of mycobacteria. Acta Tuberc Scand Suppl. 1960;48:1–119. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


