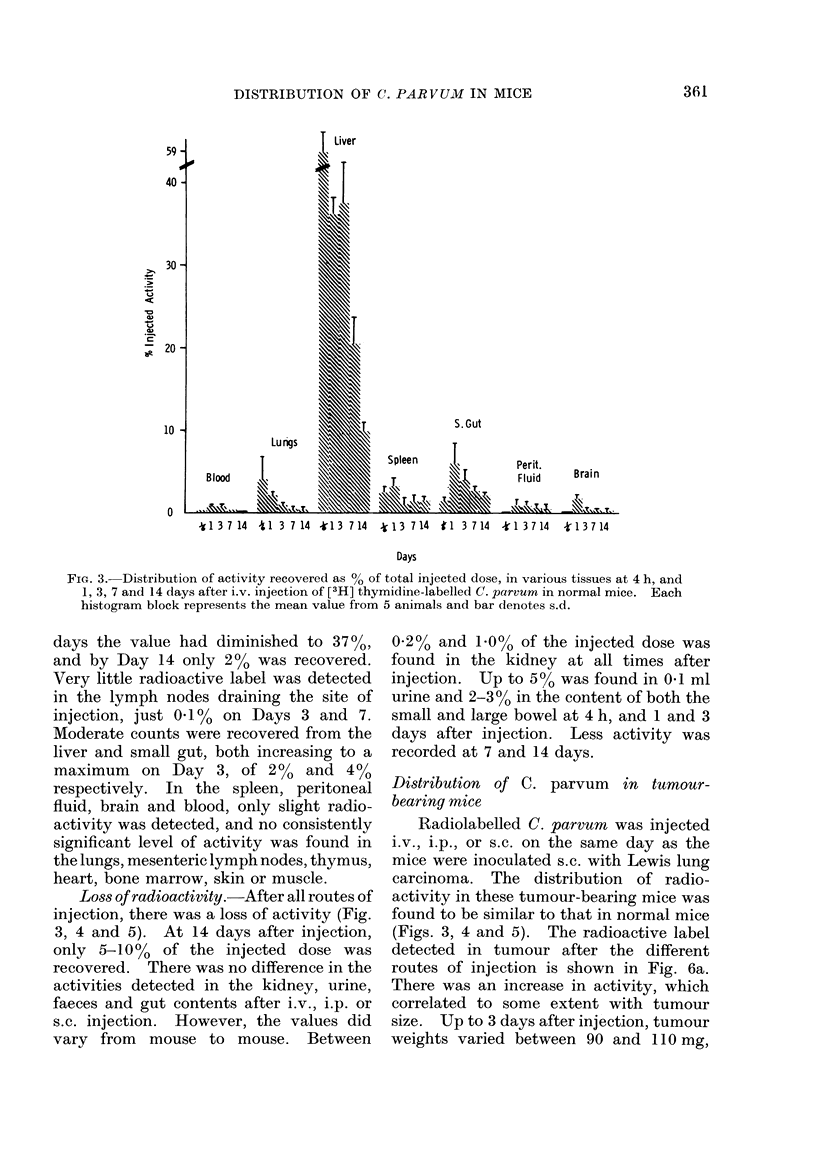
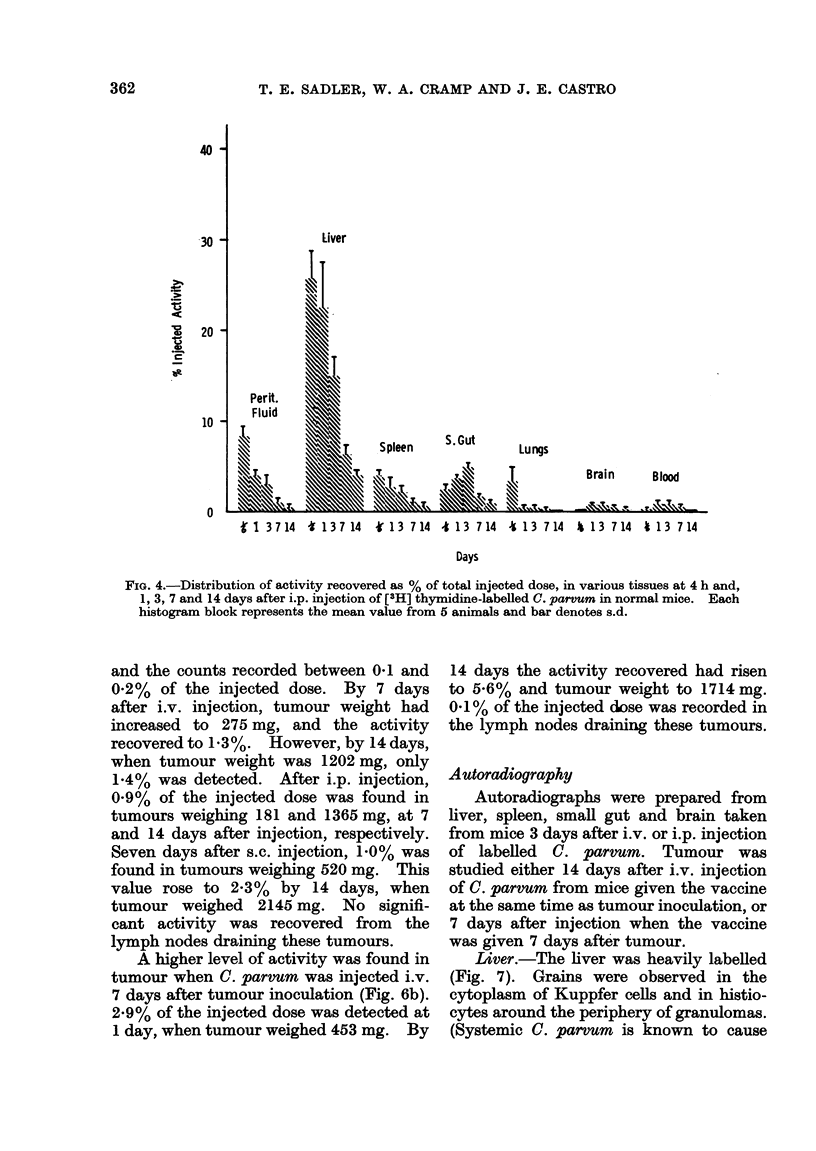
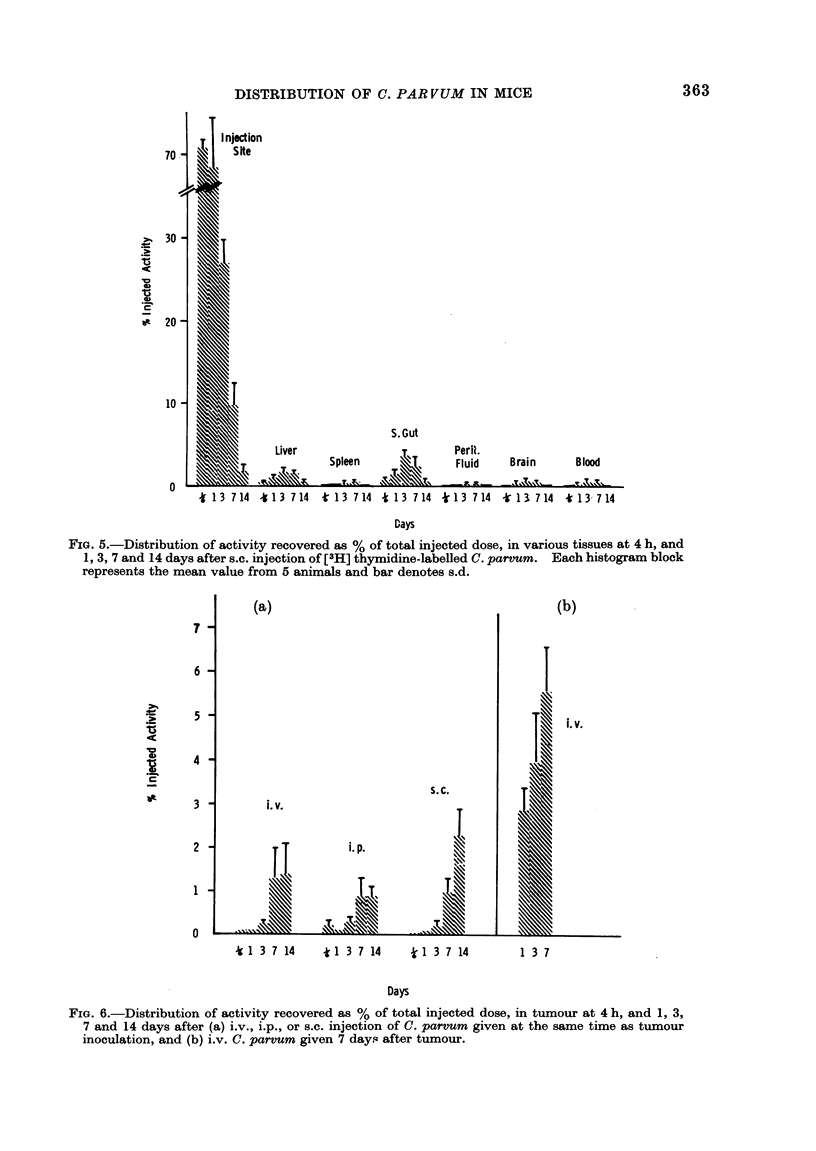
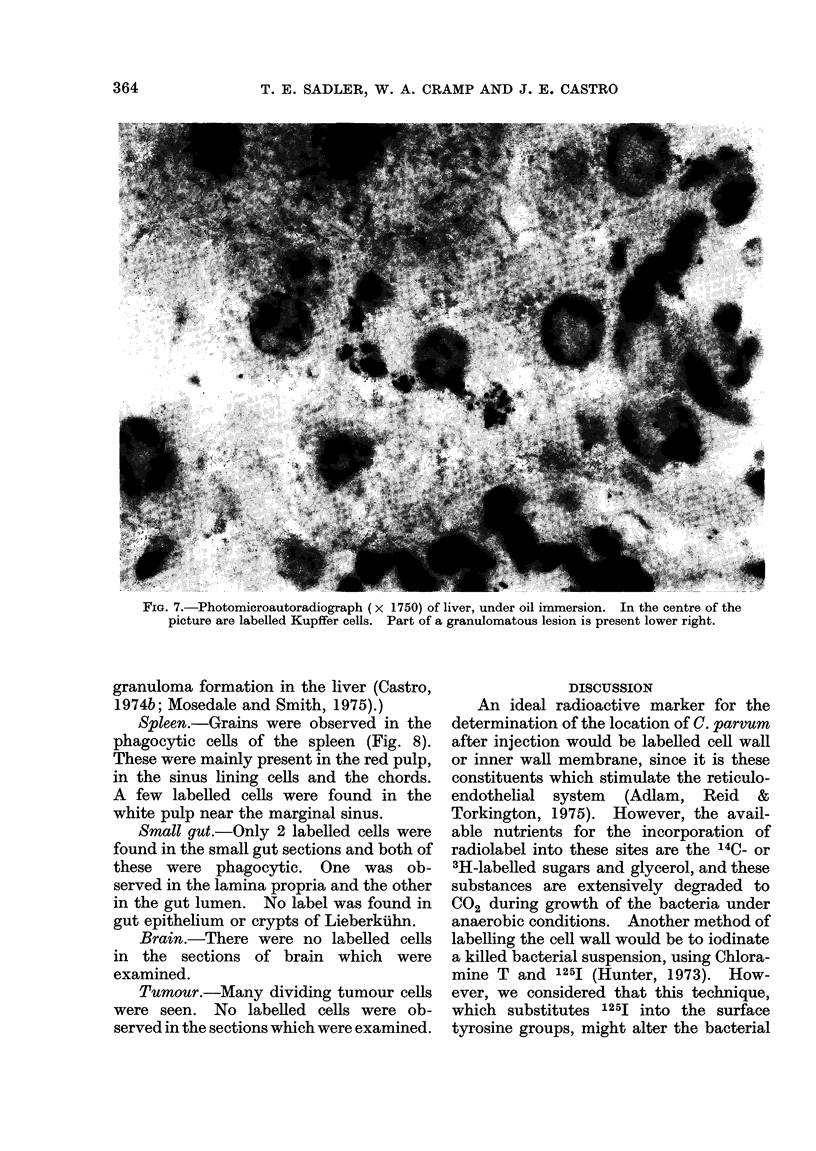
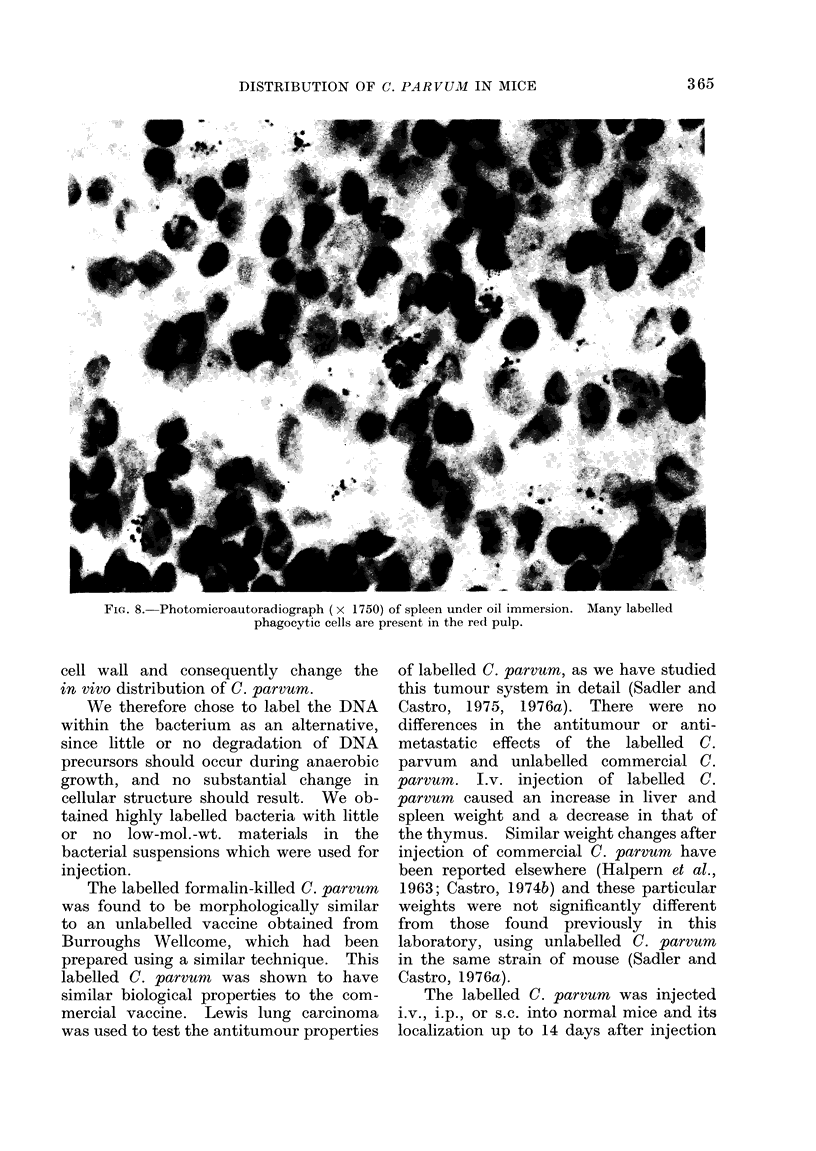
Abstract
Corynebacterium parvum was labelled by growing live bacteria in the presence of [3H]thymidine. The bacteria were killed by formalin, washed thoroughly and resuspended at a concentration of 7 mg dry weight/ml. An activity of 1-6 X 10(5) ct/min/0-1 ml was obtained. The biological properties (inhibition of tumour growth and hepatosplenomegaly) of the labelled C. parvum were compared with those of commercially available vaccine, and were found to be similar. Labelled C. parvum was injected i.v., i.p., or s.c. into normal C57BL mice and the localization of activity determined at 4 h and 1,3,7 and 14 days after injection. After i.v. or i.p. injection, highest counts were recorded in the liver. Moderate activity was found in the spleen, lungs and small gut. After s.c. injection, the majority of radioactive label was detected at the site of injection and little found in other tissues. The distribution of injected C. parvum was also studied in mice bearing Lewis tumour, and was found to be similar to that in normal mice. Moderate amounts of labelled C. parvum were recovered from tumour. There appeared to be no relationship between the antitumour effect of C. parvum given by a particular route of injection and the concentration of C. parvum recovered from the tumour.