Abstract
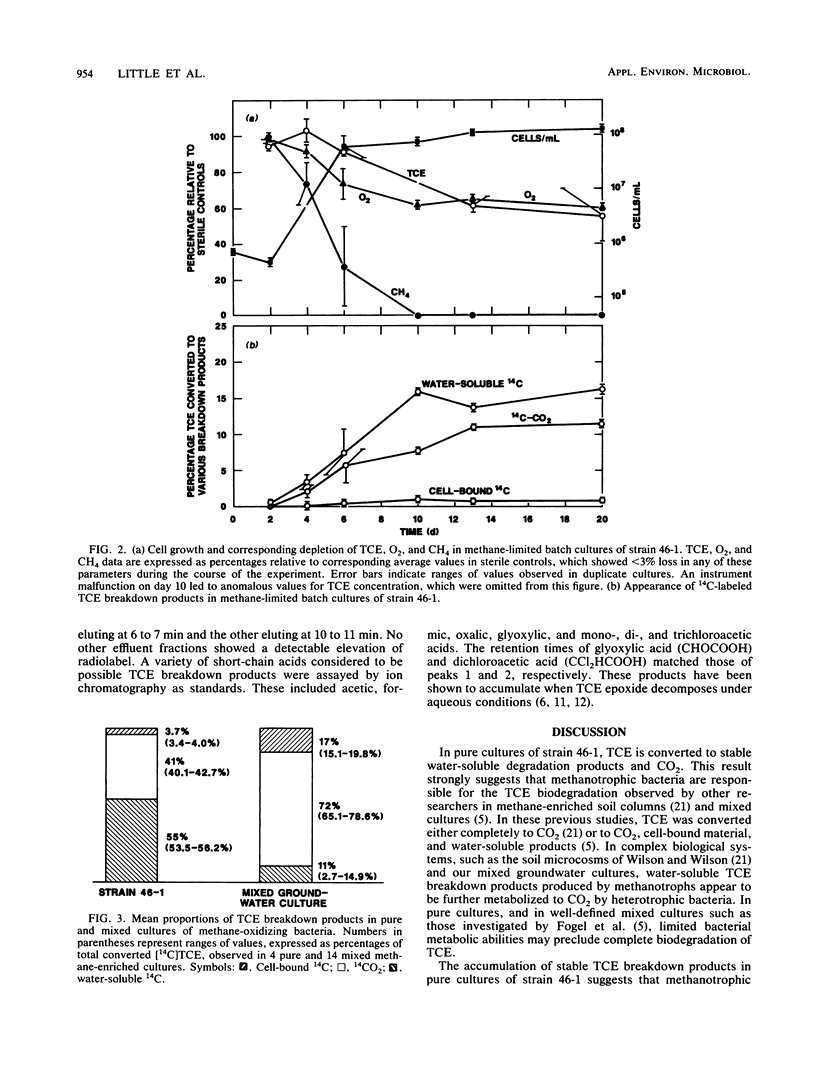
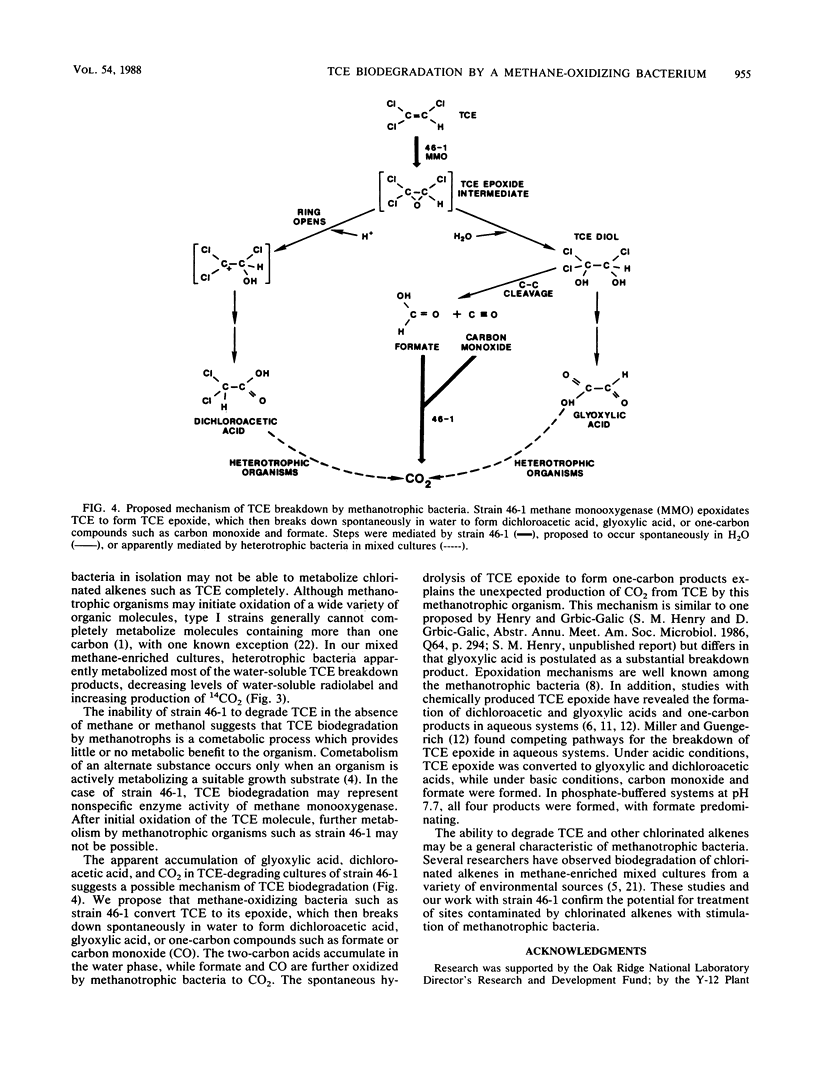
Trichloroethylene (TCE), a common groundwater contaminant, is a suspected carcinogen that is highly resistant to aerobic biodegradation. An aerobic, methane-oxidizing bacterium was isolated that degrades TCE in pure culture at concentrations commonly observed in contaminated groundwater. Strain 46-1, a type I methanotrophic bacterium, degraded TCE if grown on methane or methanol, producing CO2 and water-soluble products. Gas chromatography and 14C radiotracer techniques were used to determine the rate, methane dependence, and mechanism of TCE biodegradation. TCE biodegradation by strain 46-1 appears to be a cometabolic process that occurs when the organism is actively metabolizing a suitable growth substrate such as methane or methanol. It is proposed that TCE biodegradation by methanotrophs occurs by formation of TCE epoxide, which breaks down spontaneously in water to form dichloroacetic and glyoxylic acids and one-carbon products.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Dalton H., Stirling D. I. Co-metabolism. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1982 Jun 11;297(1088):481–496. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1982.0056. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fogel M. M., Taddeo A. R., Fogel S. Biodegradation of chlorinated ethenes by a methane-utilizing mixed culture. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Apr;51(4):720–724. doi: 10.1128/aem.51.4.720-724.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henschler D., Hoos W. R., Fetz H., Dallmeier E., Metzler M. Reactions of trichloroethylene epoxide in aqueous systems. Biochem Pharmacol. 1979;28(4):543–548. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(79)90251-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins I. J., Best D. J., Hammond R. C. New findings in methane-utilizing bacteria highlight their importance in the biosphere and their commercial potential. Nature. 