Abstract
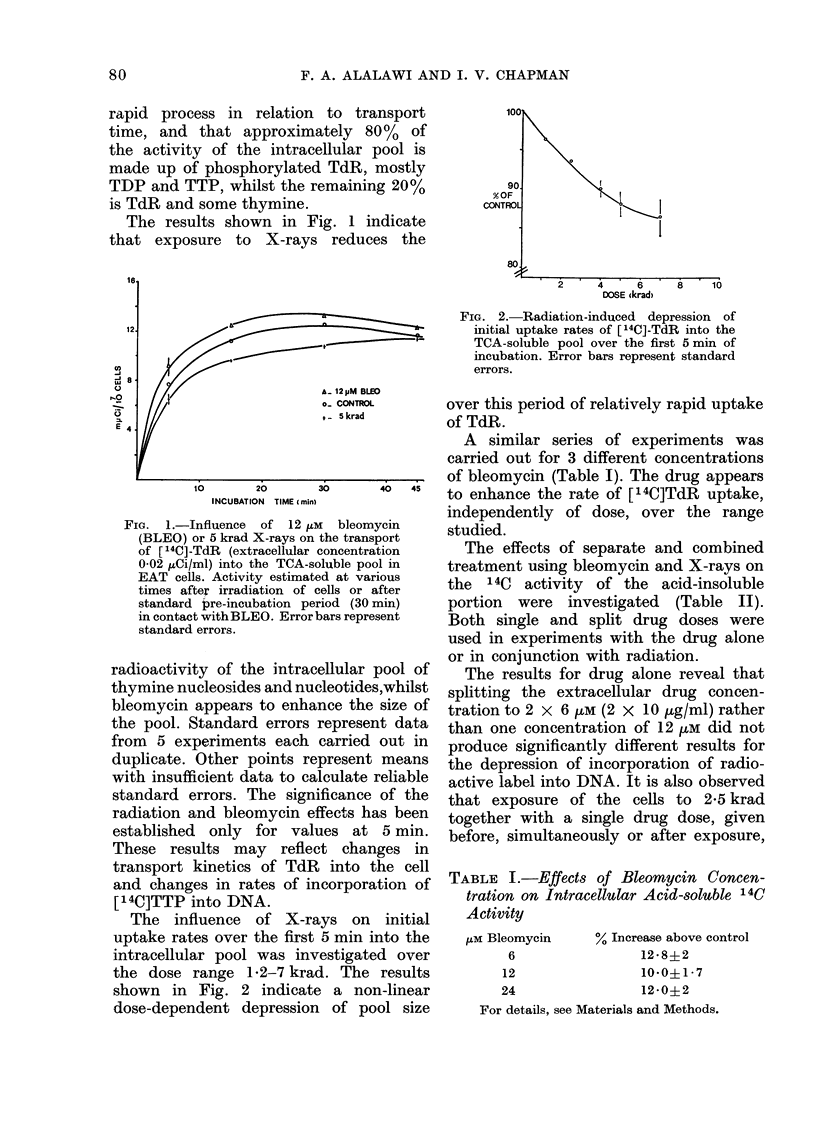
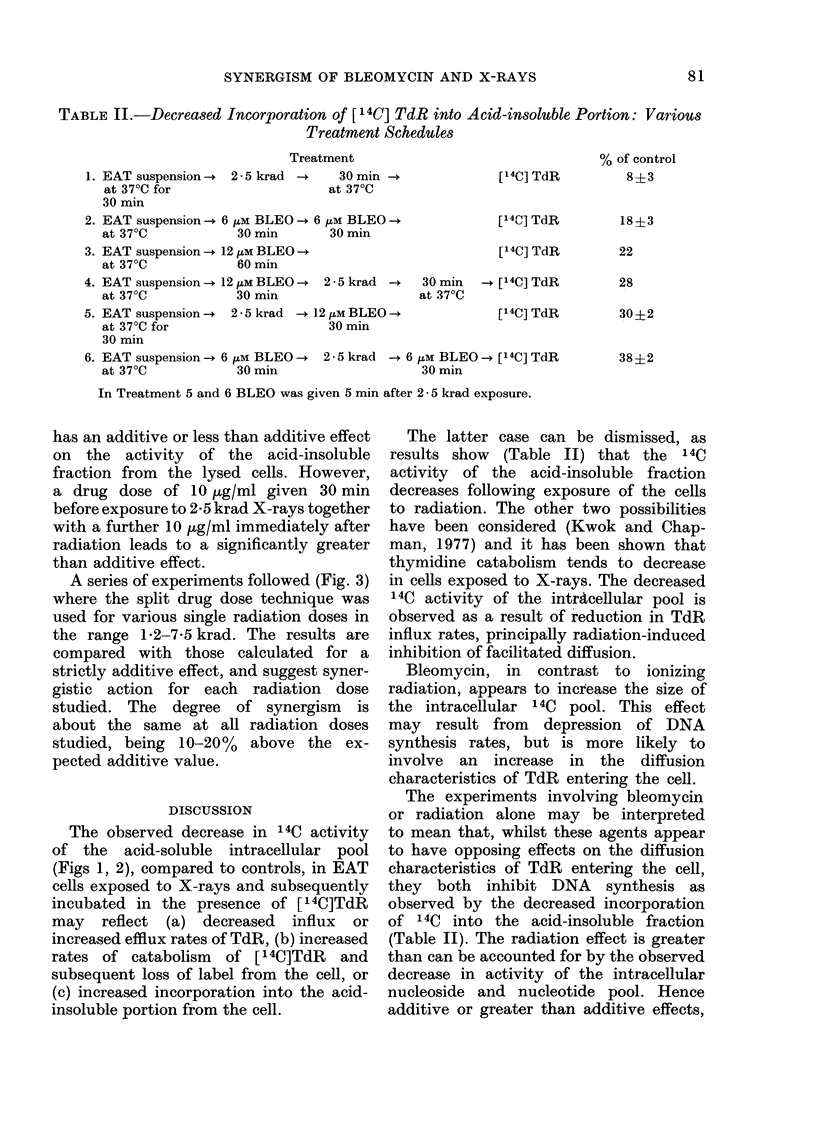
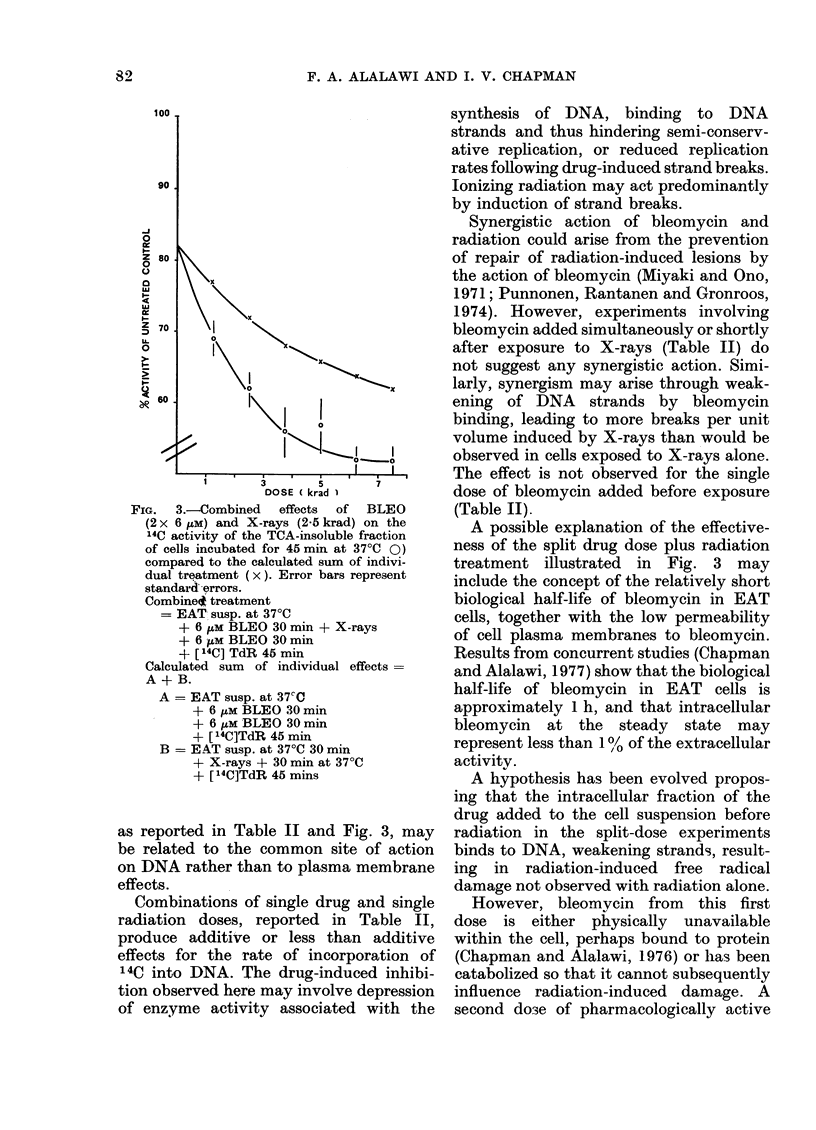
Separate and combined effects of bleomycin and X-rays on rates of uptake of [14C]thymidine into Ehrlich ascites cells were assessed for extracellular drug concentrations of 12 micron (20 microgram/ml) and radiation doses of 2-5 krad. Rates of DNA synthesis were followed by monitoring the activity of the acid-insoluble portion of the asynchronous culture. The 14C activity of the acid-soluble pool was assessed in determining the rate of passage of 14C-TdR across the cell membrane. The results reveal that whilst the effects of each agent on TdR uptake rates are markedly different, they both inhibit DNA synthesis. Combined studies with both agents, 2-5 krad X-rays plus 20 microgram/ml bleomycin before, simultaneously or after exposure to X-rays, produced additive or less than additive effects on rates of incorporation of TdR into DNA. However, when the drug dose is split 2 X 10 microgram/ml before and after exposure to 2-5 krad X-rays, a synergistic effect on inhibition of DNA synthesis is observed.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bleehen N. M., Gillies N. E., Twentyman P. R. The effect of bleomycin and radiation in combination on bacteria and mammalian cells in culture. Br J Radiol. 1974 Jun;47(558):346–351. doi: 10.1259/0007-1285-47-558-346. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujiwara Y., Kondo T. Strand-scission of HeLa cell deoxyribonucleic acid by bleomycin in vitro and in vivo. Biochem Pharmacol. 1973 Feb 1;22(3):323–333. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(73)90413-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grey P., Michaels L. Bleomycin in advanced squamous-cell carcinoma of head and neck. Med J Aust. 1972 Jul 29;2(5):246–249. doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.1972.tb47265.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haidle C. W., Bearden J., Jr Effect of bleomycin on an RNA-DNA hybrid. