Abstract
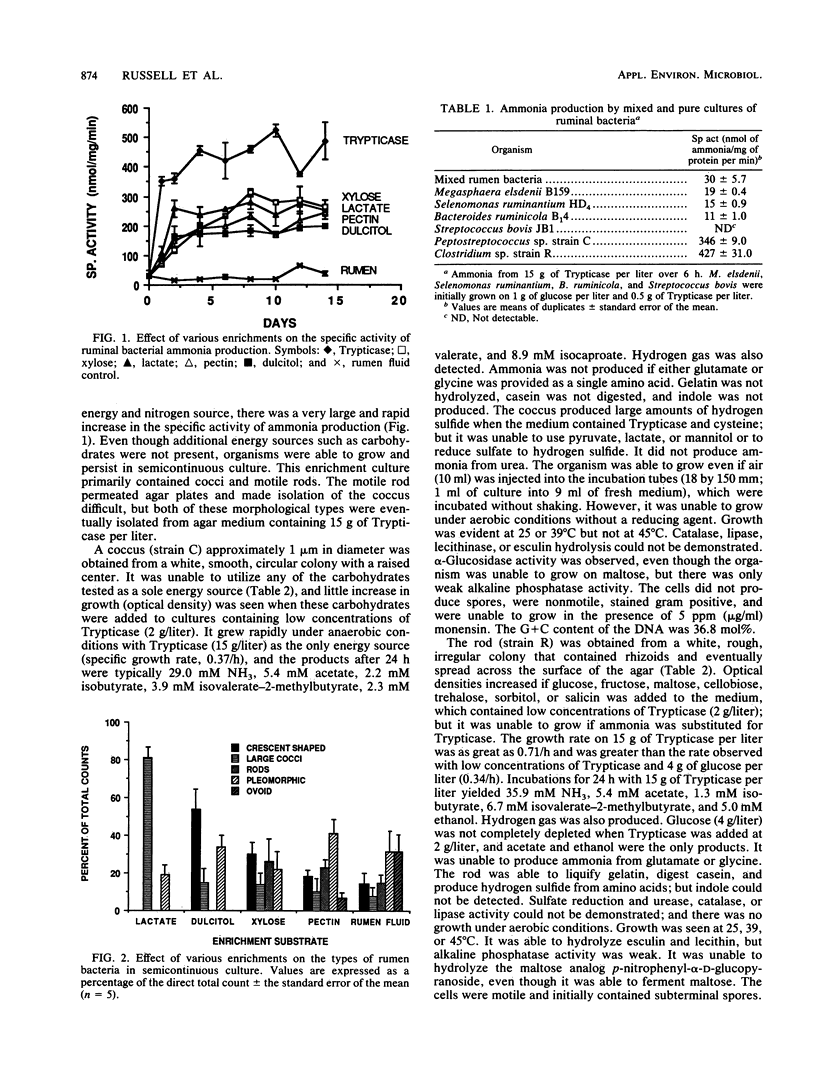
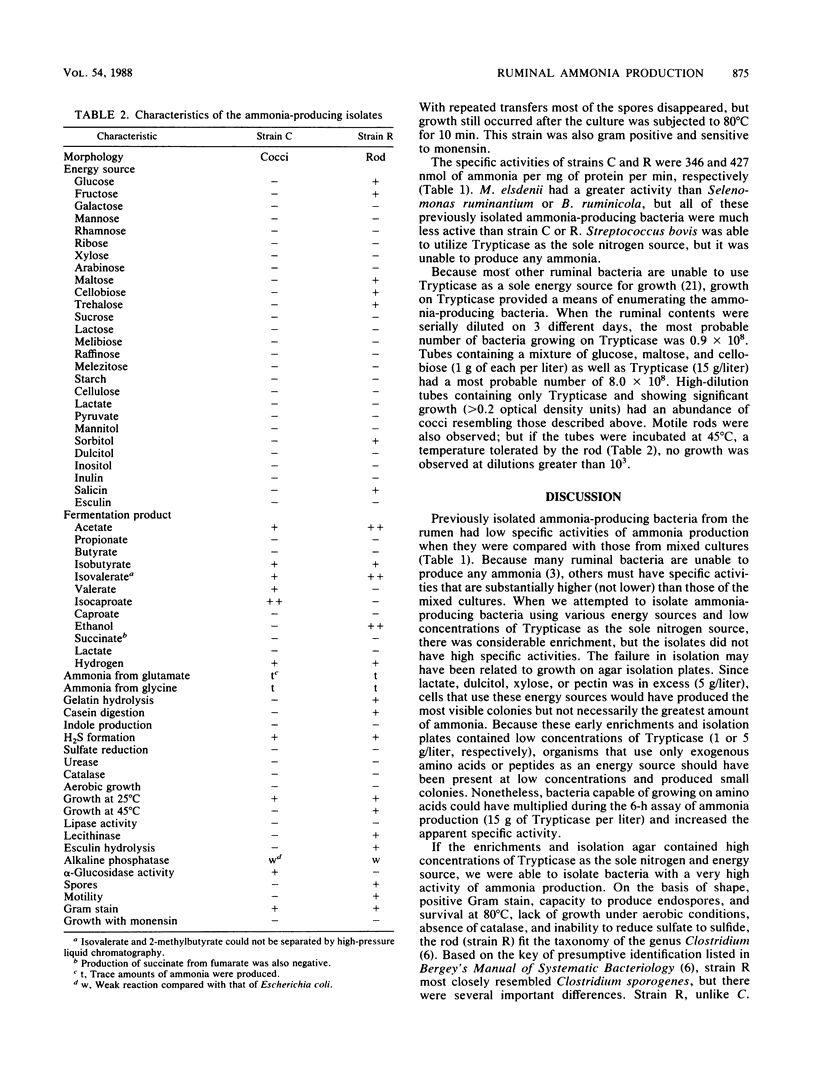
When mixed ruminal bacteria were inoculated into semicontinuous cultures (25% transfer every other day) containing lactate, dulcitol, pectin, or xylose and Trypticase (1 g/liter) as the sole nitrogen source, the specific activity of ammonia production increased. The greatest enrichment was observed with lactate and xylose, and in these cases the specific rate of ammonia production was eightfold higher than that of the ruminal fluid control (approximately 35 nmol of ammonia per mg of protein per min). Isolates with different morphologies were obtained from each of the enrichments, but in no case did the specific activity of any isolate exceed that of the mixed ruminal bacteria. If Trypticase (15 g/liter) was used as the only energy and nitrogen source, there was an even greater increase in ammonia production, and two monensin-sensitive bacteria, a Peptostreptococcus species and a Clostridium species, were obtained. The Peptostreptococcus species was unable to grow on any of 25 carbohydrate or carbohydrate derivatives tested; but the Clostridium species was able to use glucose, maltose, fructose, cellobiose, trehalose, sorbitol, and salicin as energy sources. Neither organism was able to grow in the absence of an amino acid source, but growth rates on Trypticase were greater than 0.35/h. The specific activities of ammonia production were 346 and 427 nmol/mg of protein per min for strains of Peptostreptococcus and Clostridium, respectively. Megasphaera elsdenii and Bacteroides ruminicola, previously isolated ruminal ammonia producers, had specific activities of only 11 and 19 nmol of ammonia per mg of protein per min, respectively. The most probable number of Clostridium species in ruminal fluid was less than 10(3)/ml, but the Peptostreptococcus species was present at 10(8)/ml.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANNISON E. F. Nitrogen metabolism in the sheep; protein digestion in the rumen. Biochem J. 1956 Dec;64(4):705–714. doi: 10.1042/bj0640705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERNS K. I., THOMAS C. A., Jr ISOLATION OF HIGH MOLECULAR WEIGHT DNA FROM HEMOPHILUS INFLUENZAE. J Mol Biol. 1965 Mar;11:476–490. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80004-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bladen H. A., Bryant M. P., Doetsch R. N. A Study of Bacterial Species from the Rumen Which Produce Ammonia from Protein Hydrolyzate. Appl Microbiol. 1961 Mar;9(2):175–180. doi: 10.1128/am.9.2.175-180.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHANEY A. L., MARBACH E. P. Modified reagents for determination of urea and ammonia. Clin Chem. 1962 Apr;8:130–132. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen G., Sniffen C. J., Russell J. B. Concentration and estimated flow of peptides from the rumen of dairy cattle: effects of protein quantity, protein solubility, and feeding frequency. J Dairy Sci. 1987 May;70(5):983–992. doi: 10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(87)80103-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen M., Wolin M. J. Effect of monensin and lasalocid-sodium on the growth of methanogenic and rumen saccharolytic bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Jul;38(1):72–77. doi: 10.1128/aem.38.1.72-77.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donius D. A., Simpson M. E., Marsh P. B. Effect of monensin fed with forage on digestion and the ruminal ecosystem of steers. J Anim Sci. 1976 Jan;42(1):229–234. doi: 10.2527/jas1976.421229x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hino T., Russell J. B. Effect of reducing-equivalent disposal and NADH/NAD on deamination of amino acids by intact rumen microorganisms and their cell extracts. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Dec;50(6):1368–1374. doi: 10.1128/aem.50.6.1368-1374.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hino T., Russell J. B. Relative contributions of ruminal bacteria and protozoa to the degradation of protein in vitro. J Anim Sci. 1987 Jan;64(1):261–270. doi: 10.2527/jas1987.641261x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanigan G. W. Peptococcus heliotrinreducans, sp. nov., a cytochrome-producing anaerobe which metabolizes pyrrolizidine alkaloids. J Gen Microbiol. 1976 May;94(1):1–10. doi: 10.1099/00221287-94-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell J. B. A proposed mechanism of monensin action in inhibiting ruminal bacterial growth: effects on ion flux and protonmotive force. J Anim Sci. 1987 May;64(5):1519–1525. doi: 10.2527/jas1987.6451519x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell J. B., Baldwin R. L. Substrate preferences in rumen bacteria: evidence of catabolite regulatory mechanisms. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Aug;36(2):319–329. doi: 10.1128/aem.36.2.319-329.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell J. B. Fermentation of Peptides by Bacteroides ruminicola B(1)4. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 May;45(5):1566–1574. doi: 10.1128/aem.45.5.1566-1574.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell J. B., Sniffen C. J., Van Soest P. J. Effect of carbohydrate limitation on degradation and utilization of casein by mixed rumen bacteria. J Dairy Sci. 1983 Apr;66(4):763–775. doi: 10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(83)81856-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Nevel C. J., Demeyer D. I. Effect of monensin on rumen metabolism in vitro. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Sep;34(3):251–257. doi: 10.1128/aem.34.3.251-257.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