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Castro J. E. Antitumour effects of Corynebacterium parvum in mice. Eur J Cancer. 1974 Feb;10(2):121–127. doi: 10.1016/0014-2964(74)90063-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castro J. E. The effect of Corynebacterium parvum on the structure and function of the lymphoid system in mice. Eur J Cancer. 1974 Feb;10(2):115–120. doi: 10.1016/0014-2964(74)90062-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christie G. H., Bomford R. Mechanisms of macrophage activation by Corynebacterium parvum. I. In vitro experiments. Cell Immunol. 1975 May;17(1):141–149. doi: 10.1016/s0008-8749(75)80014-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denlinger R. H., Axler D. A., Koestner A., Liss L. Tumor-specific transplantation immunity to intracerebral challenge with cells from a methylnitrosourea- induced brain tumor. J Med. 1975;6(3-4):249–259. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fielding P., Fox C. F. Evidence for stable attachment of DNA to membrane at the replication origin of Escherichia coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Oct 9;41(1):157–162. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)90482-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghaffar A., Cullen R. T., Woodruff M. A. Further analysis of the anti-tumour effect in vitro of peritoneal exudate cells from mice treated with Corynebacterium parvum. Br J Cancer. 1975 Jan;31(1):15–24. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1975.3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holman B. L. The blood brain barrier: anatomy and physiology. Prog Nucl Med. 1972;1:236–248. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Likhite V. V., Halpern B. N. Lasting rejection of mammary adenocarcinoma cell tumors in DBA-2 mice with intratumor injection of killed Corynebacterium parvum. Cancer Res. 1974 Feb;34(2):341–344. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PELC S. R. The stripping-film technique of autoradiography. Int J Appl Radiat Isot. 1956 Nov;1(3):172–177. doi: 10.1016/0020-708x(56)90003-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SUGIURA K., STOCK C. C. Studies in a tumor spectrum. III. The effect of phosphoramides on the growth of a variety of mouse and rat tumors. Cancer Res. 1955 Jan;15(1):38–51. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadler T. E., Castro J. E. Abrogation of the anti-metastatic activity of C. parvum by antilymphocyte serum. Br J Cancer. 1976 Sep;34(3):291–295. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1976.165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadler T. E., Castro J. E. Lack of immunological and anti-tumour effects of orally administered Corynebacterium papvum in mice. Br J Cancer. 1975 Mar;31(3):359–363. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1975.71. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadler T. E., Castro J. E. The effects of Corynebacterium parvum and surgery on the Lewis lung carcinoma and its metastases. Br J Surg. 1976 Apr;63(4):292–296. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800630410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott M. T. Corynebacterium parvum as a therapeutic antitumor agent in mice. II. Local injection. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1974 Sep;53(3):861–865. doi: 10.1093/jnci/53.3.861. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott M. T. Corynebacterium parvum as an immunotherapeutic anticancer agent. Semin Oncol. 1974 Dec;1(4):367–378. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott M. T. Depression of delayed-type hypersensitivity by Corynebacterium parvum: mandatory role of the spleen. Cell Immunol. 1974 Aug;13(2):251–263. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(74)90243-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith S. E., Scott M. T. Biological effects of Corynebacterium parvum. 3. Amplification of resistance and impairment of active immunity to murine tumours. Br J Cancer. 1972 Oct;26(5):361–367. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1972.47. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wexler H. Accurate identification of experimental pulmonary metastases. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1966 Apr;36(4):641–645. doi: 10.1093/jnci/36.4.641. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodruff M. F., Boak J. L. Inhibitory effect of injection of Corynebacterium parvum on the growth of tumour transplants in isogenic hosts. Br J Cancer. 1966 Jun;20(2):345–355. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1966.42. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodruff M. F., Dunbar N. Effect of local injection of Corynebacterium parvum on the growth of a murine fibrosarcoma. Br J Cancer. 1975 Jul;32(1):34–41. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1975.131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodruff M. F., Inchley M. P. Synergistic inhibition of mammary carcinoma transplants in A-strain mice by antitumour globulin and C. parvum. Br J Cancer. 1971 Sep;25(3):584–593. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1971.74. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]