1980 Aug 7;286(5773):561–564. doi: 10.1038/286561a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Large P. J., Quayle J. R. Microbial growth on C(1) compounds. 5. Enzyme activities in extracts of Pseudomonas AM1. Biochem J. 1963 May;87(2):386–396. doi: 10.1042/bj0870386. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. E., Guengerich F. P. Oxidation of trichloroethylene by liver microsomal cytochrome P-450: evidence for chlorine migration in a transition state not involving trichloroethylene oxide. Biochemistry. 1982 Mar 2;21(5):1090–1097. doi: 10.1021/bi00534a041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson M. J., Montgomery S. O., O'neill E. J., Pritchard P. H. Aerobic metabolism of trichloroethylene by a bacterial isolate. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Aug;52(2):383–384. doi: 10.1128/aem.52.2.383-384.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabita F. R., Caruso P., Whitman W. Facile assay of enzymes unique to the Calvin cycle in intact cells, with special reference to ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase. Anal Biochem. 1978 Feb;84(2):462–472. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90064-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittenbury R., Phillips K. C., Wilkinson J. F. Enrichment, isolation and some properties of methane-utilizing bacteria. J Gen Microbiol. 1970 May;61(2):205–218. doi: 10.1099/00221287-61-2-205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson J. T., Wilson B. H. Biotransformation of trichloroethylene in soil. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Jan;49(1):242–243. doi: 10.1128/aem.49.1.242-243.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhao S. J., Hanson R. S. Isolate 761M: a New Type I Methanotroph That Possesses a Complete Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Dec;48(6):1237–1242. doi: 10.1128/aem.48.6.1237-1242.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