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Aug 4;65(3):815–821. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(75)80458-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haidle C. W. Fragmentation of deoxyribonucleic acid by bleomycin. Mol Pharmacol. 1971 Nov;7(6):645–652. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haidle C. W., Kuo M. T., Weiss K. K. Nucleic acid--specificity of bleomycin. Biochem Pharmacol. 1972 Dec 15;21(24):3308–3312. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(72)90096-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haidle C. W., Weiss K. K., Kuo M. T. Release of free bases from deoxyribonucleic acid after reaction with bleomycin. Mol Pharmacol. 1972 Sep;8(5):531–537. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halnan K. E., Bleehen N. M., Brewin T. B., Deeley T. J., Harrison D. F., Howland C., Kunkler P. B., Ritchie G. L., Wiltshaw E., Todd I. D. Early clinical experience with bleomycin in the United Kingdom in series of 105 patients. Br Med J. 1972 Dec 16;4(5841):635–638. doi: 10.1136/bmj.4.5841.635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorgensen S. J. Time-dose relationships in combined bleomycin treatment and radiotherapy. Eur J Cancer. 1972 Oct;8(5):531–534. doi: 10.1016/0014-2964(72)90105-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunimoto T., Hori M., Umezawa H. Modes of action of phleomycin, bleomycin and formycin on HeLa S3 cells in synchronized culture. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1967 Sep;20(5):277–281. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuzawa T., Onozawa M., Morita K., Kakehi M. Radiosensitization of bleomycin on lethal effect of mouse cancer cell in vitro. Strahlentherapie. 1972 Nov;144(5):614–617. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyaki M., Ono T., Umezawa H. Inhibition of ligase reaction by bleomycin. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1971 Sep;24(9):587–592. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.24.587. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Punnonen R., Rantanen J., Grönroos M. Effects of bleomycin on 3H-thymidine incorporation in the skin and on the DNA, RNA and ATP syntheses in the primary tumour of patients with vulval carcinoma. Ann Chir Gynaecol Fenn. 1974;63(2):146–151. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki H., Nagai K., Yamaki H., Tanaka N., Umezawa H. Mechanism of action of bleomycin. Studies with the growing culture of bacterial and tumor cells. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1968 Jun;21(6):379–386. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.21.379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki H., Nagai K., Yamaki H., Tanaka N., Umezawa H. On the mechanism of action of bleomycin: scission of DNA strands in vitro and in vivo. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1969 Sep;22(9):446–448. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.22.446. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terasima T., Yasukawa M., Umezawa H. Breaks and rejoining of DNA in cultured mammalian cells treated with bleomycin. Gan. 1970 Oct;61(5):513–516. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umezawa H., Maeda K., Takeuchi T., Okami Y. New antibiotics, bleomycin A and B. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1966 Sep;19(5):200–209. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umezawa H., Takeuchi T., Hori S., Sawa T., Ishizuka M. Studies on the mechanism of antitumor effect of bleomycin of squamous cell carcinoma. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1972 Jul;25(7):409–420. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.25.409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wharam M. D., Phillips T. L., Kane L., Utley J. F. Response of a murine solid tumor to in vivo combined chemotherapy and irradiation. Radiology. 1973 Nov;109(2):451–455. doi: 10.1148/109.2.451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


